Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T12808
(Former ID: TTDC00182)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Protein kinase C alpha (PRKCA)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Protein kinase C alpha type; PRKACA; PKCalpha; PKCA; PKC-alpha; PKC-A
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PRKCA
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Muscular atrophy [ICD-11: 8B61] | |||||
| Function |
Involved in cell proliferation and cell growth arrest by positive and negative regulation of the cell cycle. Can promote cell growth by phosphorylating and activating RAF1, which mediates the activation of the MAPK/ERK signaling cascade, and/or by up-regulating CDKN1A, which facilitates active cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) complex formation in glioma cells. In intestinal cells stimulated by the phorbol ester PMA, can trigger a cell cycle arrest program which is associated with the accumulation of the hyper-phosphorylated growth-suppressive form of RB1 and induction of the CDK inhibitors CDKN1A and CDKN1B. Exhibits anti-apoptotic function in glioma cells and protects them from apoptosis by suppressing the p53/TP53-mediated activation of IGFBP3, and in leukemia cells mediates anti-apoptotic action by phosphorylating BCL2. During macrophage differentiation induced by macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF1), is translocated to the nucleus and is associated with macrophage development. After wounding, translocates from focal contacts to lamellipodia and participates in the modulation of desmosomal adhesion. Plays a role in cell motility by phosphorylating CSPG4, which induces association of CSPG4 with extensive lamellipodia at the cell periphery and polarization of the cell accompanied by increases in cell motility. During chemokine-induced CD4(+) T cell migration, phosphorylates CDC42-guanine exchange factor DOCK8 resulting in its dissociation from LRCH1 and the activation of GTPase CDC42. Is highly expressed in a number of cancer cells where it can act as a tumor promoter and is implicated in malignant phenotypes of several tumors such as gliomas and breast cancers. Negatively regulates myocardial contractility and positively regulates angiogenesis, platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in