Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T02974
(Former ID: TTDI02609)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Interleukin1 receptor 3; Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein; Interleukin-1 receptor 3; IL1RAcP; IL1R3; IL1 receptor accessory protein; IL-1RAcP; IL-1R3; IL-1R-3; IL-1 receptor accessory protein; C3orf13
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
IL1RAP
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||||
| Function |
Coreceptor with IL1R1 in the IL-1 signaling system. Associates with IL1R1 bound to IL1B to form the high affinity interleukin-1 receptor complex which mediates interleukin-1-dependent activation of NF-kappa-B and other pathways. Signaling involves the recruitment of adapter molecules such as TOLLIP, MYD88, and IRAK1 or IRAK2 via the respective TIR domains of the receptor/coreceptor subunits. Recruits TOLLIP to the signaling complex. Does not bind to interleukin-1 alone; binding of IL1RN to IL1R1, prevents its association with IL1R1 to form a signaling complex. The cellular response is modulated through a non-signaling association with the membrane IL1R2 decoy receptor. Coreceptor for IL1RL1 in the IL-33 signaling system. Can bidirectionally induce pre- and postsynaptic differentiation of neurons by trans-synaptically binding to PTPRD. May play a role in IL1B-mediated costimulation of IFNG production from T-helper 1 (Th1) cells. Coreceptor for IL1RL2 in the IL-36 signaling system.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Cytokine receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MTLLWCVVSLYFYGILQSDASERCDDWGLDTMRQIQVFEDEPARIKCPLFEHFLKFNYST
