Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T14602
(Former ID: TTDS00205)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Coagulation factor VIII (F8)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Procoagulant component; F8C; Antihemophilic factor; AHF
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
F8
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Cerebral ischaemia [ICD-11: 8B1Z] | |||||
| 2 | Coagulation defect [ICD-11: 3B10] | |||||
| 3 | Sepsis [ICD-11: 1G40-1G41] | |||||
| Function |
Factor VIII, along with calcium and phospholipid, acts as a cofactor for F9/factor IXa when it converts F10/factor X to the activated form, factor Xa.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MQIELSTCFFLCLLRFCFSATRRYYLGAVELSWDYMQSDLGELPVDARFPPRVPKSFPFN
TSVVYKKTLFVEFTDHLFNIAKPRPPWMGLLGPTIQAEVYDTVVITLKNMASHPVSLHAV GVSYWKASEGAEYDDQTSQREKEDDKVFPGGSHTYVWQVLKENGPMASDPLCLTYSYLSH VDLVKDLNSGLIGALLVCREGSLAKEKTQTLHKFILLFAVFDEGKSWHSETKNSLMQDRD AASARAWPKMHTVNGYVNRSLPGLIGCHRKSVYWHVIGMGTTPEVHSIFLEGHTFLVRNH RQASLEISPITFLTAQTLLMDLGQFLLFCHISSHQHDGMEAYVKVDSCPEEPQLRMKNNE EAEDYDDDLTDSEMDVVRFDDDNSPSFIQIRSVAKKHPKTWVHYIAAEEEDWDYAPLVLA PDDRSYKSQYLNNGPQRIGRKYKKVRFMAYTDETFKTREAIQHESGILGPLLYGEVGDTL LIIFKNQASRPYNIYPHGITDVRPLYSRRLPKGVKHLKDFPILPGEIFKYKWTVTVEDGP TKSDPRCLTRYYSSFVNMERDLASGLIGPLLICYKESVDQRGNQIMSDKRNVILFSVFDE NRSWYLTENIQRFLPNPAGVQLEDPEFQASNIMHSINGYVFDSLQLSVCLHEVAYWYILS IGAQTDFLSVFFSGYTFKHKMVYEDTLTLFPFSGETVFMSMENPGLWILGCHNSDFRNRG MTALLKVSSCDKNTGDYYEDSYEDISAYLLSKNNAIEPRSFSQNSRHPSTRQKQFNATTI PENDIEKTDPWFAHRTPMPKIQNVSSSDLLMLLRQSPTPHGLSLSDLQEAKYETFSDDPS PGAIDSNNSLSEMTHFRPQLHHSGDMVFTPESGLQLRLNEKLGTTAATELKKLDFKVSST SNNLISTIPSDNLAAGTDNTSSLGPPSMPVHYDSQLDTTLFGKKSSPLTESGGPLSLSEE NNDSKLLESGLMNSQESSWGKNVSSTESGRLFKGKRAHGPALLTKDNALFKVSISLLKTN KTSNNSATNRKTHIDGPSLLIENSPSVWQNILESDTEFKKVTPLIHDRMLMDKNATALRL NHMSNKTTSSKNMEMVQQKKEGPIPPDAQNPDMSFFKMLFLPESARWIQRTHGKNSLNSG QGPSPKQLVSLGPEKSVEGQNFLSEKNKVVVGKGEFTKDVGLKEMVFPSSRNLFLTNLDN LHENNTHNQEKKIQEEIEKKETLIQENVVLPQIHTVTGTKNFMKNLFLLSTRQNVEGSYD GAYAPVLQDFRSLNDSTNRTKKHTAHFSKKGEEENLEGLGNQTKQIVEKYACTTRISPNT SQQNFVTQRSKRALKQFRLPLEETELEKRIIVDDTSTQWSKNMKHLTPSTLTQIDYNEKE KGAITQSPLSDCLTRSHSIPQANRSPLPIAKVSSFPSIRPIYLTRVLFQDNSSHLPAASY RKKDSGVQESSHFLQGAKKNNLSLAILTLEMTGDQREVGSLGTSATNSVTYKKVENTVLP KPDLPKTSGKVELLPKVHIYQKDLFPTETSNGSPGHLDLVEGSLLQGTEGAIKWNEANRP GKVPFLRVATESSAKTPSKLLDPLAWDNHYGTQIPKEEWKSQEKSPEKTAFKKKDTILSL NACESNHAIAAINEGQNKPEIEVTWAKQGRTERLCSQNPPVLKRHQREITRTTLQSDQEE IDYDDTISVEMKKEDFDIYDEDENQSPRSFQKKTRHYFIAAVERLWDYGMSSSPHVLRNR AQSGSVPQFKKVVFQEFTDGSFTQPLYRGELNEHLGLLGPYIRAEVEDNIMVTFRNQASR PYSFYSSLISYEEDQRQGAEPRKNFVKPNETKTYFWKVQHHMAPTKDEFDCKAWAYFSDV DLEKDVHSGLIGPLLVCHTNTLNPAHGRQVTVQEFALFFTIFDETKSWYFTENMERNCRA PCNIQMEDPTFKENYRFHAINGYIMDTLPGLVMAQDQRIRWYLLSMGSNENIHSIHFSGH VFTVRKKEEYKMALYNLYPGVFETVEMLPSKAGIWRVECLIGEHLHAGMSTLFLVYSNKC QTPLGMASGHIRDFQITASGQYGQWAPKLARLHYSGSINAWSTKEPFSWIKVDLLAPMII HGIKTQGARQKFSSLYISQFIIMYSLDGKKWQTYRGNSTGTLMVFFGNVDSSGIKHNIFN PPIIARYIRLHPTHYSIRSTLRMELMGCDLNSCSMPLGMESKAISDAQITASSYFTNMFA TWSPSKARLHLQGRSNAWRPQVNNPKEWLQVDFQKTMKVTGVTTQGVKSLLTSMYVKEFL ISSSQDGHQWTLFFQNGKVKVFQGNQDSFTPVVNSLDPPLLTRYLRIHPQSWVHQIALRM EVLGCEAQDLY Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Drotrecogin alfa | Drug Info | Approved | Cerebrovascular ischaemia | [4], [5], [6] | |