arteries. Mediates hypertrophic growth of neonatal cardiomyocytes, in part through a MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2)-dependent signaling pathway, and upon PMA treatment, is required to induce cardiomyocyte hypertrophy up to heart failure and death, by increasing protein synthesis, protein-DNA ratio and cell surface area. Regulates cardiomyocyte function by phosphorylating cardiac troponin T (TNNT2/CTNT), which induces significant reduction in actomyosin ATPase activity, myofilament calcium sensitivity and myocardial contractility. In angiogenesis, is required for full endothelial cell migration, adhesion to vitronectin (VTN), and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA)-dependent regulation of kinase activation and vascular tube formation. Involved in the stabilization of VEGFA mRNA at post-transcriptional level and mediates VEGFA-induced cell proliferation. In the regulation of calcium-induced platelet aggregation, mediates signals from the CD36/GP4 receptor for granule release, and activates the integrin heterodimer ITGA2B-ITGB3 through the RAP1GAP pathway for adhesion. During response to lipopolysaccharides (LPS), may regulate selective LPS-induced macrophage functions involved in host defense and inflammation. But in some inflammatory responses, may negatively regulate NF-kappa-B-induced genes, through IL1A-dependent induction of NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (NFKBIA/IKBA). Upon stimulation with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), phosphorylates EIF4G1, which modulates EIF4G1 binding to MKNK1 and may be involved in the regulation of EIF4E phosphorylation. Phosphorylates KIT, leading to inhibition of KIT activity. Phosphorylates ATF2 which promotes cooperation between ATF2 and JUN, activating transcription. Calcium-activated, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that is involved in positive and negative regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, migration and adhesion, tumorigenesis, cardiac hypertrophy, angiogenesis, platelet function and inflammation, by directly phosphorylating targets such as RAF1, BCL2, CSPG4, TNNT2/CTNT, or activating signaling cascade involving MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2) and RAP1GAP.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.13
