Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0G3LM
|
|||
| Former ID |
DNC000451
|
|||
| Drug Name |
Clomethiazole
|
|||
| Synonyms |
Clomethiazole; 533-45-9; Chlormethiazole; 5-(2-CHLOROETHYL)-4-METHYLTHIAZOLE; Distraneurin; Emineurina; Clomethiazolum; Chlormethiazol; Chlorethiazol; Chlorethiazole; Somnevrin; Clometiazole; Clomethiazol; 5-(2-Chloroethyl)-4-methyl-1,3-thiazole; Thiazole, 5-(2-chloroethyl)-4-methyl-; Clometiazolo [DCIT]; Chloro-S.C.T.Z.; C6H8ClNS; UNII-0C5DBZ19HV; Clometiazol [INN-Spanish]; Clomethiazolum [INN-Latin]; WY 1485; Clomethiazole [INN]; SCTZ [as edisylate]; EINECS 208-565-7; 4-Methyl-5-(beta-chloroethyl)thiazole; BRN 0114244; 0C5DBZ19HV
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Stroke [ICD-11: 8B20; ICD-10: I64] | Phase 3 | [1] | |
| Structure |
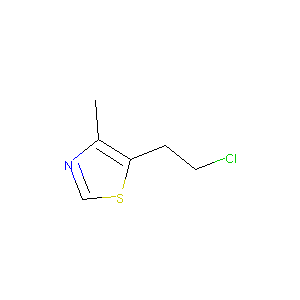 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C6H8ClNS
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(SC=N1)CCCl
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C6H8ClNS/c1-5-6(2-3-7)9-4-8-5/h4H,2-3H2,1H3
|
|||
| InChIKey |
PCLITLDOTJTVDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 533-45-9
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
4619295, 7978970, 8157813, 10525682, 11113756, 15147015, 26751938, 29229242, 47362786, 47513076, 48415802, 50051831, 50612685, 51091667, 53788240, 57326461, 57393846, 58106916, 85788326, 90341262, 92717222, 93305289, 99233257, 99246227, 99437078, 103293356, 104324248, 117472036, 117673459, 118317990, 124757151, 124886951, 125163955, 125352389, 126654022, 126689028, 127339752, 127339753, 127339754, 127339755, 128896018, 131383406, 134339873, 134977038, 135692098, 136974770, 137005027, 142483186, 144204482, 147484835
|
|||
| ChEBI ID |
CHEBI:92875
|
|||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
N05CM02
|
|||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=000533459
|
|||
| Interaction between the Drug and Microbe | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Abundace of Studied Microbe(s) Regulated by Drug | ||||
| The Order in the Taxonomic Hierarchy of the following Microbe(s): Eubacteriales | ||||
|
Studied Microbe: Ruminococcus torques
Show/Hide Hierarchy
|
[2] | |||
| Hierarchy | ||||
| Abundance Change | Decrease | |||
| Experiment Method | High-throughput screening | |||
| Description | The abundance of Ruminococcus torques was decreased by Methiazole (adjusted p-values: 1.64E-04). | |||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | GABA(A) receptor gamma-3 (GABRG3) | Target Info | Modulator | [3] |
| KEGG Pathway | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | ||||
| GABAergic synapse | ||||
| Morphine addiction | ||||
| Nicotine addiction | ||||
| Reactome | Ligand-gated ion channel transport | |||
| GABA A receptor activation | ||||
| WikiPathways | SIDS Susceptibility Pathways | |||
| Neurotransmitter Receptor Binding And Downstream Transmission In The Postsynaptic Cell | ||||
| Iron uptake and transport | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02374567) Pharmacovigilance in Gerontopsychiatric Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||
| REF 2 | Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature. 2018 Mar 29;555(7698):623-628. | |||
| REF 3 | Electrophysiological actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and clomethiazole on recombinant GABA(A) receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002 Oct 11;452(3):255-62. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

