Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T14912
(Former ID: TTDC00048)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein Mcl-1 (MCL1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
mcl1/EAT; Bcl2-L-3; Bcl-2-related protein EAT/mcl1; Bcl-2-like protein 3; BCL2L3
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MCL1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 6 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| 2 | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||||
| 3 | Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33] | |||||
| 4 | Mature B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85] | |||||
| 5 | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||||
| 6 | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83] | |||||
| Function |
Mediates its effects by interactions with a number of other regulators of apoptosis. Isoform 1 inhibits apoptosis. Isoform 2 promotes apoptosis. Involved in the regulation of apoptosis versus cell survival, and in the maintenance of viability but not of proliferation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
B-cell lymphoma Bcl-2
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MFGLKRNAVIGLNLYCGGAGLGAGSGGATRPGGRLLATEKEASARREIGGGEAGAVIGGS
AGASPPSTLTPDSRRVARPPPIGAEVPDVTATPARLLFFAPTRRAAPLEEMEAPAADAIM SPEEELDGYEPEPLGKRPAVLPLLELVGESGNNTSTDGSLPSTPPPAEEEEDELYRQSLE IISRYLREQATGAKDTKPMGRSGATSRKALETLRRVGDGVQRNHETAFQGMLRKLDIKNE DDVKSLSRVMIHVFSDGVTNWGRIVTLISFGAFVAKHLKTINQESCIEPLAESITDVLVR TKRDWLVKQRGWDGFVEFFHVEDLEGGIRNVLLAFAGVAGVGAGLAYLIR Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T75HMM | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 3 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Obatoclax | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [1] | |
| 2 | AMG 176 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Multiple myeloma | [6] | |
| 3 | AZD5991 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Haematological malignancy | [6] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BITHIONOL | Drug Info | Withdrawn from market | Trematode infection | [7], [8] | |