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MADVFPGNDSTASQDVANRFARKGALRQKNVHEVKDHKFIARFFKQPTFCSHCTDFIWGF
GKQGFQCQVCCFVVHKRCHEFVTFSCPGADKGPDTDDPRSKHKFKIHTYGSPTFCDHCGS LLYGLIHQGMKCDTCDMNVHKQCVINVPSLCGMDHTEKRGRIYLKAEVADEKLHVTVRDA KNLIPMDPNGLSDPYVKLKLIPDPKNESKQKTKTIRSTLNPQWNESFTFKLKPSDKDRRL SVEIWDWDRTTRNDFMGSLSFGVSELMKMPASGWYKLLNQEEGEYYNVPIPEGDEEGNME LRQKFEKAKLGPAGNKVISPSEDRKQPSNNLDRVKLTDFNFLMVLGKGSFGKVMLADRKG TEELYAIKILKKDVVIQDDDVECTMVEKRVLALLDKPPFLTQLHSCFQTVDRLYFVMEYV NGGDLMYHIQQVGKFKEPQAVFYAAEISIGLFFLHKRGIIYRDLKLDNVMLDSEGHIKIA DFGMCKEHMMDGVTTRTFCGTPDYIAPEIIAYQPYGKSVDWWAYGVLLYEMLAGQPPFDG EDEDELFQSIMEHNVSYPKSLSKEAVSVCKGLMTKHPAKRLGCGPEGERDVREHAFFRRI DWEKLENREIQPPFKPKVCGKGAENFDKFFTRGQPVLTPPDQLVIANIDQSDFEGFSYVN PQFVHPILQSAV Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A03834 ; BADD_A06356 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T78ZF2 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Sodium phenylbutyrate | Drug Info | Approved | Spinal muscular atrophy | [2] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Sotrastaurin acetate | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Renal transplantation | [1] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Acteoside | Drug Info | Terminated | Nephritis | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 2 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Sodium phenylbutyrate | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 2 | ISIS 3521 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 40 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Sotrastaurin acetate | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Acteoside | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 3 | BALANOL | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 4 | RO-320432 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 5 | (-)-Cercosporamide | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 6 | 1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycerol | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 7 | 2,3,3-Triphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 8 | 2-(4-Hydroxy-phenyl)-3,3-diphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 9 | 3,3-Bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-phenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 