Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D05ALG
|
|||
| Former ID |
DNC001244
|
|||
| Drug Name |
RWJ-49815
|
|||
| Synonyms |
2-[2-[4-(3,3,3-Triphenylpropoxy)phenyl]ethyl]guanidine; AC1LAN8D; SCHEMBL13339359; AJKCPFPHDCULCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N; 2-(4-(3,3,3-triphenylpropoxy)phenyl)ethylguanidine; 1-[2-[4-(3,3,3-triphenylpropoxy)phenyl]ethyl]guanidine; 2-[2-[4-(3,3,3-triphenylpropoxy)phenyl]ethyl]guanidine; RJW-57926
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Fungal infection [ICD-11: 1F29-1F2F; ICD-10: B35-B49; ICD-9: 110-118] | Terminated | [1] | |
| Eating disorder [ICD-11: 6B82] | Investigative | [2] | ||
| Obesity [ICD-11: 5B81; ICD-10: E66] | Investigative | [2] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antifungal Agents
|
|||
| Structure |
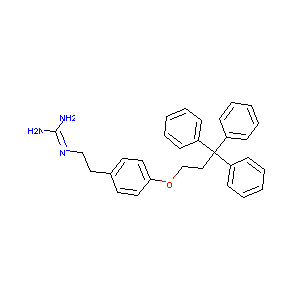 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C30H31N3O
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(CCOC2=CC=C(C=C2)CCN=C(N)N)(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C30H31N3O/c31-29(32)33-22-20-24-16-18-28(19-17-24)34-23-21-30(25-10-4-1-5-11-25,26-12-6-2-7-13-26)27-14-8-3-9-15-27/h1-19H,20-23H2,(H4,31,32,33)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
AJKCPFPHDCULCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID | ||||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Bacterial Sporulation kinase A (Bact kinA) | Target Info | Inhibitor | [3] |
| Neuropeptide Y receptor type 5 (NPY5R) | Target Info | Antagonist | [2] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||
| Reactome | Peptide ligand-binding receptors | |||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | ||||
| WikiPathways | GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||
| Peptide GPCRs | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800009390) | |||
| REF 2 | Emerging drugs for eating disorder treatment. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 May;11(2):315-36. | |||
| REF 3 | Histidine kinases as targets for new antimicrobial agents. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002 Apr;10(4):855-67. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