| 2 | Sch-45752 | Drug Info | Terminated | Asthma | [9] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 37 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Obatoclax | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | AMG 176 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 3 | AZD5991 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 4 | Biphenyl carboxylic acid derivative 1 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 5 | Biphenyl carboxylic acid derivative 2 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 6 | Indole-based analog 1 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 7 | Indole-based analog 2 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 8 | Indole-based analog 3 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 9 | PMID27744724-Compound-10 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 10 | PMID27744724-Compound-13 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 11 | PMID27744724-Compound-18 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 12 | PMID27744724-Compound-19 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 13 | PMID27744724-Compound-20 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 14 | PMID27744724-Compound-21 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 15 | PMID27744724-Compound-22 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 16 | PMID27744724-Compound-23 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 17 | PMID27744724-Compound-26 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 18 | PMID27744724-Compound-27 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 19 | PMID27744724-Compound-28 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 20 | PMID27744724-Compound-29 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 21 | PMID27744724-Compound-3 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 22 | PMID27744724-Compound-4 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 23 | PMID27744724-Compound-5 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 24 | PMID27744724-Compound-6 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 25 | PMID27744724-Compound-Fomula2 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 26 | BITHIONOL | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 27 | Sch-45752 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 28 | ALTENUSIN | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 29 | AMENTOFLAVONE | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 30 | GNF-PF-1591 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 31 | GNF-PF-3955 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 32 | GNF-PF-5134 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 33 | MORIN | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 34 | QEDIIRNIARHLAQVGDSMDR | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 35 | ROSMARINIC ACID | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 36 | SULFURETIN | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 37 | TW-37 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Norleucine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human Mcl-1 in complex with a modified unnatural Bim BH3 peptide | PDB:6UAB | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.10 Å | Mutation | No | [13] |
| PDB Sequence |
SDELYRQSLE
180 IISRYLREQA190 TGAKDTKPMG200 RSGATSRKAL210 ETLRRVGDGV220 QRNHETAFQG 230 MLRKLDIKNE240 DDVKSLSRVM250 IHVFSDGVTN260 WGRIVTLISF270 GAFVAKHLKT 280 INQESCIEPL290 AESITDVLVR300 TKRDWLVKQR310 GWDGFVEFFH320 VEDLE |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: AZD5991 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | INDUCED MYELOID LEUKEMIA CELL DIFFERENTIATION PROTEIN FABCOMPLEX IN COMPLEX WITH AZD5991 | PDB:6FS0 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.25 Å | Mutation | No | [14] |
| PDB Sequence |
GPLGSEDDLY
175 RQSLEIISRY185 LREQATGSKD195 SKPLGEAGAA205 GRRALETLRR215 VGDGVQRNHE 225 TAFQGMLRKL235 DIKNEDDVKS245 LSRVMIHVFS255 DGVTNWGRIV265 TLISFGAFVA 275 KHLKTINQES285 CIEPLAESIT295 DVLVRTKRDW305 LVKQRGWDGF315 VEFFHV |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
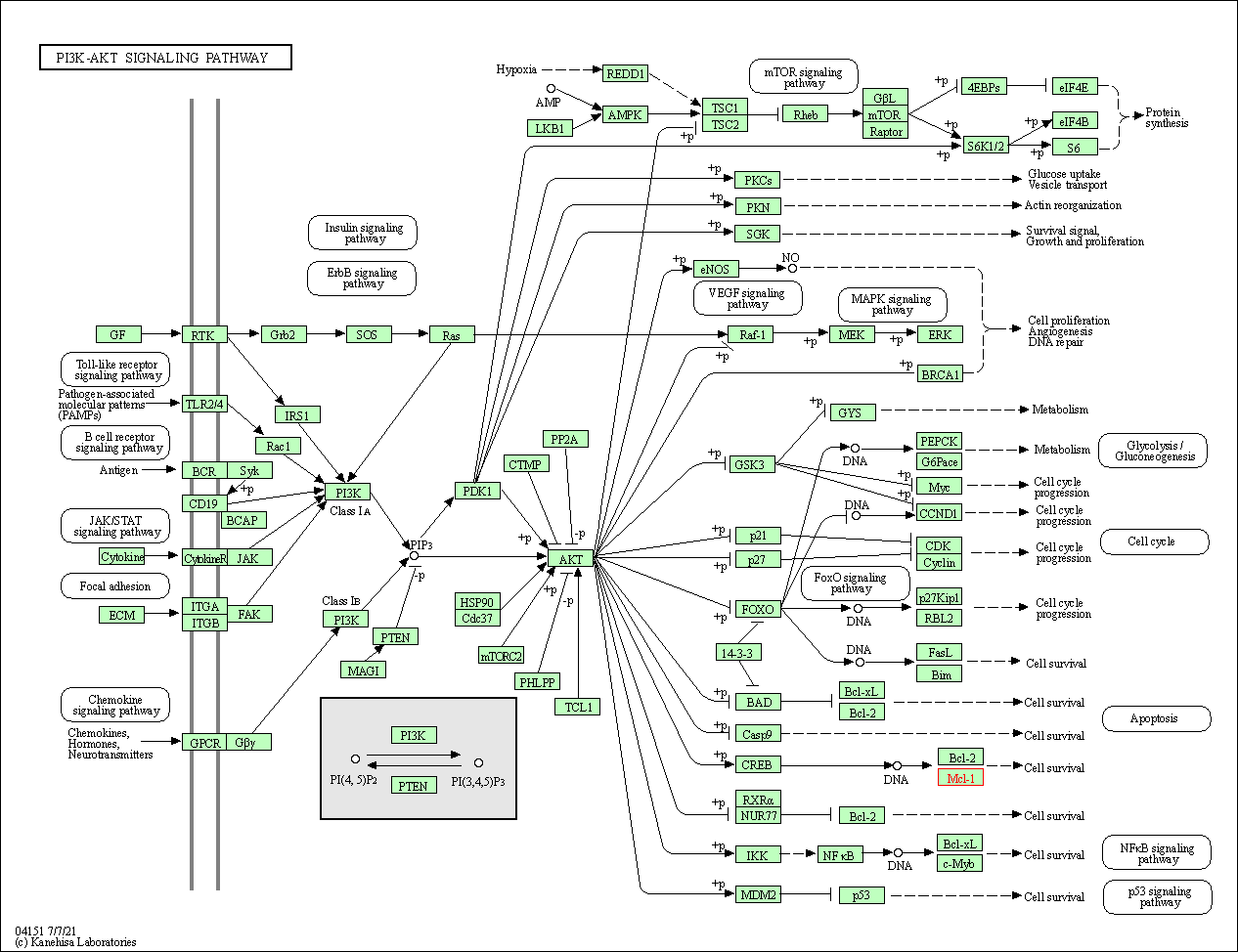
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |
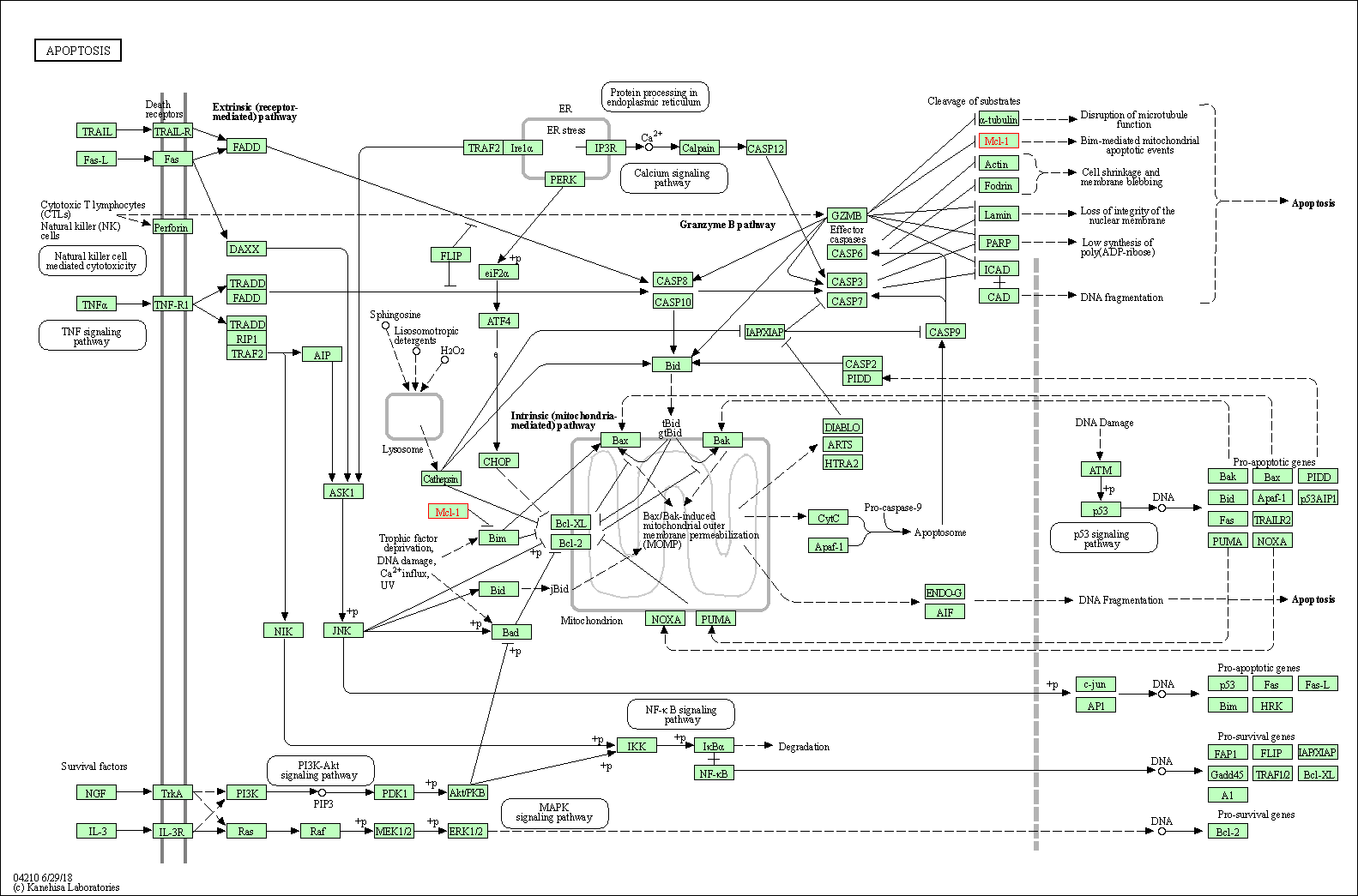
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |
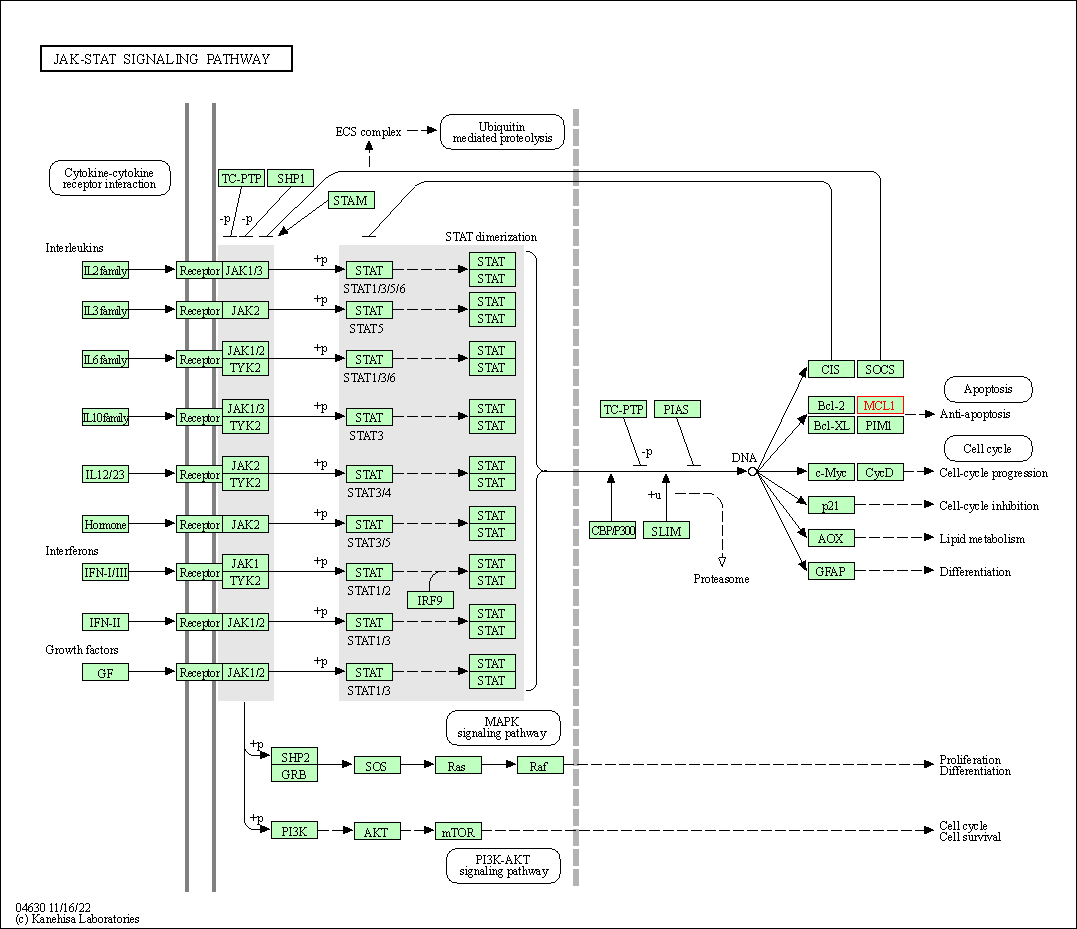
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 25 | Degree centrality | 2.69E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.20E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.56E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.70E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.34E+01 | Topological coefficient | 6.01E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 2 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | MicroRNAs in cancer | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TCR Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 2 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Apoptosis signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | CCKR signaling map ST | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 4 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | E2F transcription factor network | |||||