10 | 3,3-Bis-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-2-phenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 11 | 3,4-di-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 12 | 3,4-diphenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 13 | 3-(4-Hydroxy-phenyl)-2,3-diphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 14 | 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 15 | 3-(indole-3-yl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 16 | 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 17 | 4-cycloheptyliden(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylphenol | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 18 | 4-cyclopentyliden(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylphenol | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 19 | 4-[1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1-butenyl]phenol | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 20 | CALCEOLARIOSIDE A | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 21 | CI-1040 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 22 | Diheptan-3-yl 5-(hydroxymethyl)isophthalate | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 23 | Dihexan-3-yl 5-(hydroxymethyl)isophthalate | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 24 | FORSYTHIASIDE | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 25 | Go 6983 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 26 | KN-62 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 27 | KT-5720 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 28 | LEUCOSCEPTOSIDE A | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 29 | LY-326449 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 30 | Plantainoside D | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 31 | PROSTRATIN | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 32 | PUNICAFOLIN | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 33 | RO-316233 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 34 | Ro-32-0557 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 35 | Ro31-8220 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 36 | STAUROSPORINONE | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 37 | TANNIN | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 38 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophen-4-yl-methanol | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 39 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophene-4,5''-dicarbaldehyde | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 40 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophene-4-carbaldehyde | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: L-serine-O-phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Human Protein Kinase C Alpha in Complex with Compound 28 ((R)-6-((3S,4S)-1,3-Dimethyl-piperidin-4-yl)-7-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-4-methyl-2,10-dihydro-9-oxa-1,2,4a-triaza-phenanthren-3-one) | PDB:4RA4 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.63 Å | Mutation | Yes | [21] |
| PDB Sequence |
DRVKLTDFNF
341 LMVLGKGSFG351 KVMLADRKGT361 EELYAIKILK371 KDVVIQDDDV381 ECTMVEKRVL 391 ALLDKPPFLT401 QLHSCFQTVD411 RLYFVMEYVN421 GGDLMYHIQQ431 VGKFKEPQAV 441 FYAAEISIGL451 FFLHKRGIIY461 RDLKLDNVML471 DSEGHIKIAD481 FGMCKEHMMD 491 GVTTRFCGTP502 DYIAPEIIAY512 QPYGKSVDWW522 AYGVLLYEML532 AGQPPFDGED 542 EDELFQSIME552 HNVSYPKSLS562 KEAVSICKGL572 MTKHPAKRLG582 CGPEGERDVR 592 EHAFFRRIDW602 EKLENREIQP612 PFKPKGQPVL637 PPDQLVIANI648 DQSDFEGFYV 659 NPQFVHP
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Phosphonothreonine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Human Protein Kinase C Alpha in Complex with Compound 28 ((R)-6-((3S,4S)-1,3-Dimethyl-piperidin-4-yl)-7-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-4-methyl-2,10-dihydro-9-oxa-1,2,4a-triaza-phenanthren-3-one) | PDB:4RA4 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.63 Å | Mutation | Yes | [21] |
| PDB Sequence |
DRVKLTDFNF
341 LMVLGKGSFG351 KVMLADRKGT361 EELYAIKILK371 KDVVIQDDDV381 ECTMVEKRVL 391 ALLDKPPFLT401 QLHSCFQTVD411 RLYFVMEYVN421 GGDLMYHIQQ431 VGKFKEPQAV 441 FYAAEISIGL451 FFLHKRGIIY461 RDLKLDNVML471 DSEGHIKIAD481 FGMCKEHMMD 491 GVTTRFCGTP502 DYIAPEIIAY512 QPYGKSVDWW522 AYGVLLYEML532 AGQPPFDGED 542 EDELFQSIME552 HNVSYPKSLS562 KEAVSICKGL572 MTKHPAKRLG582 CGPEGERDVR 592 EHAFFRRIDW602 EKLENREIQP612 PFKPKGQPVL637 PPDQLVIANI648 DQSDFEGFYV 659 NPQFVHP
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
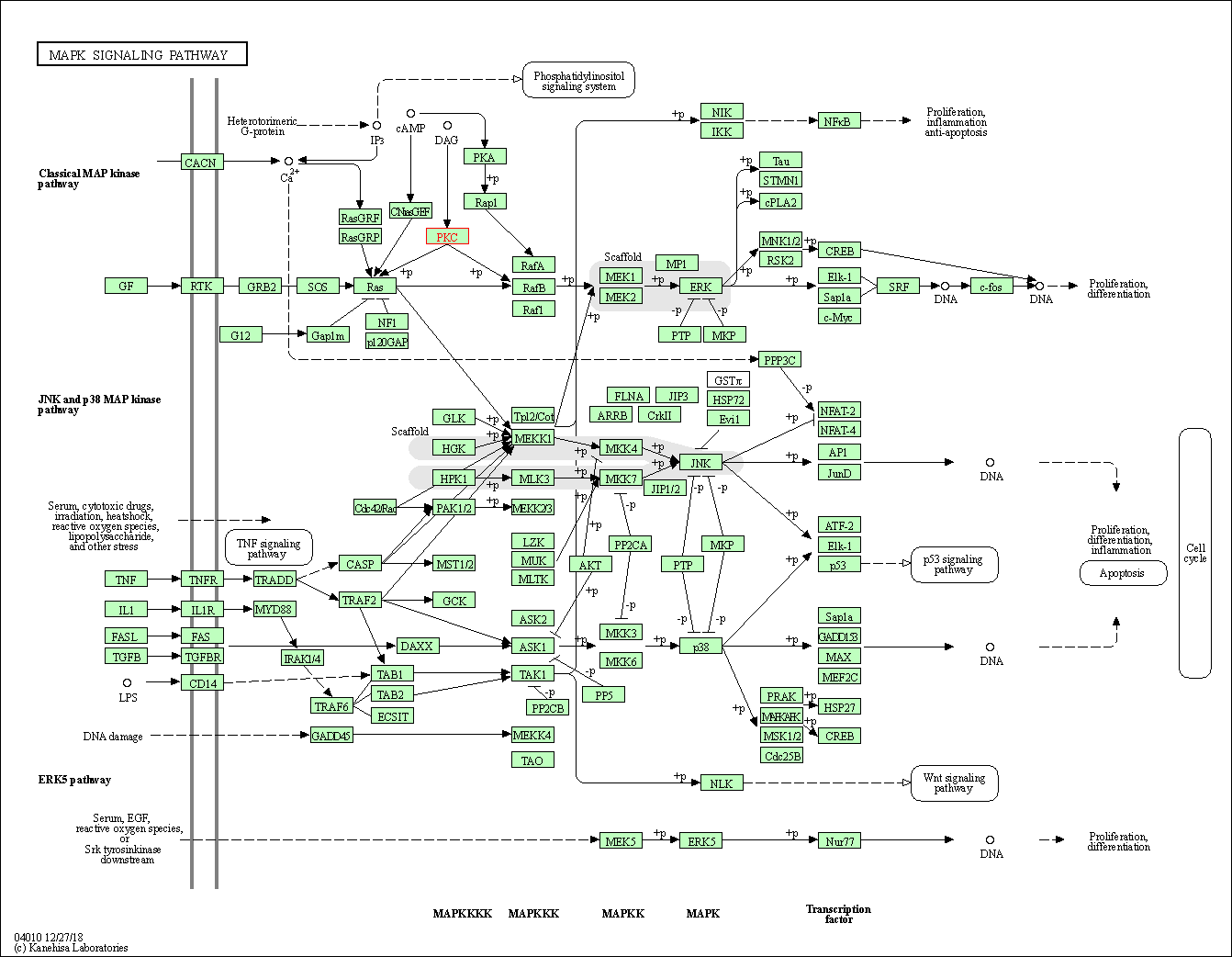
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |
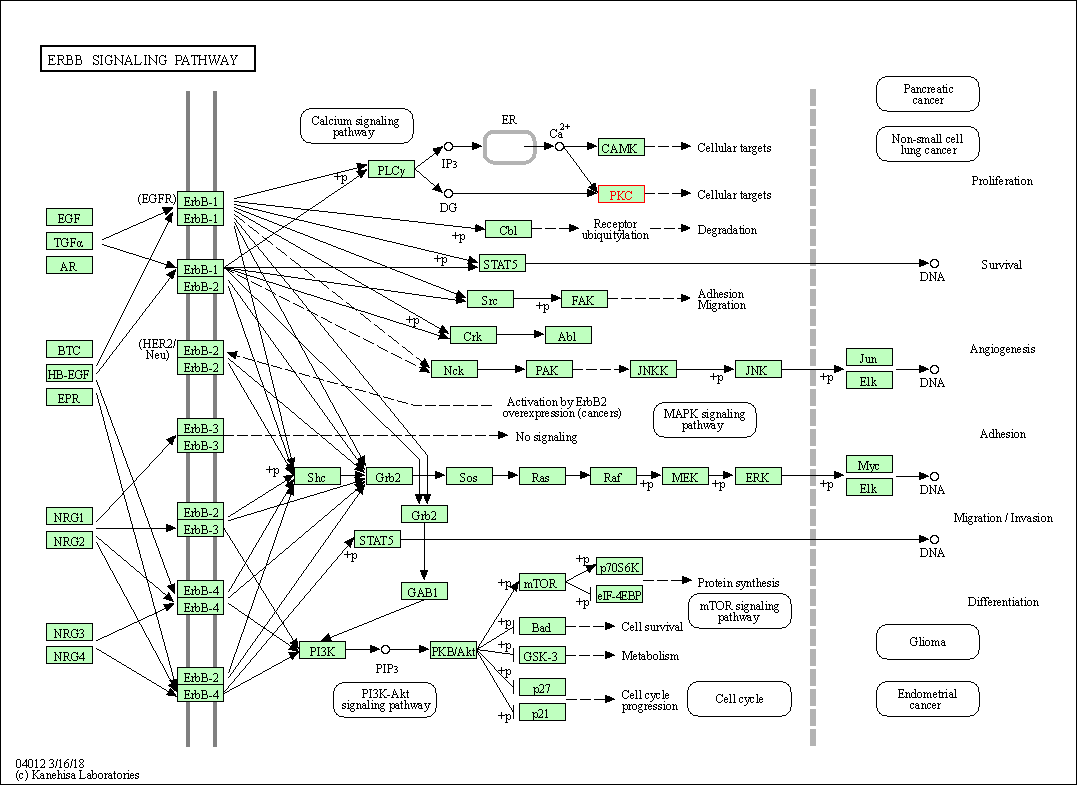
