Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T02318
(Former ID: TTDC00196)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
B-cell-activating factor (TNFSF13B)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
ZTNF4; UNQ401/PRO738; Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B; TNFSF20; TNF-and APOL-related leukocyte expressed ligand 1; TNF- and APOL-related leukocyte expressed ligand 1; TALL1; TALL-1; Dendritic cell-derived TNF-like molecule; CD257; BLyS; BAFF; B lymphocyte stimulator; B cell-activating factor
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TNFSF13B
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Lupus erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40] | |||||
| Function |
TNFSF13/APRIL binds to the same 2 receptors. Together, they form a 2 ligands -2 receptors pathway involved in the stimulation of B- and T-cell function and the regulation of humoral immunity. A third B-cell specific BAFF-receptor (BAFFR/BR3) promotes the survival of mature B-cells and the B-cell response. Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF13B/TACI and TNFRSF17/BCMA.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Cytokine: tumor necrosis factor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MDDSTEREQSRLTSCLKKREEMKLKECVSILPRKESPSVRSSKDGKLLAATLLLALLSCC
LTVVSFYQVAALQGDLASLRAELQGHHAEKLPAGAGAPKAGLEEAPAVTAGLKIFEPPAP GEGNSSQNSRNKRAVQGPEETVTQDCLQLIADSETPTIQKGSYTFVPWLLSFKRGSALEE KENKILVKETGYFFIYGQVLYTDKTYAMGHLIQRKKVHVFGDELSLVTLFRCIQNMPETL PNNSCYSAGIAKLEEGDELQLAIPRENAQISLDGDVTFFGALKLL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T19AGJ | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Belimumab | Drug Info | Approved | Systemic lupus erythematosus | [2], [3] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Blisibimod | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | [6] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LymphoRad-131 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Lymphoma | [9] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 2 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Blisibimod | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 2 | 1,4-Diethylene Dioxide | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LymphoRad-131 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |
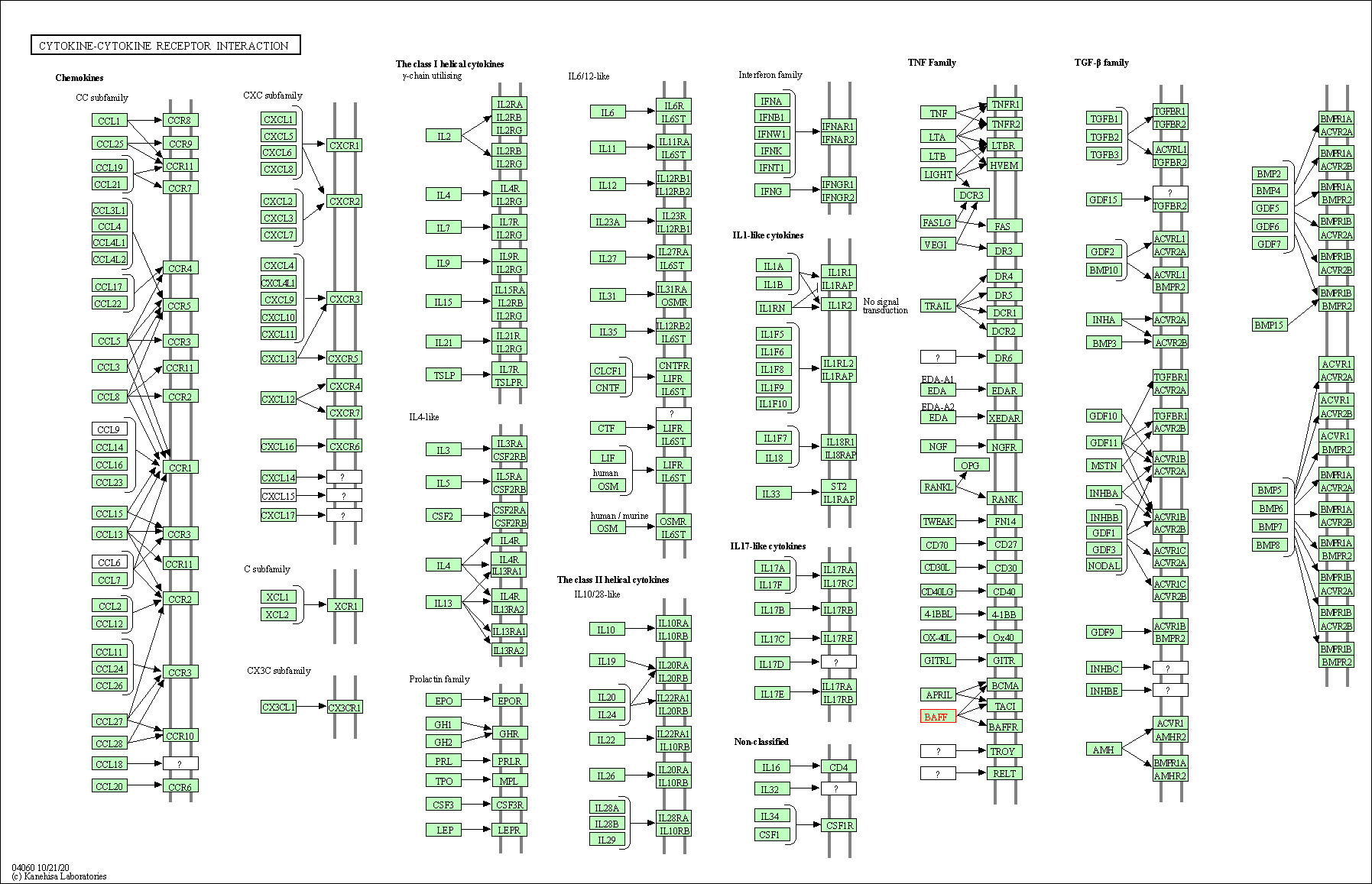
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |
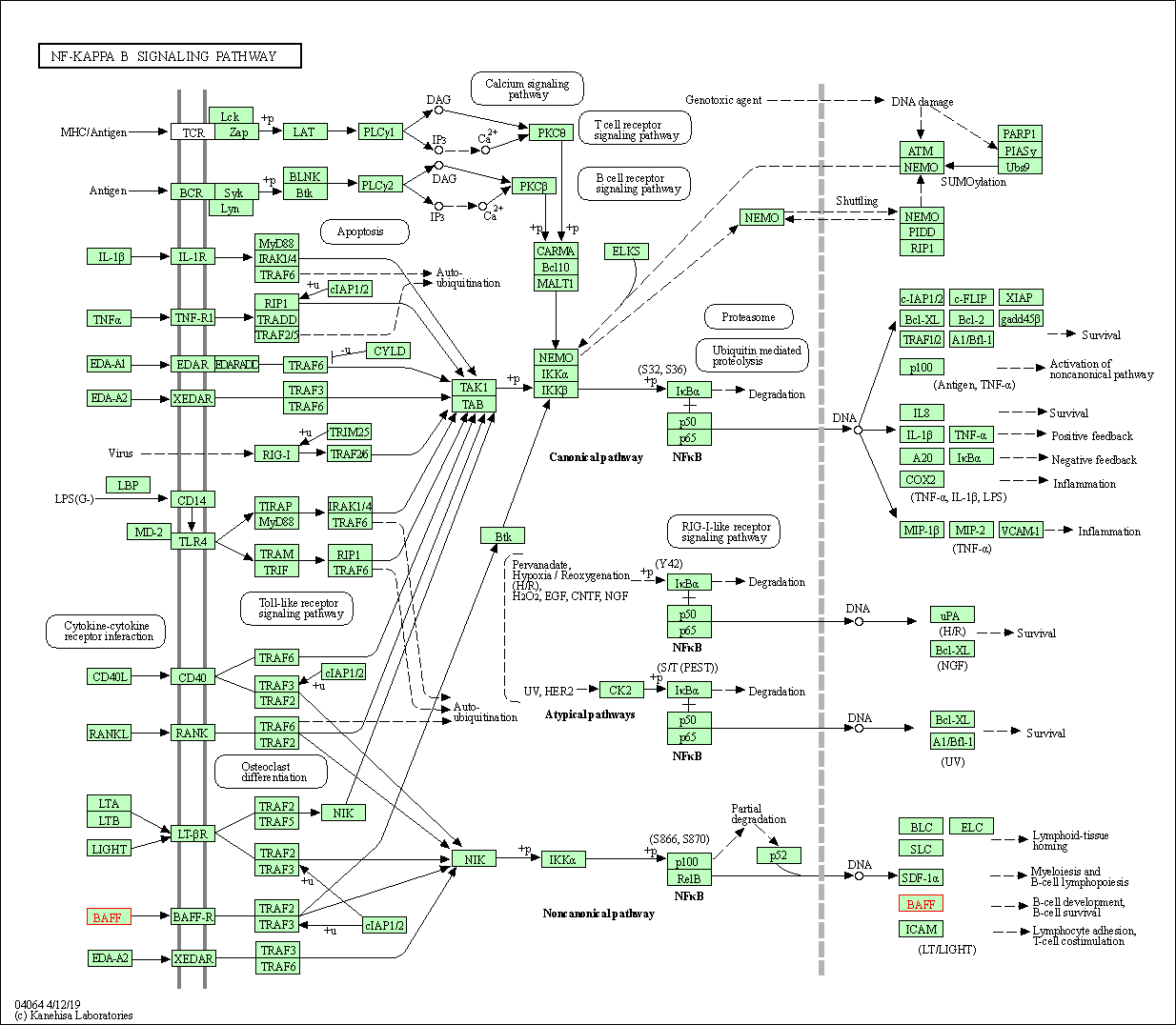
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Intestinal immune network for IgA production | hsa04672 | Affiliated Target |
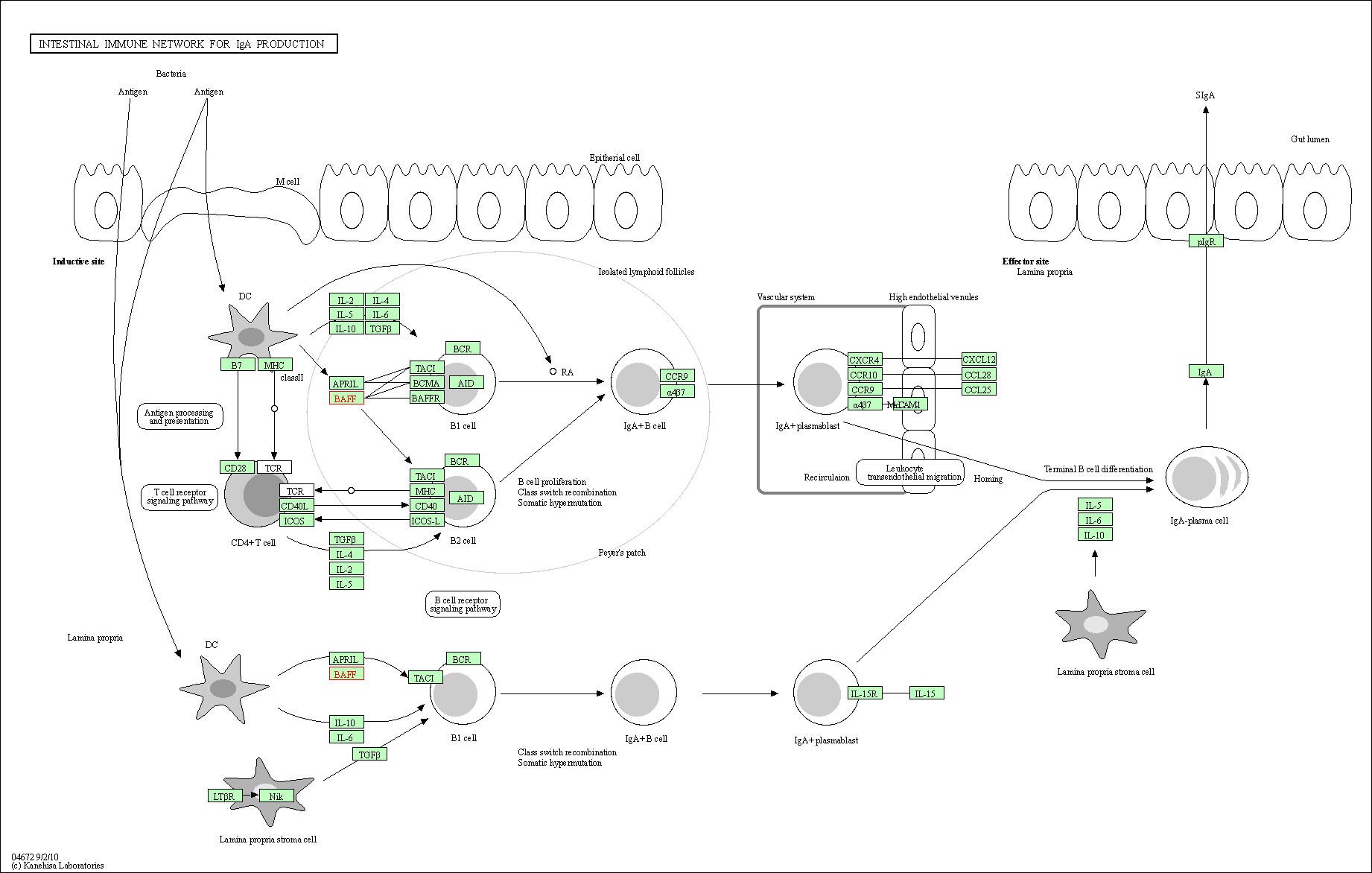
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 5 | Degree centrality | 5.37E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.50E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.95E-01 | Radiality | 1.33E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 5.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.48E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.47E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | |||||
| 2 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Intestinal immune network for IgA production | |||||
| 4 | Rheumatoid arthritis | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 3 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway | |||||
| 2 | TNFs bind their physiological receptors | |||||
| 3 | TNF receptor superfamily (TNFSF) members mediating non-canonical NF-kB pathway | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 1 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Spinal Cord Injury | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of GlaxoSmithKline (2009). | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6887). | |||||
| REF 3 | New developments in immunosuppressive therapy for heart transplantation. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):1-21. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 8000). | |||||
| REF 5 | Tabalumab, an anti-BAFF monoclonal antibody, in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to TNF inhibitors. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Sep 1;72(9):1461-8. | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04058028) Efficacy and Safety of AMG 570 in Subjects With Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Emerging drugs for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Jun;13(2):237-54. | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800016875) | |||||
| REF 10 | Fusion Toxin BLyS-Gelonin Inhibits Growth of Malignant Human B Cell Lines In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS One. 2012; 7(10): e47361. | |||||
| REF 11 | DrugBank 3.0: a comprehensive resource for 'omics' research on drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D1035-41. | |||||
| REF 12 | BAFF: B cell survival factor and emerging therapeutic target for autoimmune disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003 Feb;7(1):115-23. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