| 2 | Factor 8 | Drug Info | Approved | Hemophilia | [6] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 8 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BAY 94-9027 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Stroke | [11] | |
| 2 | N8-GP | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Factor VIII deficiency | [12] | |
| 3 | OBI-1 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Factor VIII deficiency | [13] | |
| 4 | Plasma derived factor VIII PEGylated liposomal | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Factor VIII deficiency | [14] | |
| 5 | Recombinant von Willebrand factor/recombinant Factor VIII complex | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Von willebrand disease | [15] | |
| 6 | Turoctocog alfa | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Haemophilia A | [16] | |
| 7 | BAY 794980 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Discovery agent | [17] | |
| 8 | TB-402 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Atrial fibrillation | [18] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 3 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Drotrecogin alfa | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | GPG-290 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 3 | IATX-FVIII | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 15 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Factor 8 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 2 | BAY 94-9027 | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 3 | N8-GP | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 4 | OBI-1 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 5 | Plasma derived factor VIII PEGylated liposomal | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 6 | Recombinant von Willebrand factor/recombinant Factor VIII complex | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 7 | Turoctocog alfa | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 8 | BAY 794980 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 9 | Factor VIII-XTEN | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 10 | Full-length Factor VIII molecule | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 11 | Human recombinant factor VIII | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 12 | LA-N8 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 13 | LG-889 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 14 | Long-acting factor VIII | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 15 | Simoctocog alfa | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| Stimulator | [+] 1 Stimulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LG-888 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: (2R)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)-3-[2-imino-3-(2-piperidin-1-ylethyl)benzimidazol-1-yl]propan-2-ol | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Factor VIII Trp2313-His2315 segment is involved in membrane binding as shown by crystal structure of complex between factor VIII C2 domain and an inhibitor | PDB:3HNB | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.15 Å | Mutation | No | [30] |
| PDB Sequence |
SCSMPLGMES
2182 KAISDAQITA2192 SSYFTNMFAT2202 WSPSKARLHL2212 QGRSNAWRPQ2222 VNNPKEWLQV 2232 DFQKTMKVTG2242 VTTQGVKSLL2252 TSMYVKEFLI2262 SSSQDGHQWT2272 LFFQNGKVKV 2282 FQGNQDSFTP2292 VVNSLDPPLL2302 TRYLRIHPQS2312 WVHQIALRME2322 VLGCEA |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | hsa04610 | Affiliated Target |