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |
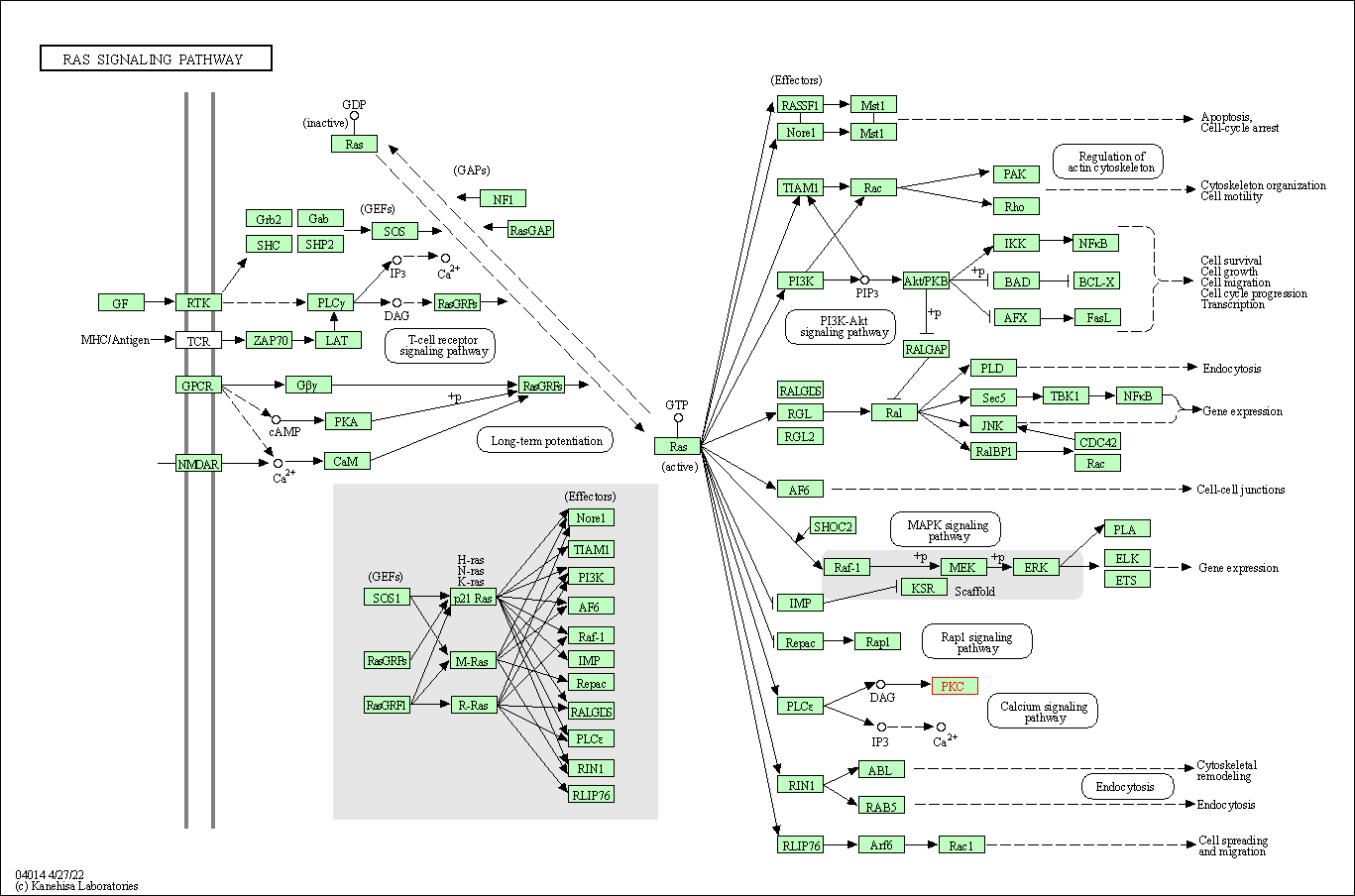
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |
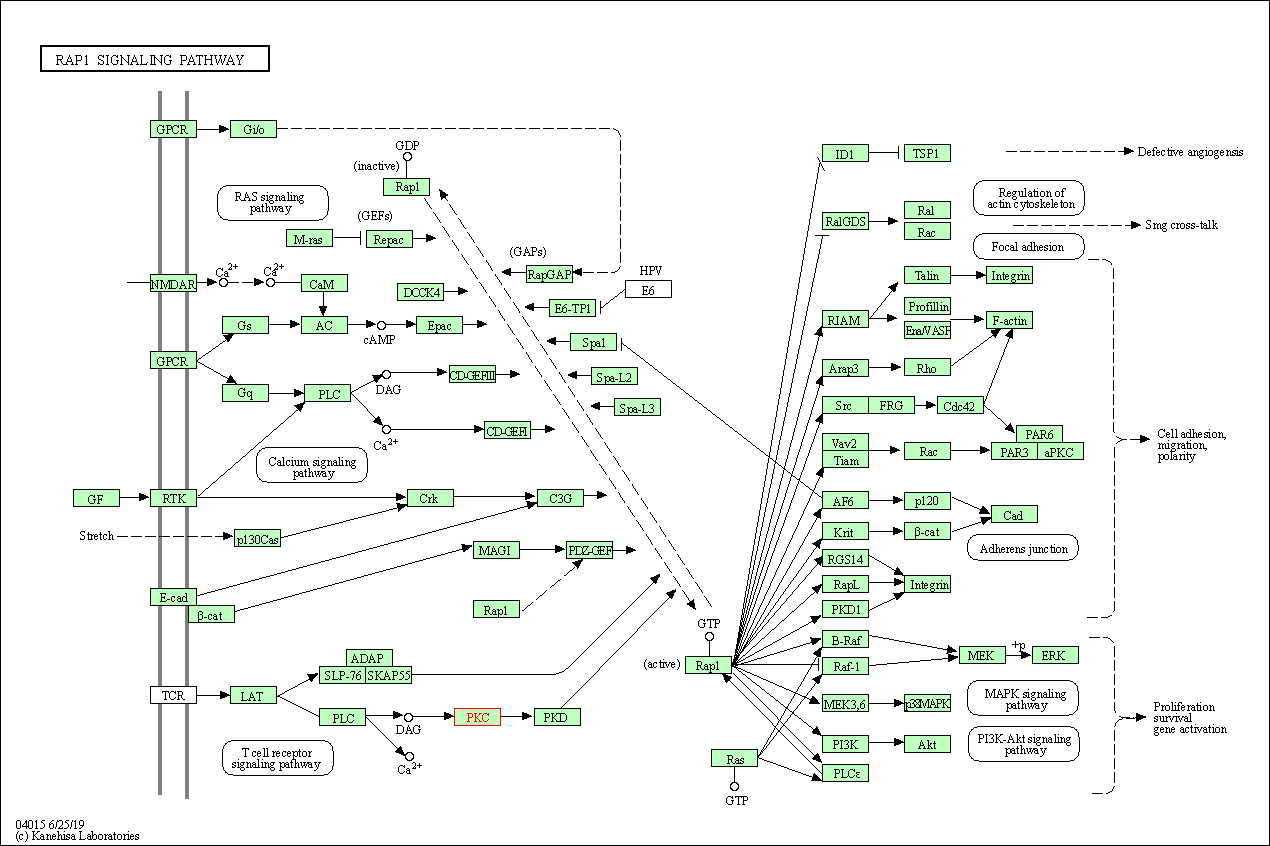
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | hsa04070 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |
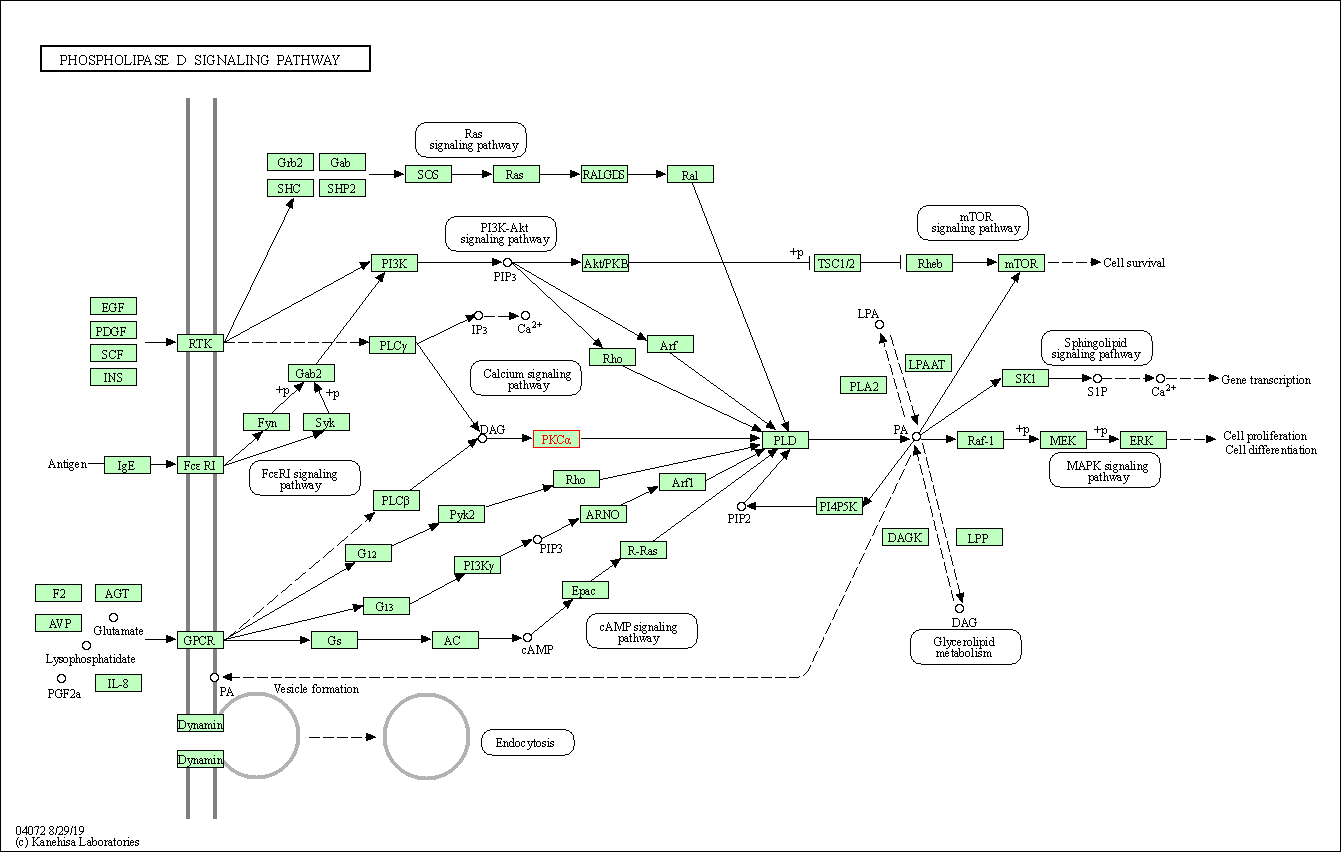
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |
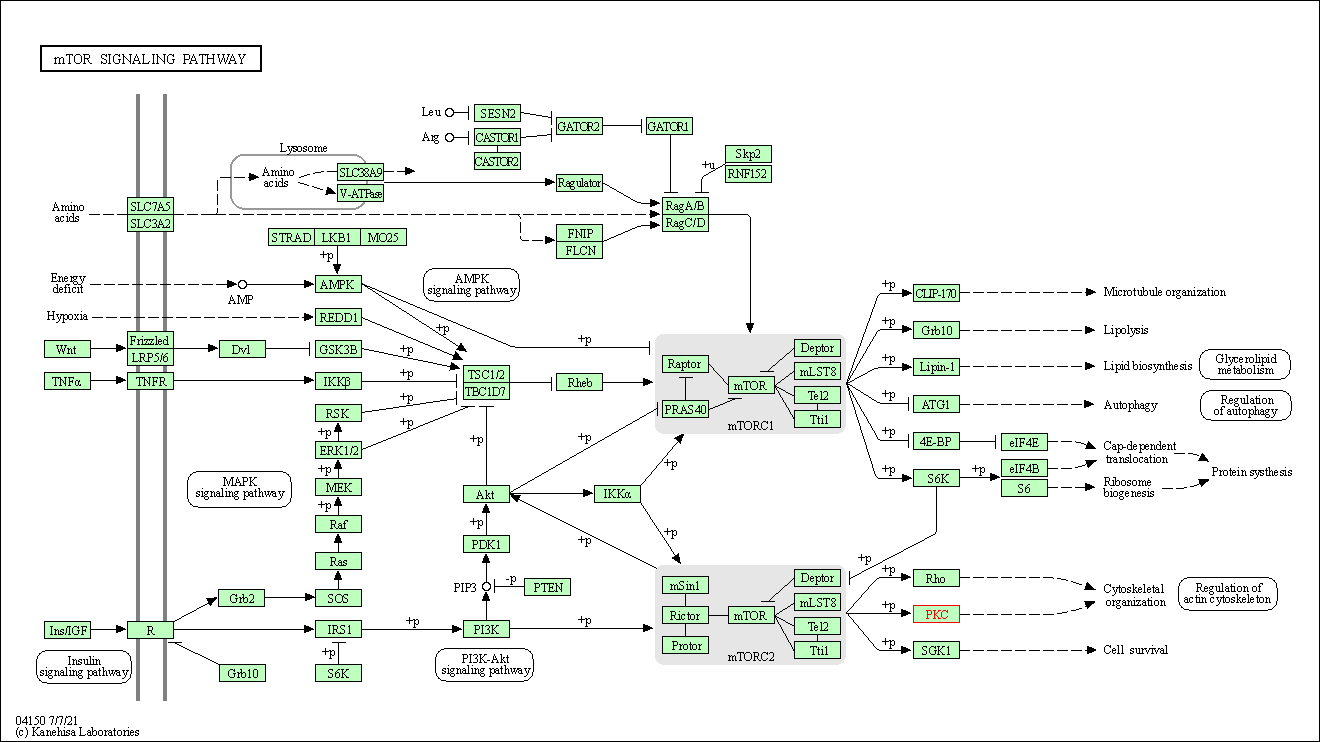
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
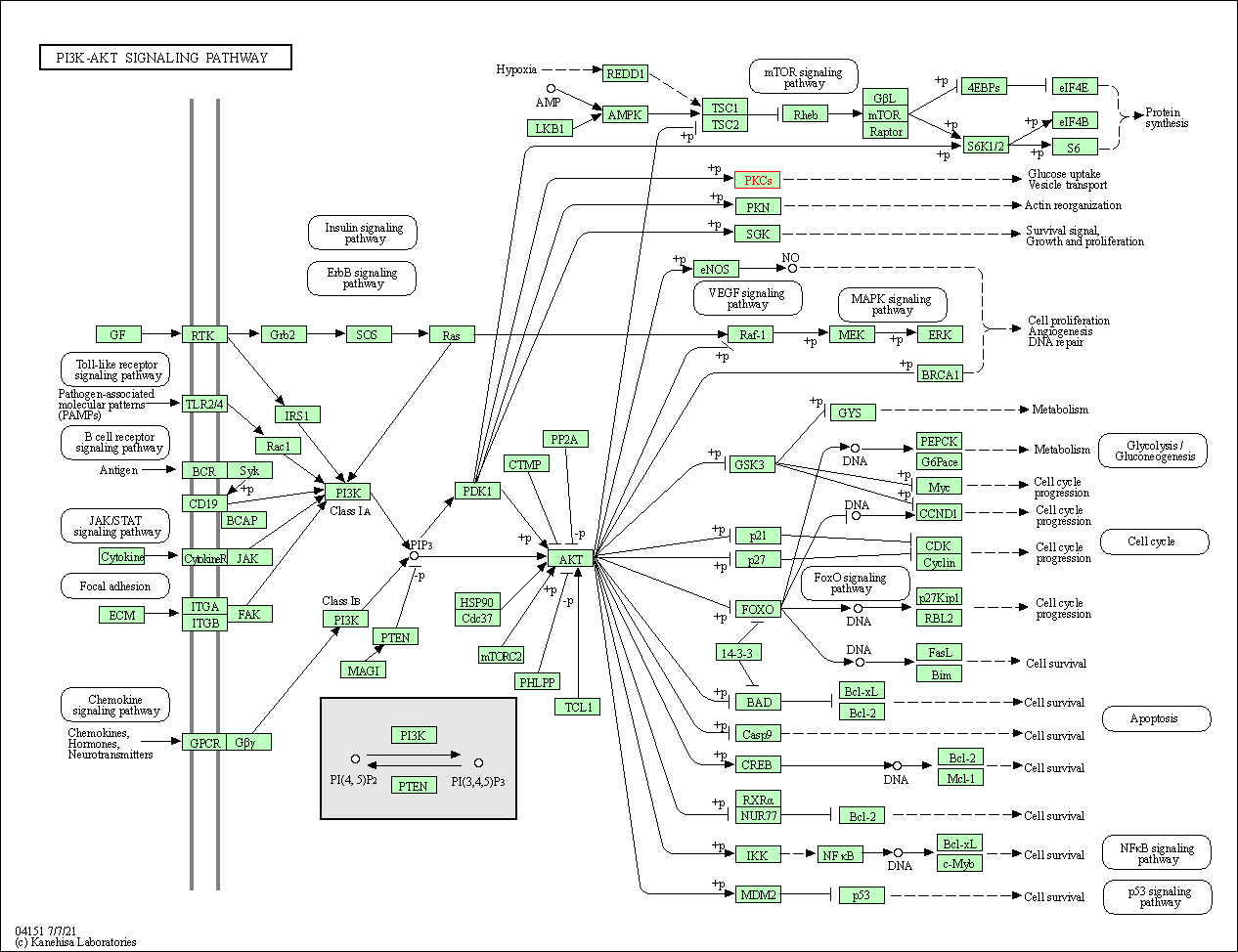
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |
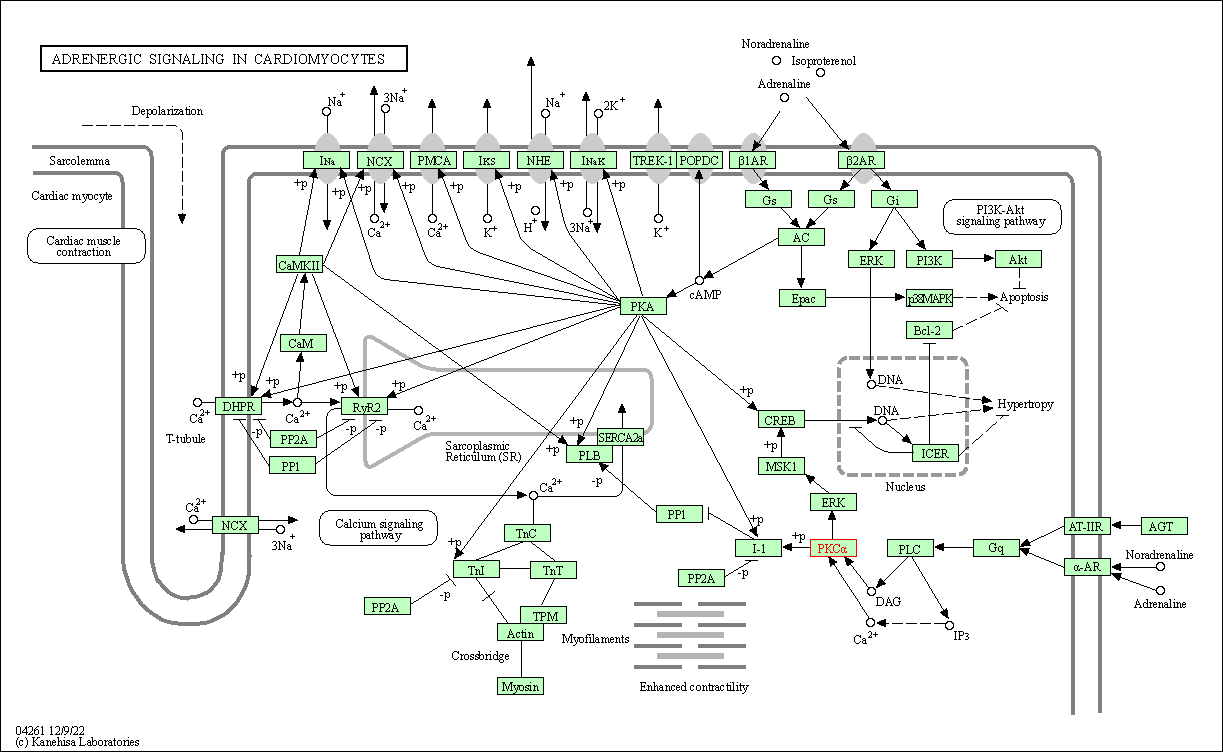
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |
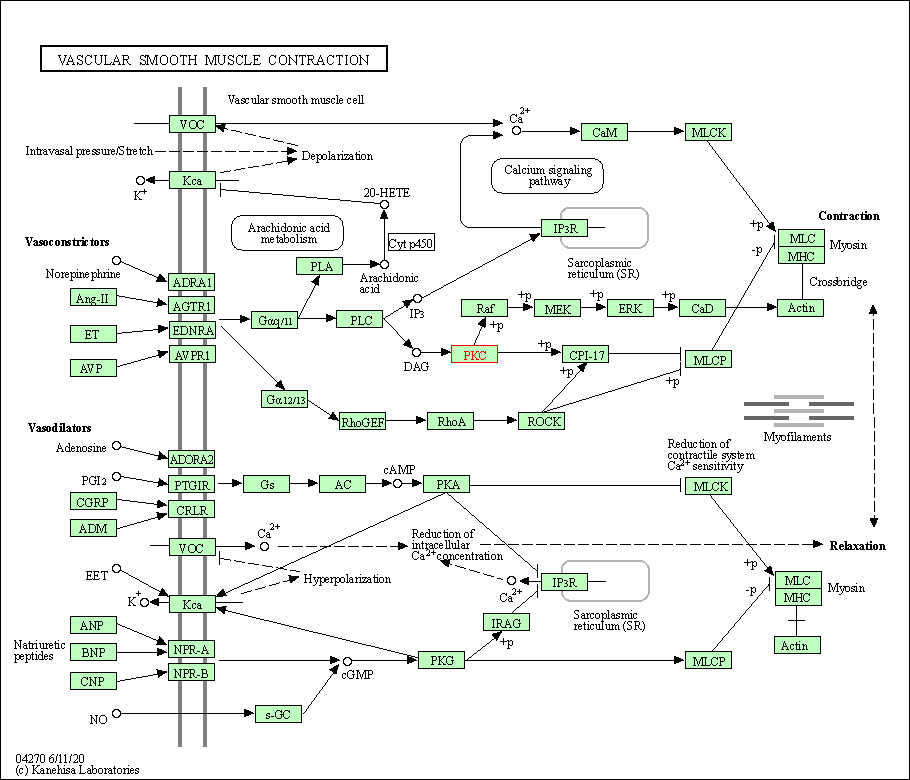
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | Affiliated Target |
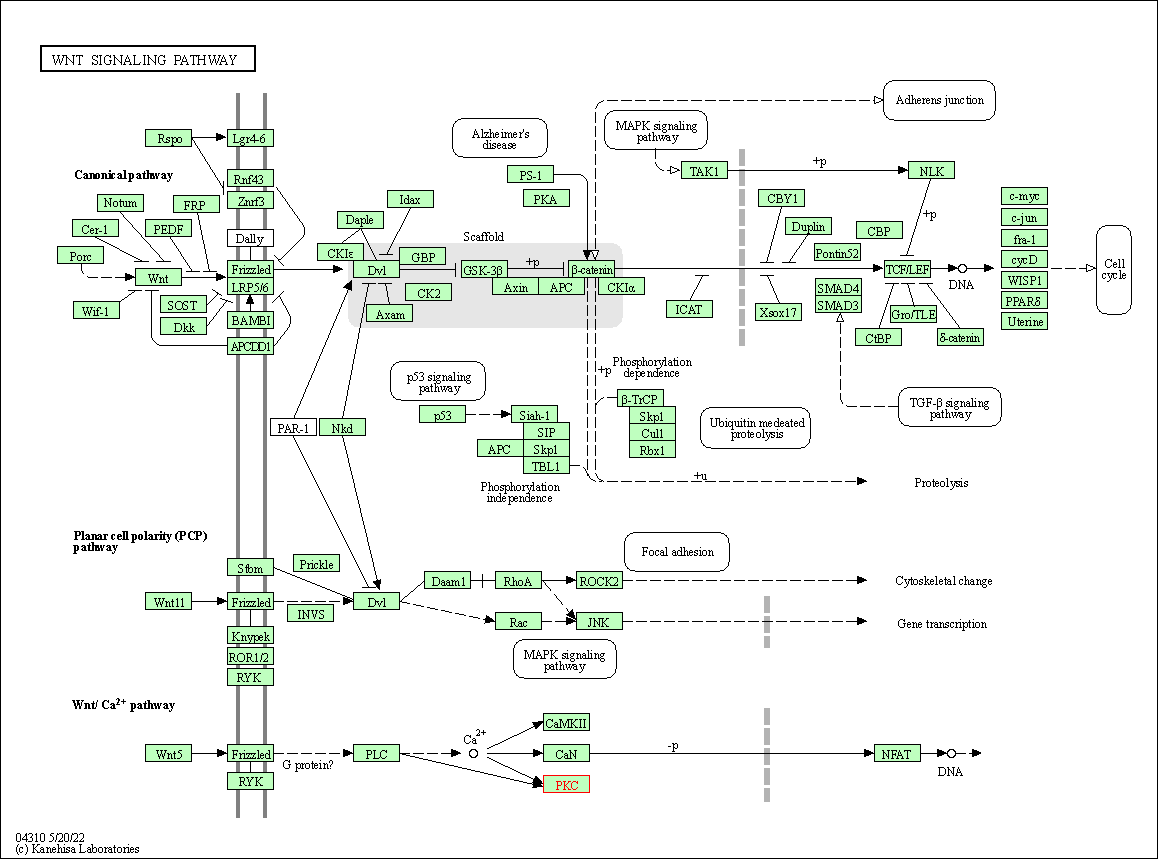
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Axon guidance | hsa04360 | Affiliated Target |
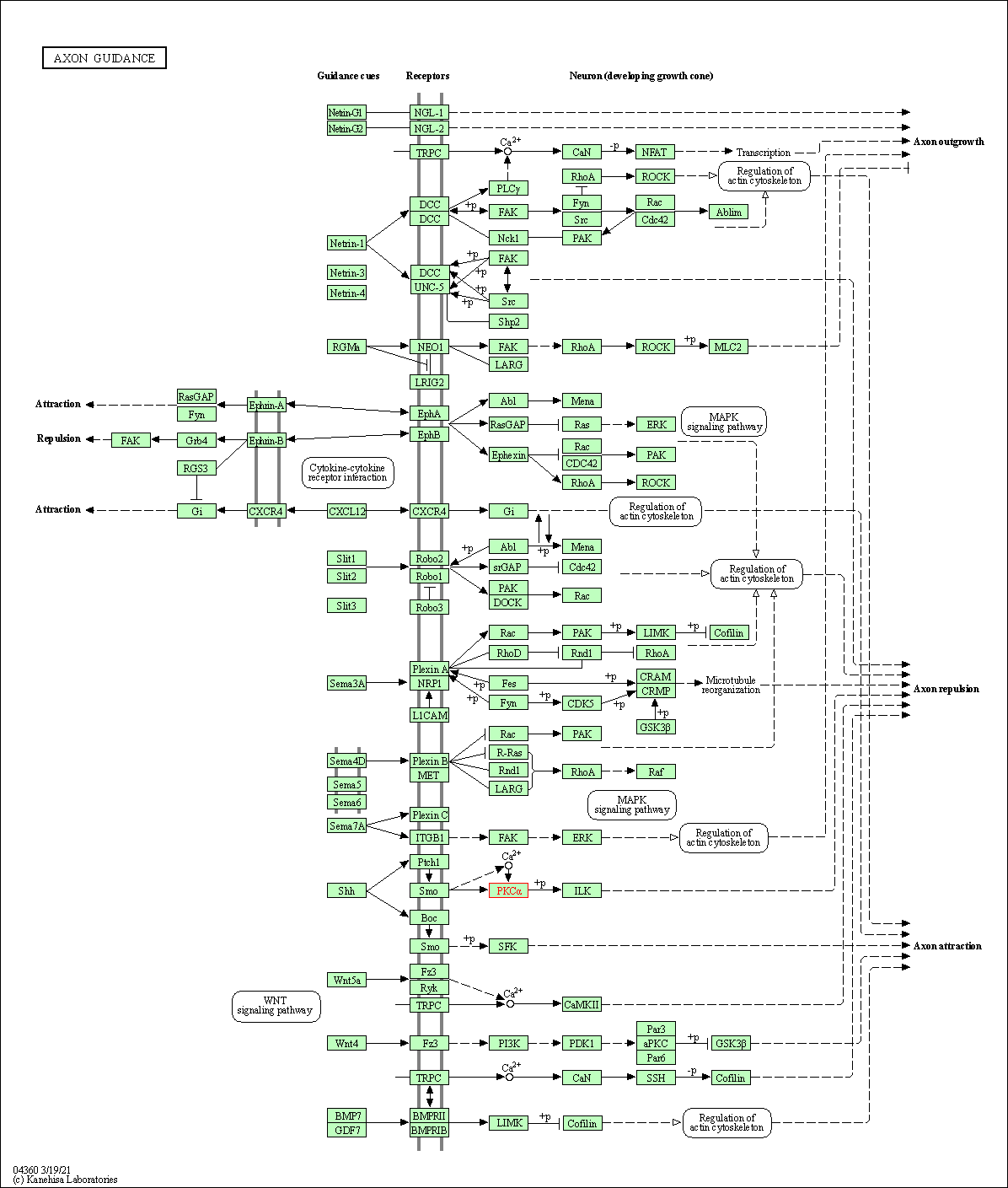
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | Affiliated Target |
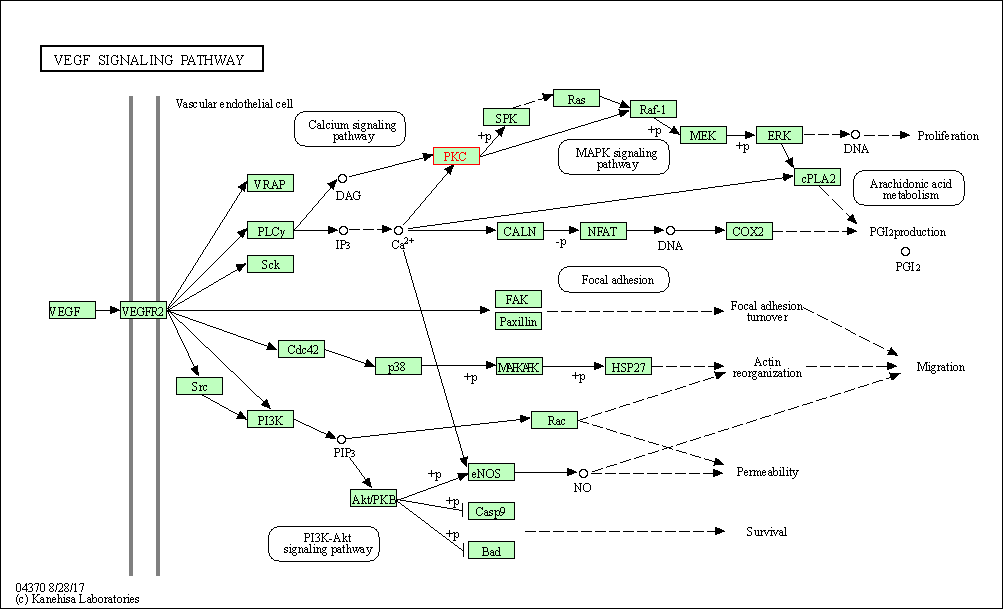
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Gap junction | hsa04540 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | hsa04670 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term potentiation | hsa04720 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glutamatergic synapse | hsa04724 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |
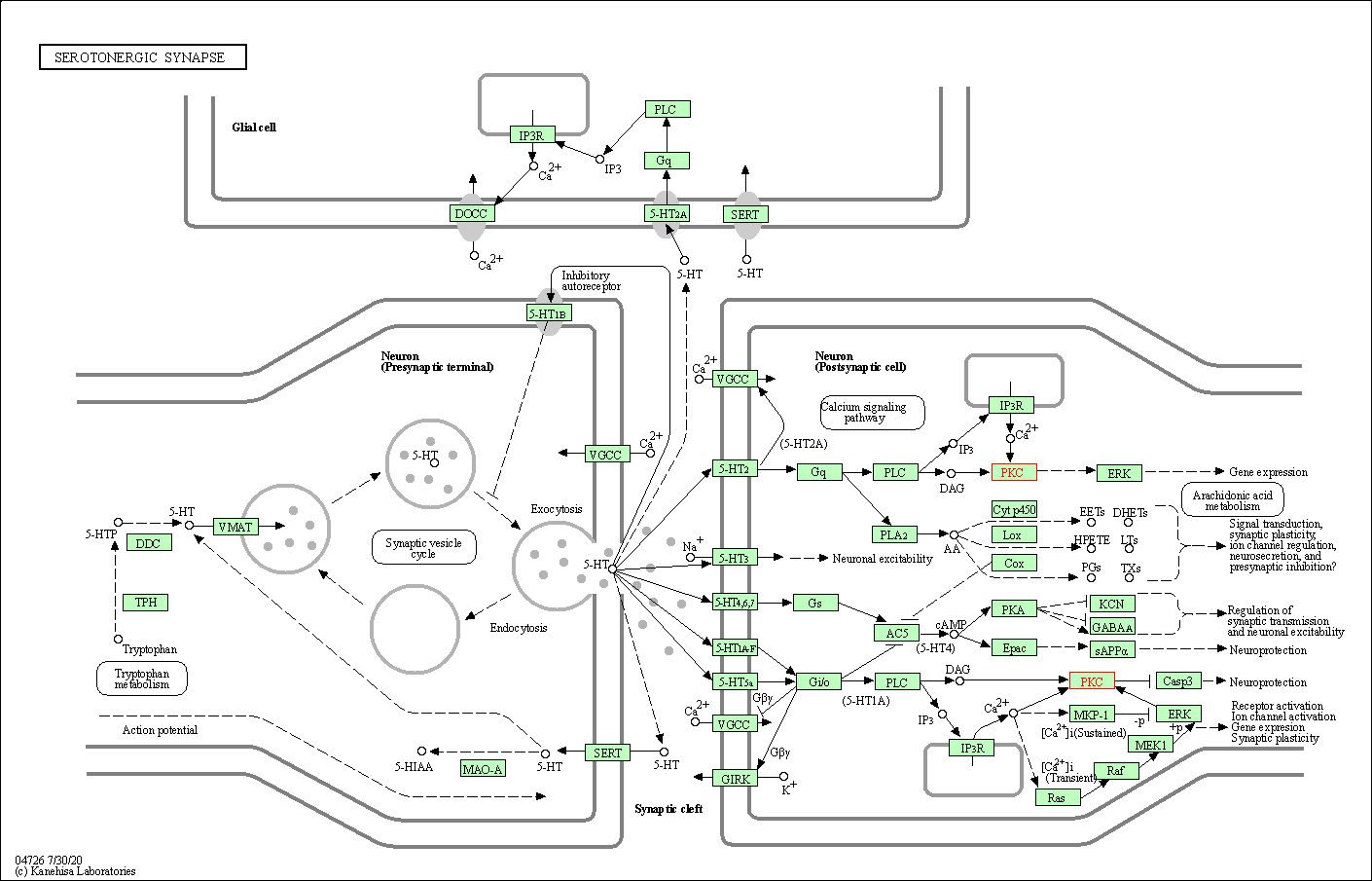
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GABAergic synapse | hsa04727 | Affiliated Target |
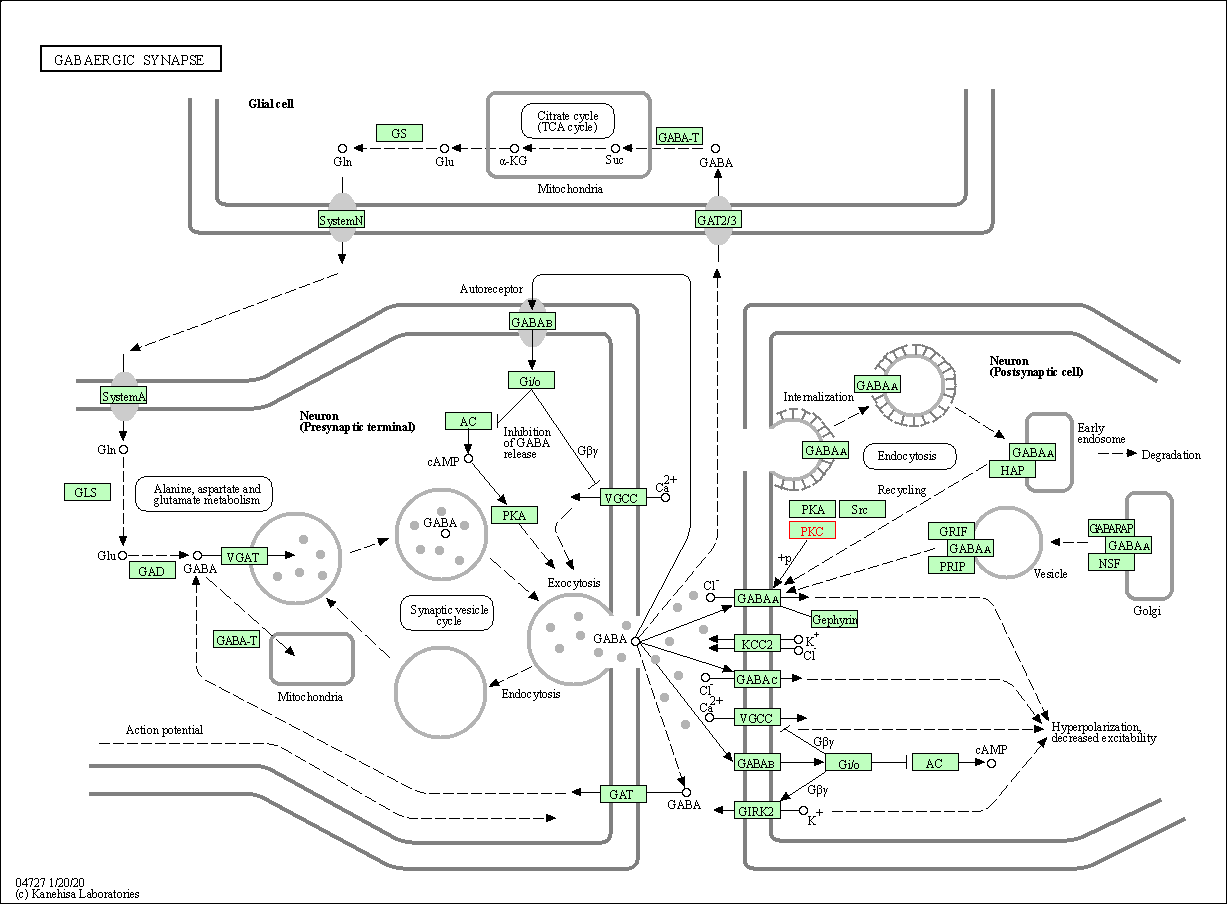
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |
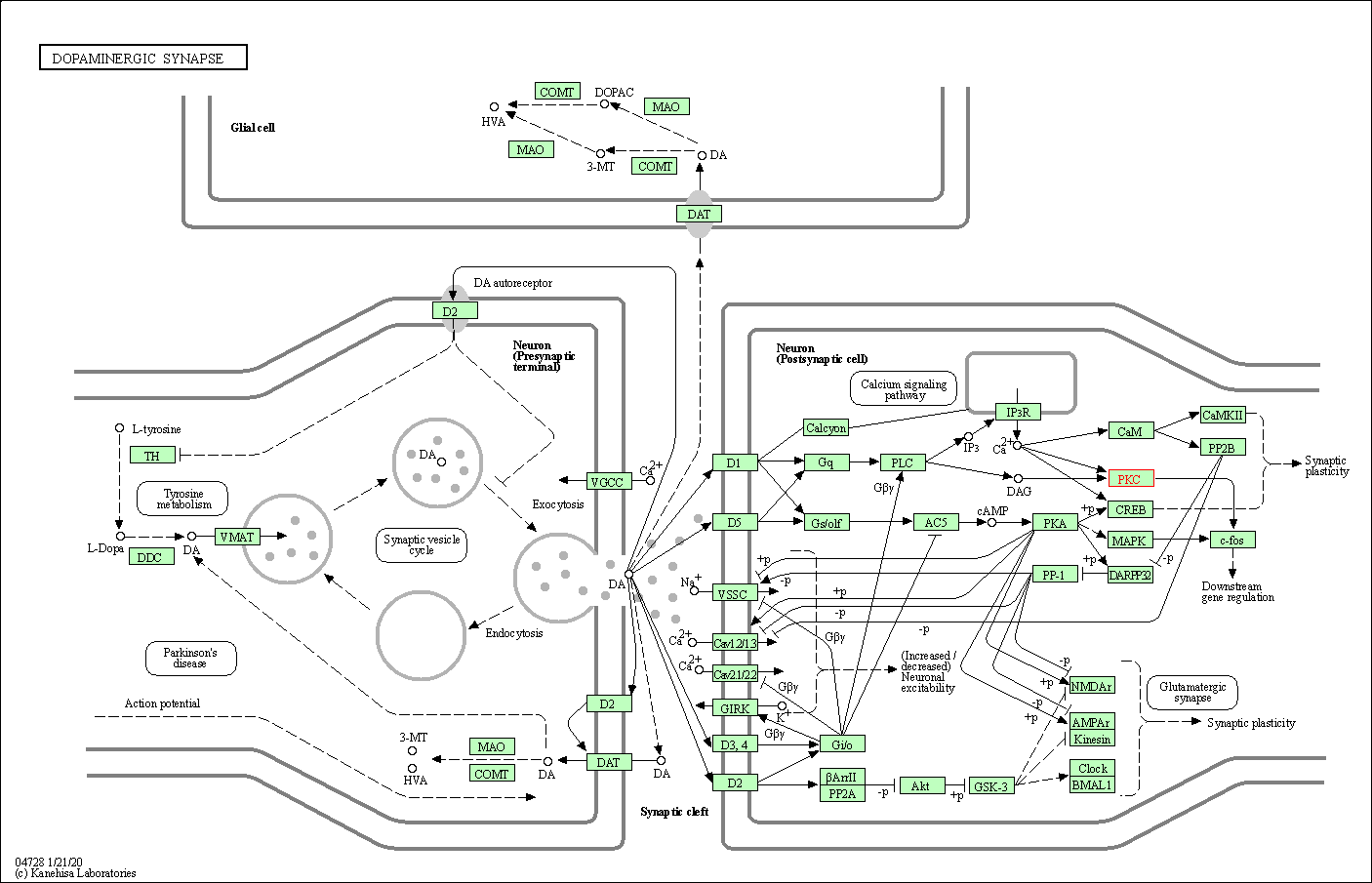
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |
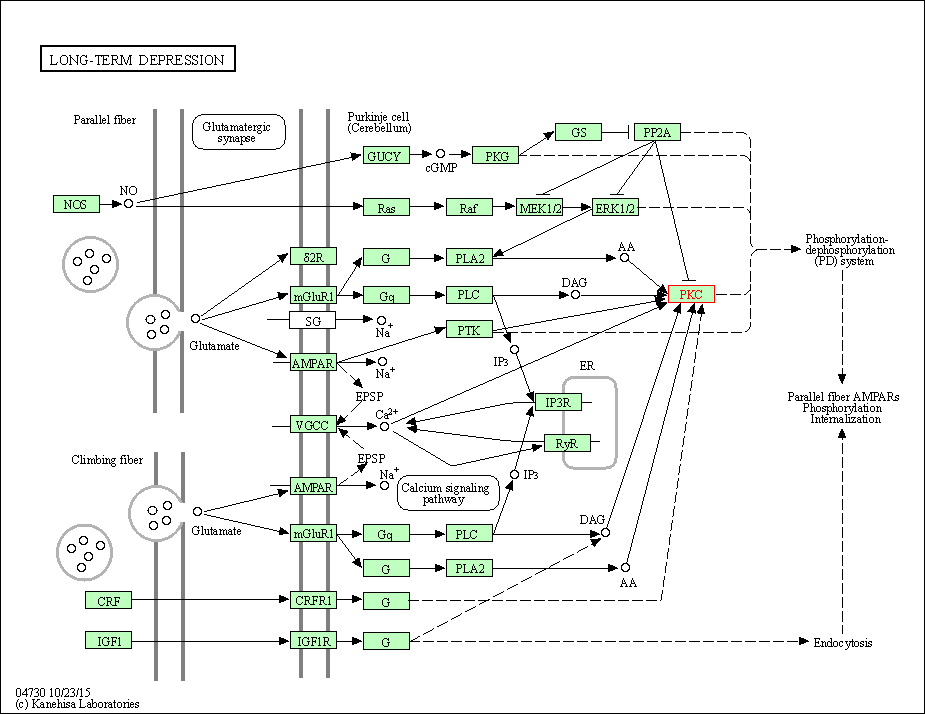
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | hsa04750 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Melanogenesis | hsa04916 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone synthesis | hsa04918 | Affiliated Target |
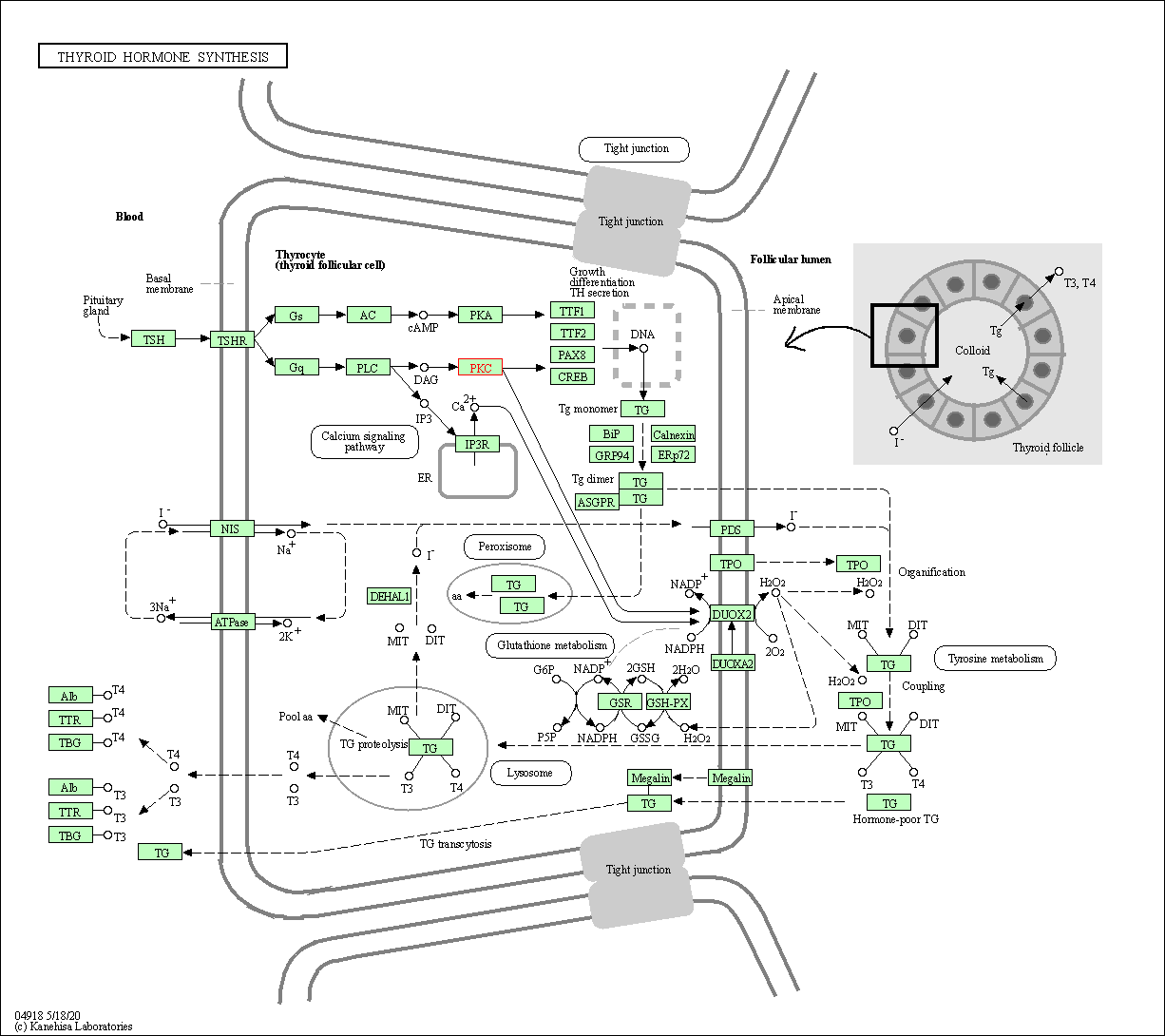
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |
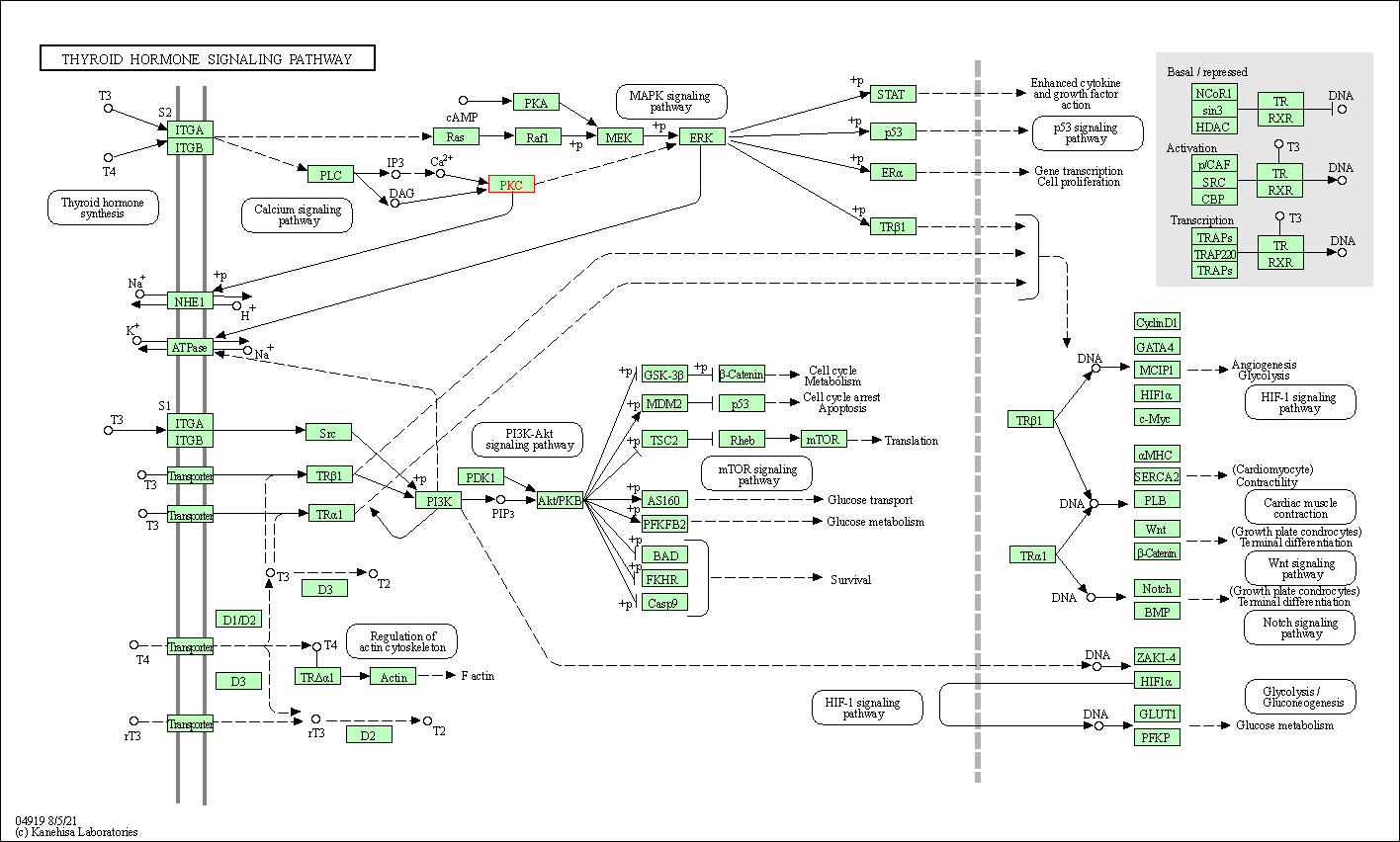
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |
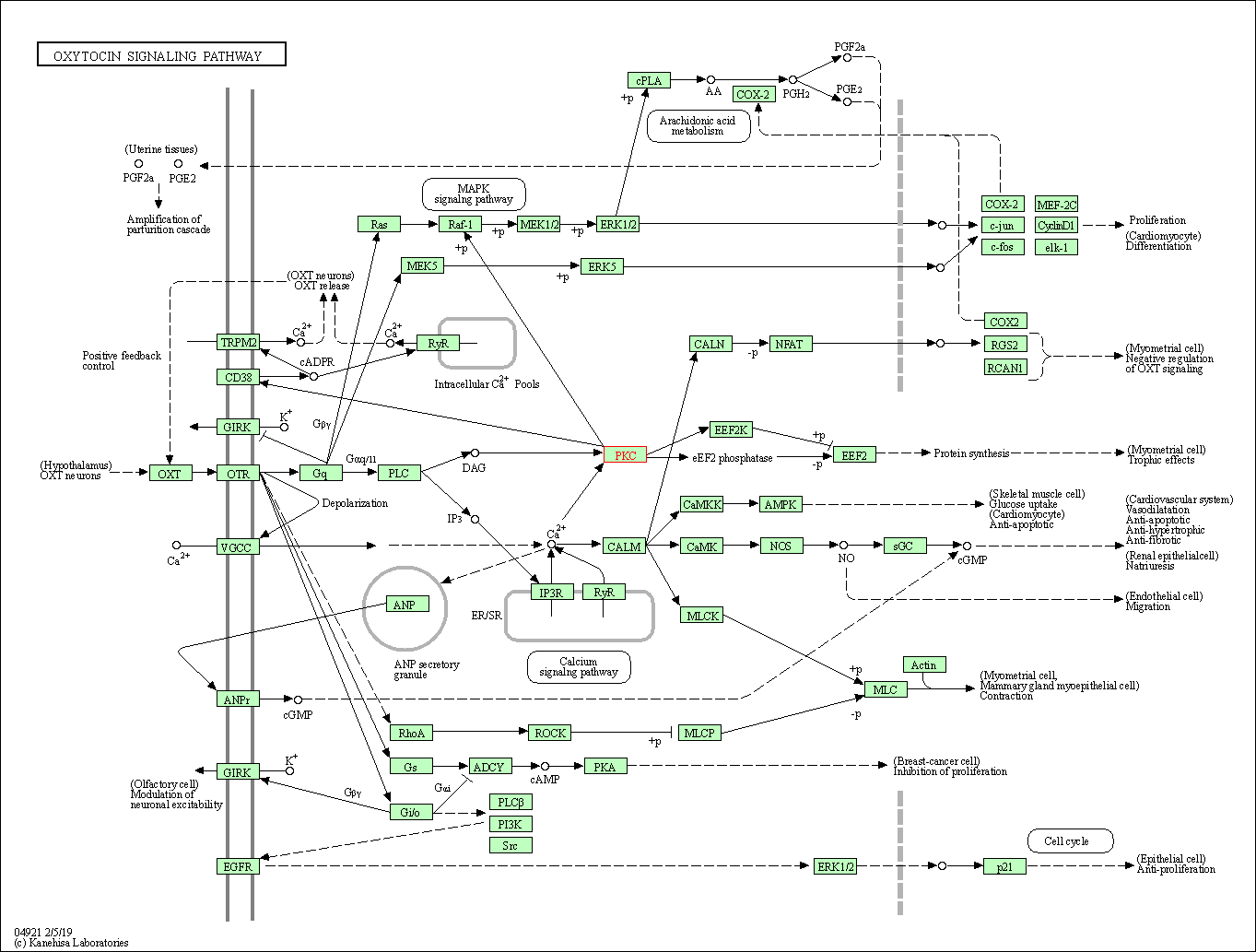