AHSAGLTLIWYWTRQDRDLEEPINFRLPENRISKEKDVLWFRPTLLNDTGNYTCMLRNTT YCSKVAFPLEVVQKDSCFNSPMKLPVHKLYIEYGIQRITCPNVDGYFPSSVKPTITWYMG CYKIQNFNNVIPEGMNLSFLIALISNNGNYTCVVTYPENGRTFHLTRTLTVKVVGSPKNA VPPVIHSPNDHVVYEKEPGEELLIPCTVYFSFLMDSRNEVWWTIDGKKPDDITIDVTINE SISHSRTEDETRTQILSIKKVTSEDLKRSYVCHARSAKGEVAKAAKVKQKVPAPRYTVEL ACGFGATVLLVVILIVVYHVYWLEMVLFYRAHFGTDETILDGKEYDIYVSYARNAEEEEF VLLTLRGVLENEFGYKLCIFDRDSLPGGIVTDETLSFIQKSRRLLVVLSPNYVLQGTQAL LELKAGLENMASRGNINVILVQYKAVKETKVKELKRAKTVLTVIKWKGEKSKYPQGRFWK QLQVAMPVKKSPRRSSSDEQGLSYSSLKNV Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interleukin 1 receptor type 2 (IL1R2) | 23.220 (75/323) | 5.07E-19 |
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
