Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0D1HW
|
|||
| Former ID |
DAP000612
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Anagrelide
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Anagrelida; Anagrelidum; BL 416201; Agrylin (TN); Anagrelida [INN-Spanish]; Anagrelide [BAN:INN]; Anagrelide [INN:BAN]; Anagrelidum [INN-Latin]; Xagrid (TN); Anagrelide (INN/BAN); 6,7-Dichlor-1,5-dihydroimidazo(2,1-b)chinazolin-2(3H)-on; 6,7-Dichloro-1,5-dihydroimidazo(2,1-b)quinazolin-2(3H)-one; 6,7-dichloro-1,5-dihydroimidazo[2,1-]quinazolin-2(3H)-one; 6,7-dichloro-5,10-dihydro-3H-imidazo[2,1-b]quinazolin-2-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Thrombocythemia [ICD-11: 3B63; ICD-9: 289.9] | Approved | [1], [2] | |
| Essential thrombocythemia [ICD-11: 3B63.1Z; ICD-9: 238.71, 289.9] | Phase 2 | [3] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antithrombotic Agents
|
|||
| Company |
Shire Phamaceuticals
|
|||
| Structure |
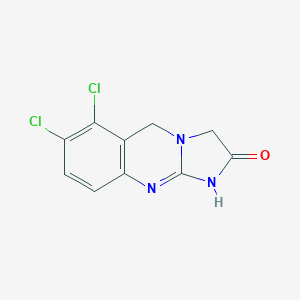 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C10H7Cl2N3O
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1C2=C(C=CC(=C2Cl)Cl)N=C3N1CC(=O)N3
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C10H7Cl2N3O/c11-6-1-2-7-5(9(6)12)3-15-4-8(16)14-10(15)13-7/h1-2H,3-4H2,(H,13,14,16)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
OTBXOEAOVRKTNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 68475-42-3
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
5128700, 14774505, 14798804, 26755034, 29221360, 46508863, 49981497, 51091786, 57321189, 71822539, 74629579, 85341952, 91610578, 92308757, 92712546, 93166869, 99375712, 103202719, 103914916, 104299847, 124892336, 124954033, 126630074, 126668392, 128857870, 128857871, 134337903, 135039796, 136342475, 137005638, 137102173, 137263428, 140705858, 142334850, 152038761, 162178765, 163414816, 164788034, 164814571, 165222687, 172896975, 175266749, 175612207, 176484104, 178103691, 179116560, 179148387, 184545488, 184675310, 185984681
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:142290
|
|||
| ADReCS Drug ID | BADD_D00139 ; BADD_D00140 | |||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
L01XX35
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=068475423
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Metabolism of Drug Affected by Studied Microbe(s) | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Bacteroidales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Anagrelide can be metabolized by Bacteroides dorei DSM 17855 (log2FC = -0.426; p = 0.031). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Anagrelide can be metabolized by Bacteroides fragilis str. 3986 T(B)9 (log2FC = -0.346; p = 0.041). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Anagrelide can be metabolized by Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM18836 (log2FC = -0.329; p = 0.028). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Odoribacter splanchnicus
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Anagrelide can be metabolized by Odoribacter splanchnicus (log2FC = -0.431; p = 0.032). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Erysipelotrichales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Eubacterium biforme DSM 3989
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Anagrelide can be metabolized by Eubacterium biforme DSM 3989 (log2FC = -0.332; p = 0.021). | |||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Blautia hansenii DSM20583
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Anagrelide can be metabolized by Blautia hansenii DSM20583 (log2FC = -0.398; p = 0.021). | |||
|
Studied Microbe: Clostridium sp.
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[4] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Experimental Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | Anagrelide can be metabolized by Clostridium sp. (log2FC = -0.387; p = 0.03). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Phosphodiesterase 3A (PDE3A) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [5] |
| KEGG Pathway | Purine metabolism | |||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | ||||
| cAMP signaling pathway | ||||
| Morphine addiction | ||||
| Reactome | cGMP effects | |||
| G alpha (s) signalling events | ||||
| WikiPathways | miR-targeted genes in muscle cell - TarBase | |||
| miR-targeted genes in lymphocytes - TarBase | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7114). | |||
| REF 2 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||
| REF 4 | Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature. 2019 Jun;570(7762):462-467. | |||
| REF 5 | Hydroxyurea compared with anagrelide in high-risk essential thrombocythemia. N Engl J Med. 2005 Jul 7;353(1):33-45. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