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | hsa04925 | Affiliated Target |
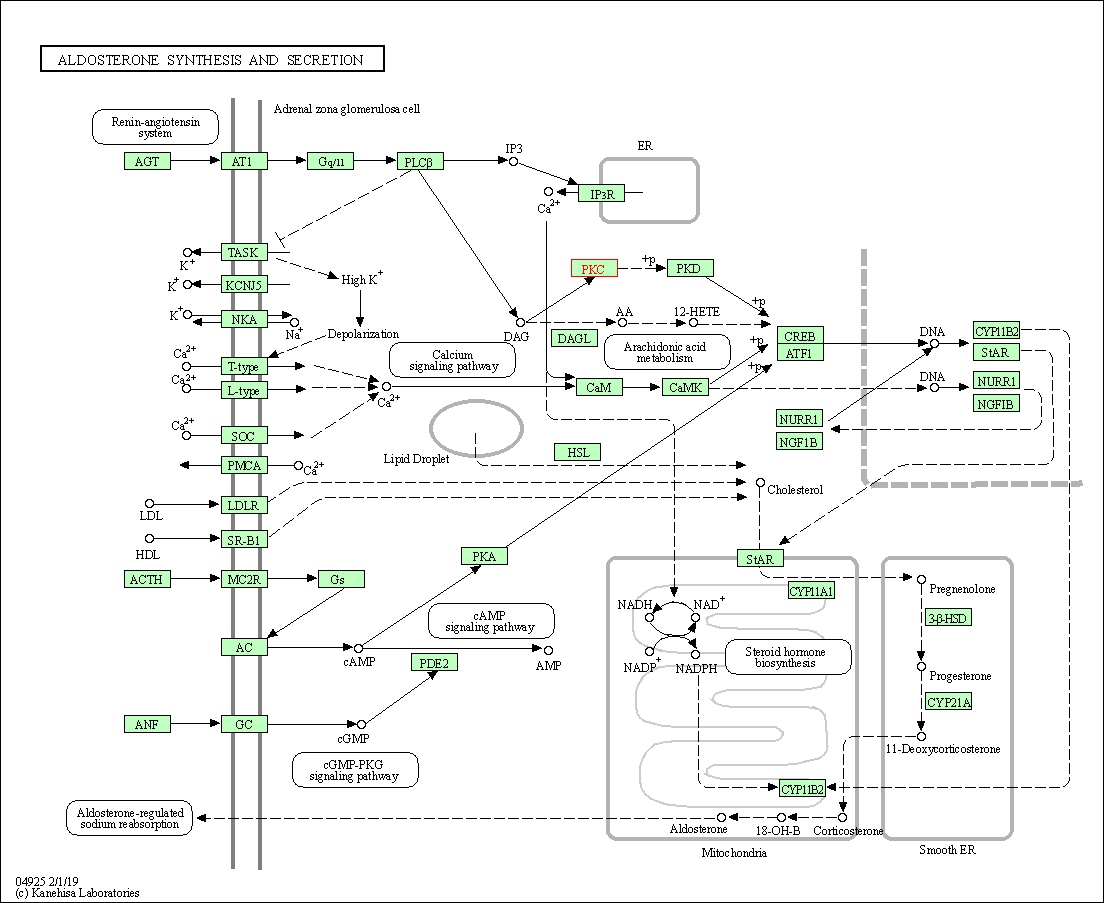
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | hsa04960 | Affiliated Target |
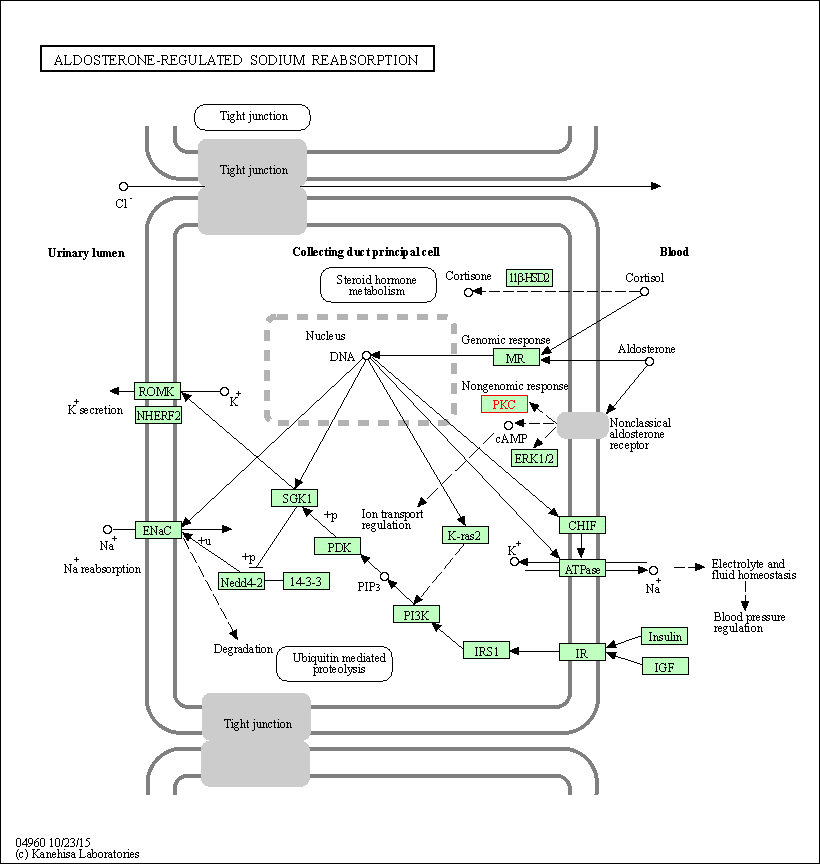
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption | hsa04961 | Affiliated Target |
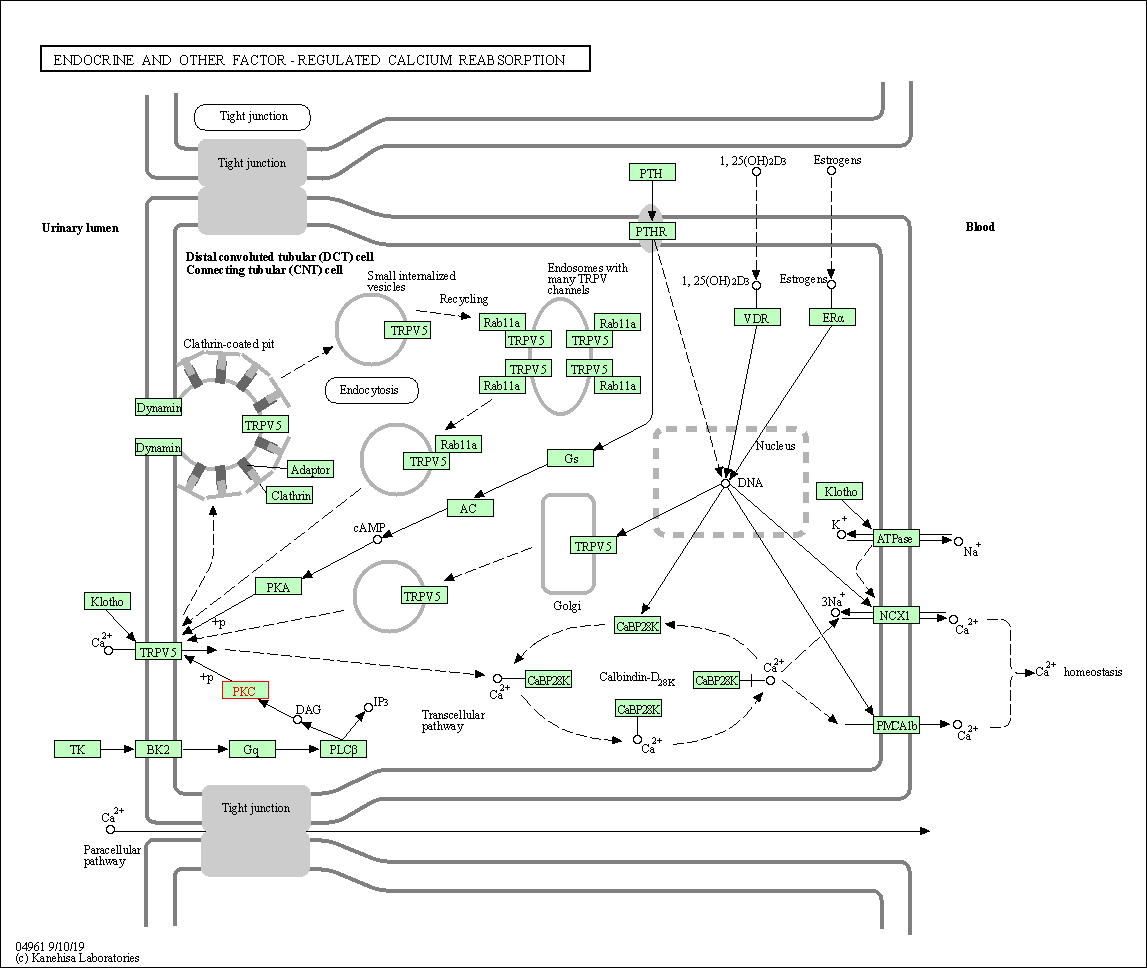
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Salivary secretion | hsa04970 | Affiliated Target |
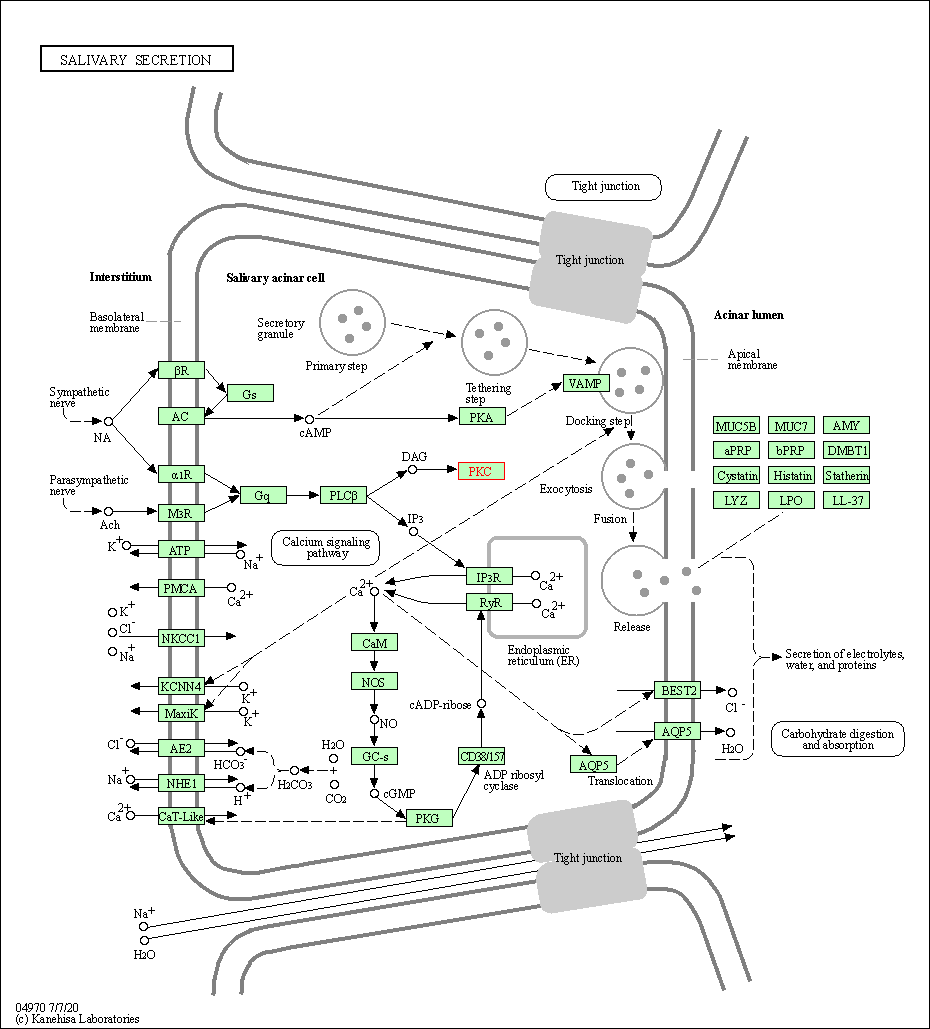
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Gastric acid secretion | hsa04971 | Affiliated Target |
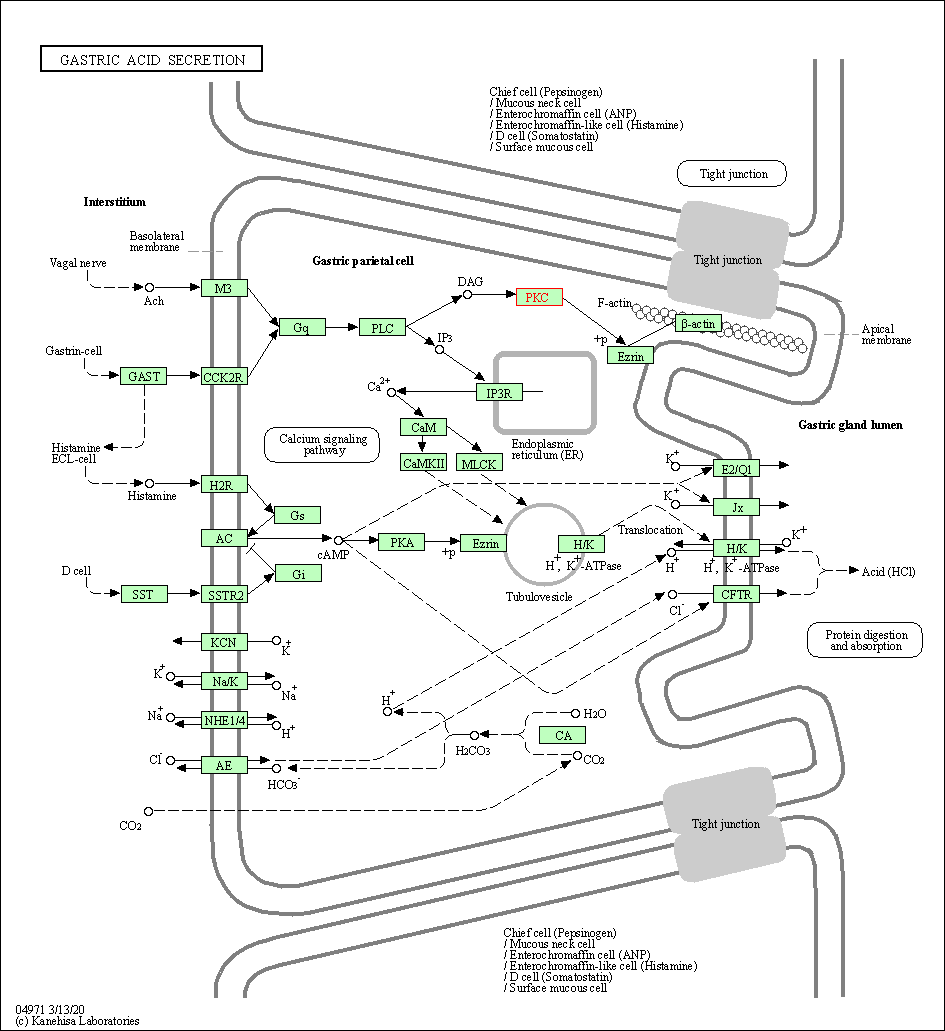
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Pancreatic secretion | hsa04972 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 31 | Degree centrality | 3.33E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 4.24E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.55E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 8.39E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.88E+01 | Topological coefficient | 4.87E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Emerging drugs for psoriasis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):145-63. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00533559) Mechanism of Fatty Acid-induced Impairment of Glucose-simulated Insulin Secretion - Effect of Buphenyl. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800003095) | |||||
| REF 4 | Polo-like kinase inhibitor Ro5203280 has potent antitumor activity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Aug;12(8):1393-401. | |||||
| REF 5 | Phase II study of PKC-alpha antisense oligonucleotide aprinocarsen in combination with gemcitabine and carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer.2006 May;52(2):173-80. | |||||
| REF 6 | Phenylethanoid glycosides from Digitalis purpurea and Penstemon linarioides with PKCalpha-inhibitory activity. J Nat Prod. 1998 Nov;61(11):1410-2. | |||||
| REF 7 | Evaluation of differential hypoxic cytotoxicity and electrochemical studies of nitro 5-deazaflavins, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 5(18):2155-2160 (1995). | |||||