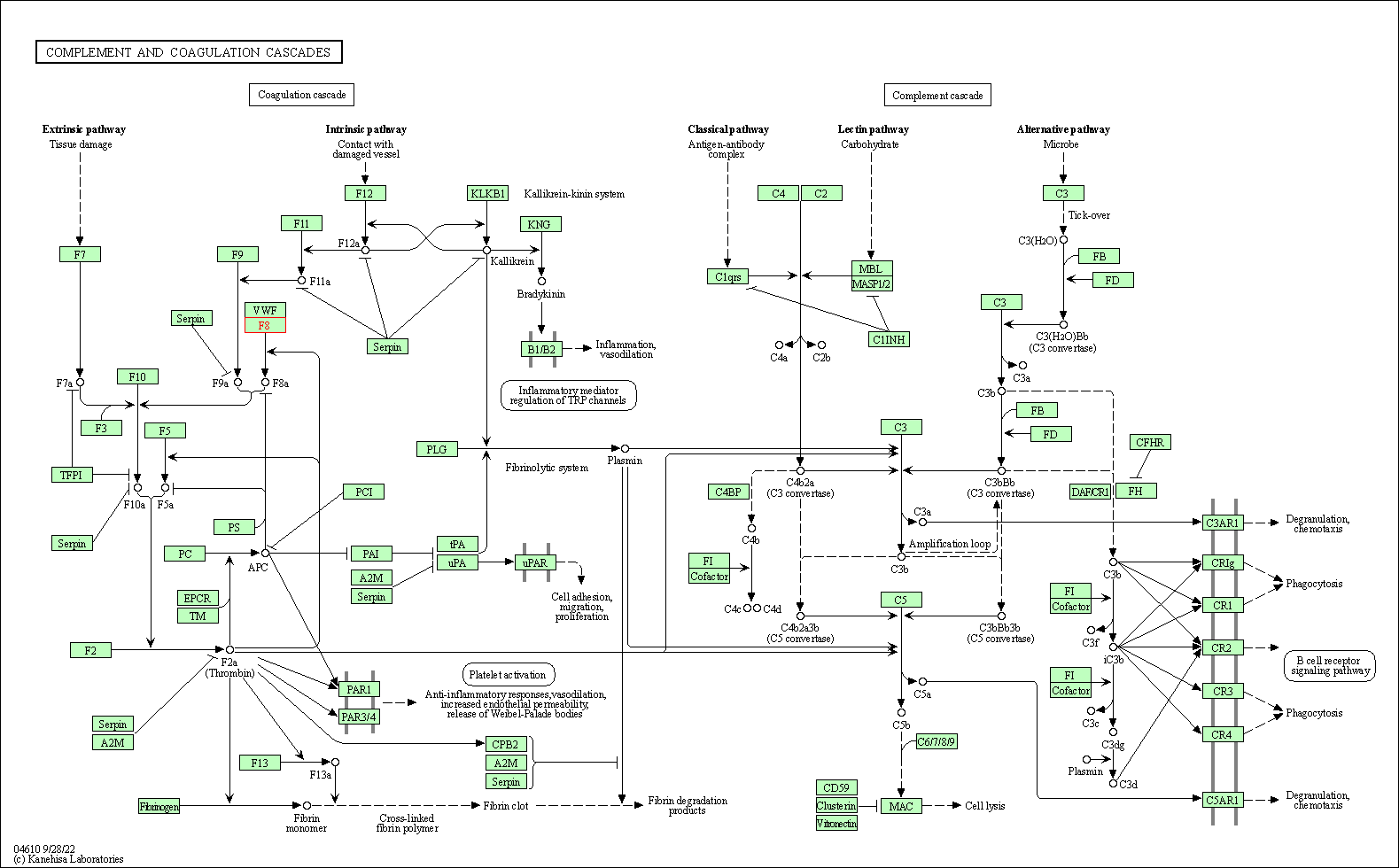
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 9 | Degree centrality | 9.67E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 2.85E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.83E-01 | Radiality | 1.31E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.61E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.14E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.04E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 1 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Complement and coagulation cascades | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Blood coagulation | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Coagulation | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 5 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Platelet degranulation | |||||
| 2 | Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation | |||||
| 3 | Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation | |||||
| 4 | COPII (Coat Protein 2) Mediated Vesicle Transport | |||||
| 5 | Cargo concentration in the ER | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Complement and Coagulation Cascades | |||||
| 2 | Blood Clotting Cascade | |||||
| 3 | Formation of Fibrin Clot (Clotting Cascade) | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Protein C in critical illness. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2009 Jun 15;66(12):1089-96. | |||||
| REF 2 | 2014 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Feb;14(2):77-81. | |||||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Sanofi | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6788). | |||||
| REF 5 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 6 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 7 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800035403) | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04370054) Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of PF-07055480 in Moderately Severe to Severe Hemophilia A Adults (AFFINE). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04323098) Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec, With Prophylactic Steroids in Hemophilia A (GENEr8-3). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04979442) A Randomized Multicenter Phase 3 Study of Milademetan Versus Trabectedin in Patients With Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021112) | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02137850) Safety and Efficacy of Turoctocog Alfa Pegol (N8-GP) in Previously Untreated Patients With Haemophilia A. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01434511) Study of Modified Recombinant Factor VIII (OBI-1) in Subjects With Congenital Hemophilia A. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 14 | Recombinant factor VIII in the management of hemophilia A: current use and future promise. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009; 5: 391-402. | |||||