| 2 | Direct p53 effectors | |||||
| 3 | IL6-mediated signaling events | |||||
| 4 | HIF-1-alpha transcription factor network | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 5 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Apoptosis | |||||
| 2 | miR-targeted genes in muscle cell - TarBase | |||||
| 3 | miR-targeted genes in lymphocytes - TarBase | |||||
| 4 | miR-targeted genes in leukocytes - TarBase | |||||
| 5 | Apoptosis Modulation and Signaling | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Phase II study of obatoclax mesylate (GX15-070), a small-molecule BCL-2 family antagonist, for patients with myelofibrosis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2010 Aug;10(4):285-9. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04178902) A Study of the Safety and Tolerability of ABBV-467 in Adult Participants With Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Multiple Myeloma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04543305) A Study of PRT1419 in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Hematologic Malignancies. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02979366) Phase I Study of S64315 Administred Intravenously in Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukaemia or Myelodysplastic Syndrome. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03465540) Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of AMG 397 in Subjects With Selected Relapsed or Refractory Hematological Malignancies. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2338). | |||||
| REF 8 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002639) | |||||
| REF 10 | Mcl-1 inhibitors: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Feb;27(2):163-178. | |||||
| REF 11 | In silico identification and biochemical evaluation of novel inhibitors of NRH:quinone oxidoreductase 2 (NQO2). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Dec 15;20(24):7331-6. | |||||
| REF 12 | Structure-based design of potent small-molecule inhibitors of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. J Med Chem. 2006 Oct 19;49(21):6139-42. | |||||
| REF 13 | Inhibitor peptides against Mcl-1 containing non-natural amino acids show potent apoptotic response. | |||||
| REF 14 | Discovery of Mcl-1-specific inhibitor AZD5991 and preclinical activity in multiple myeloma and acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 17;9(1):5341. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