| REF 8 | Bisindolylmaleimide inhibitors of protein kinase C. Further conformational restriction of a tertiary amine side chain, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 4(11):1303-1308 (1994). | |||||
| REF 9 | (-)-Cercosporamide derivatives as novel antihyperglycemic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Feb 1;19(3):724-6. | |||||
| REF 10 | Design, synthesis, and biological activity of isophthalic acid derivatives targeted to the C1 domain of protein kinase C. J Med Chem. 2009 Jul 9;52(13):3969-81. | |||||
| REF 11 | Multivariate analysis by the minimum spanning tree method of the structural determinants of diphenylethylenes and triphenylacrylonitriles implicate... J Med Chem. 1992 Feb 7;35(3):573-83. | |||||
| REF 12 | Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 3,4-diarylmaleimides as angiogenesis inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2006 Feb 23;49(4):1271-81. | |||||
| REF 13 | Optimization of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6239-47. | |||||
| REF 14 | Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95-105. | |||||
| REF 15 | Inhibition of protein kinase C mu by various inhibitors. Differentiation from protein kinase c isoenzymes. FEBS Lett. 1996 Aug 26;392(2):77-80. | |||||
| REF 16 | (S)-13-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-10,11,14,15-tetrahydro-4,9:16, 21-dimetheno-1H, 13H-dibenzo[e,k]pyrrolo[3,4-h][1,4,13]oxadiazacyclohexadecene-1,3(2H... J Med Chem. 1996 Jul 5;39(14):2664-71. | |||||
| REF 17 | A nonpromoting phorbol from the samoan medicinal plant Homalanthus nutans inhibits cell killing by HIV-1. J Med Chem. 1992 May 29;35(11):1978-86. | |||||
| REF 18 | Tannins as selective inhibitors of protein kinase C, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2(3):239-244 (1992). | |||||
| REF 19 | Inhibitors of protein kinase C. 1. 2,3-Bisarylmaleimides. J Med Chem. 1992 Jan;35(1):177-84. | |||||
| REF 20 | Novel protein kinase C inhibitors: synthesis and PKC inhibition of beta-substituted polythiophene derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999 Aug 2;9(15):2279-82. | |||||
| REF 21 | Optimized protein kinase C-Theta (PKC-Theta) inhibitors reveal only modest anti-inflammatory efficacy in a rodent model of arthritis. J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 8;58(1):333-46. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