| REF 15 | FcRn Rescues Recombinant Factor VIII Fc Fusion Protein from a VWF Independent FVIII Clearance Pathway in Mouse Hepatocytes. PLoS One. 2015 Apr 23;10(4):e0124930. | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01493778) Safety and Efficacy of Turoctocog Alfa in Prevention and Treatment of Bleeds in Previously Untreated Children With Haemophilia A. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 17 | Efficacy and safety of prophylaxis with once-weekly BAY 79-4980 compared with thrice-weekly rFVIII-FS in haemophilia A patients. A randomised, active-controlled, double-blind study. Thromb Haemost. 2012 Nov;108(5):913-22. | |||||
| REF 18 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00793234) Single Intravenous Administration of TB-402 for the Prophylaxis of Venous Thromboembolic Events (VTE) After Total Knee Replacement Surgery. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 19 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Spark Therapeutics. | |||||
| REF 20 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03734588) Dose-finding Study of SPK-8016 Gene Therapy in Patients With Hemophilia A to Support Evaluation in Individuals With FVIII Inhibitors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 21 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03370172) A Global, Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase 1/2 Study of the Safety and Dose Escalation of BAX 888, an Adeno-Associated Virus Serotype 8 (AAV8) Vector Expressing B-Domain Deleted Factor VIII (BDD-FVIII) in Severe Hemophilia A Subjects Administered a Single Intravenous Infusion. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 22 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03588299) A Phase 1/2 Open-label Safety and Dose-finding Study of BAY2599023 (DTX201), an Adeno-associated Virus (AAV) hu37-mediated Gene Transfer of B-domain Deleted Human Factor VIII, in Adults With Severe Hemophilia A. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 23 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2607). | |||||
| REF 24 | Phase I study of BAY 94-9027, a PEGylated B-domain-deleted recombinant factor VIII with an extended half-life, in subjects with hemophilia A. J Thromb Haemost. 2014 Apr;12(4):488-96. | |||||
| REF 25 | Enhancing the pharmacokinetic properties of recombinant factor VIII: first-in-human trial of glycoPEGylated recombinant factor VIII in patients with hemophilia A. J Thromb Haemost. 2013 Apr;11(4):670-8. | |||||
| REF 26 | Efficacy and safety of OBI-1, an antihaemophilic factor VIII (recombinant), porcine sequence, in subjects with acquired haemophilia A. Haemophilia. 2015 Mar;21(2):162-70. | |||||
| REF 27 | 6 Factor VIII Concentrates, Factor VIII/von Willebrand Factor Concentrates, Factor IX Concentrates, Activated Prothrombin Complex Concentrates. Transfus Med Hemother. 2009 December; 36(6): 409-418. | |||||
| REF 28 | The pharmacokinetics of a B-domain truncated recombinant factor VIII, turoctocog alfa (NovoEight ), in patients with hemophilia A. J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Mar;13(3):370-9. | |||||
| REF 29 | A new recombinant factor VIII: from genetics to clinical use | |||||
| REF 30 | Trp2313-His2315 of factor VIII C2 domain is involved in membrane binding: structure of a complex between the C2 domain and an inhibitor of membrane binding. J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 19;285(12):8824-9. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