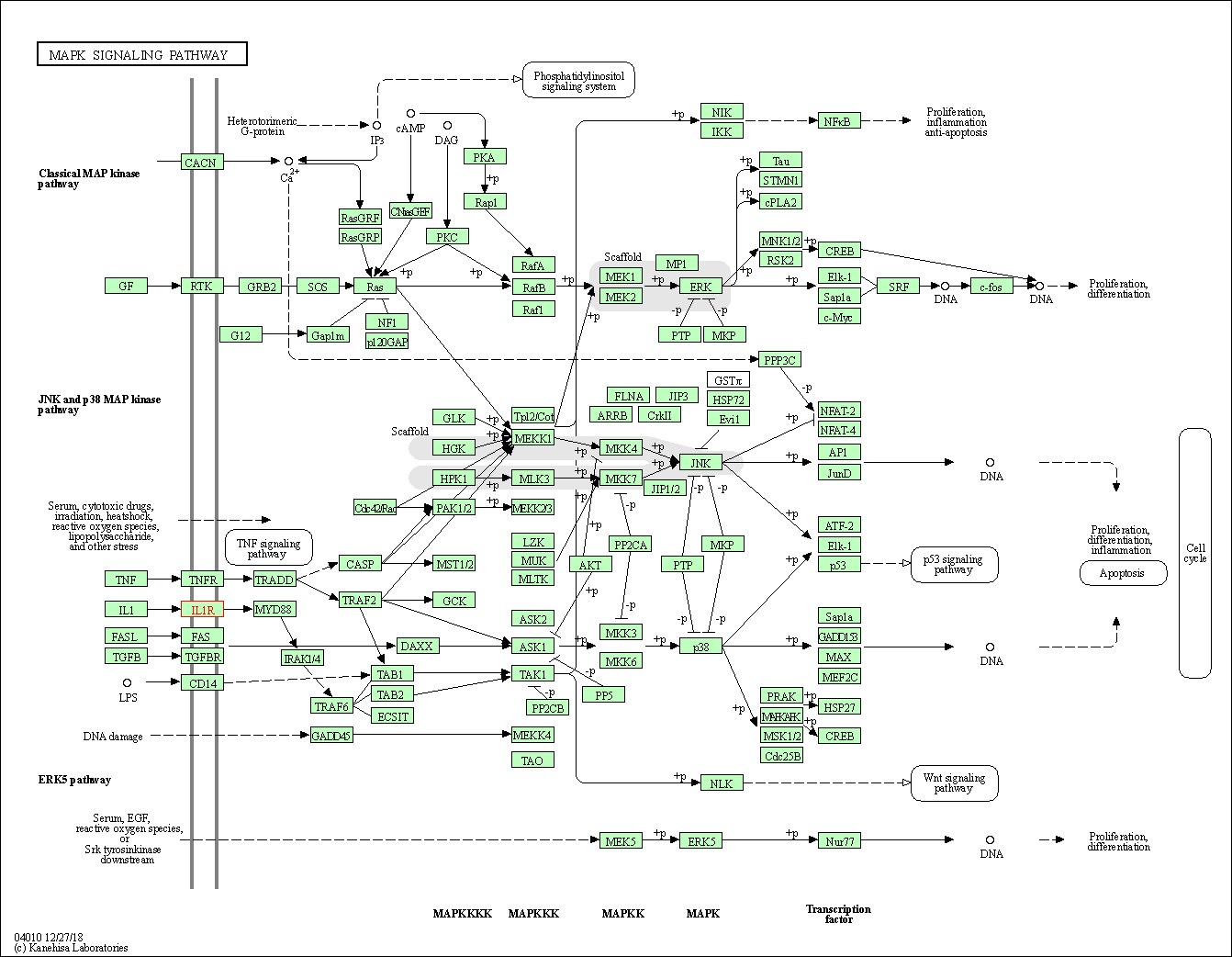
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |
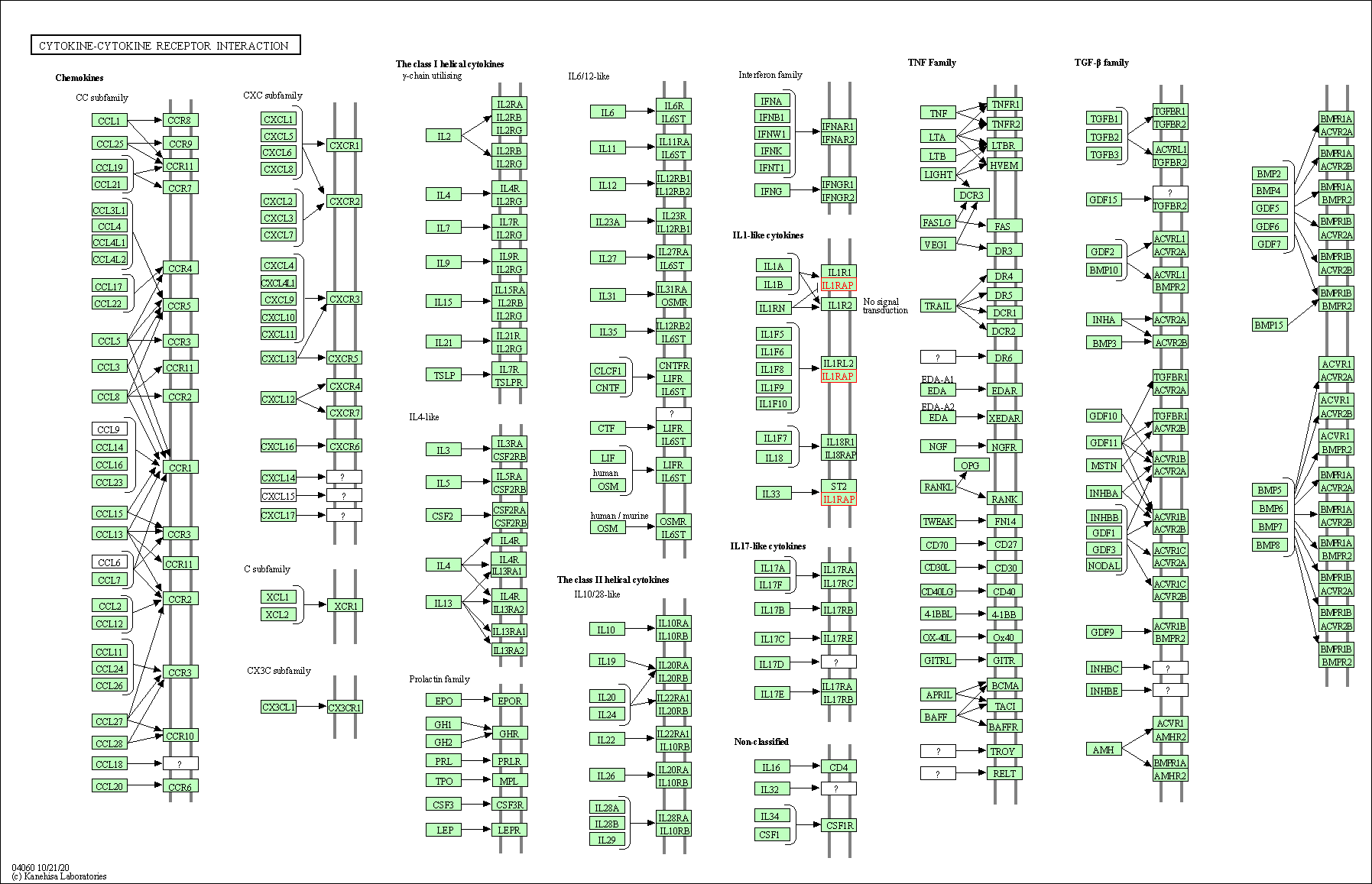
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |
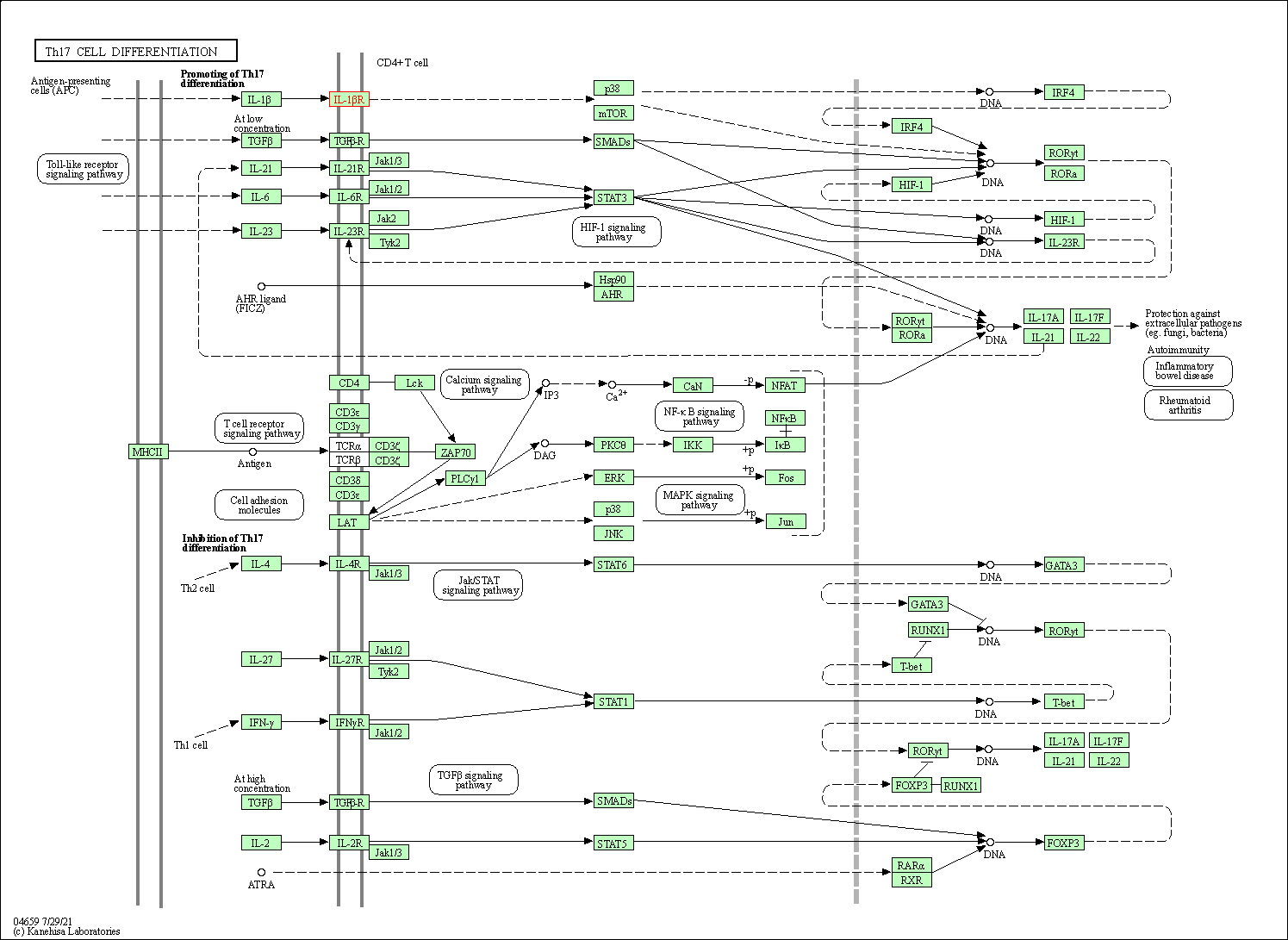
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | hsa04750 | Affiliated Target |
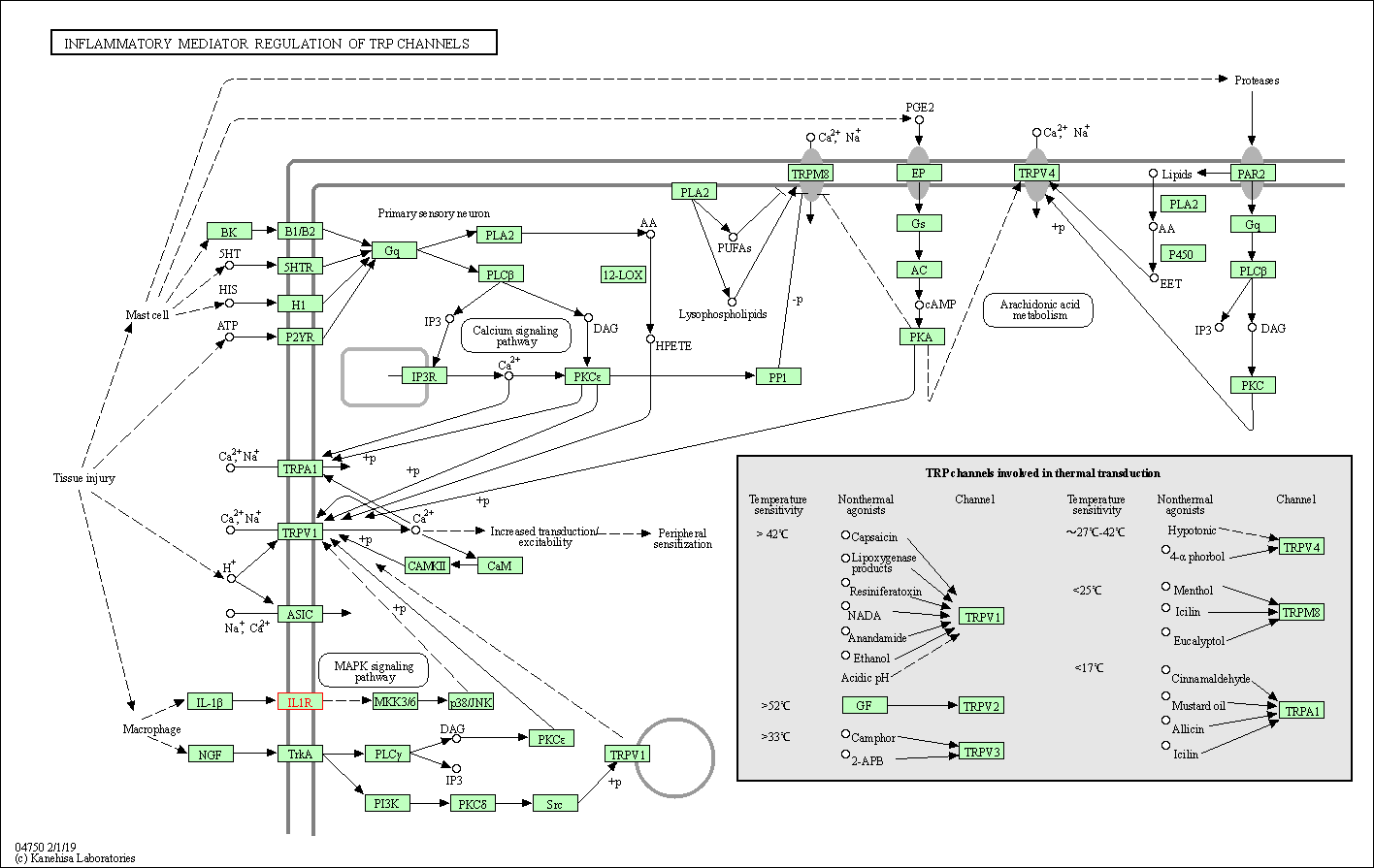
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Antibodies targeting human IL1RAP (IL1R3) show therapeutic effects in xenograft models of acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 25;112(34):10786-91. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04452214) A Study of the Safety and Tolerance of CAN04 in Combination With Pembrolizumab in Subjects With Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

