Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T16688
(Former ID: TTDS00466)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Retinol O-fatty-acyltransferase; Diglyceride acyltransferase; Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1; DGAT; Acyl-CoA retinol O-fatty-acyltransferase; ARAT; AGRP1; ACAT-related gene product 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
DGAT1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Hyper-lipoproteinaemia [ICD-11: 5C80] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the terminal and only committed step in triacylglycerol synthesis by using diacylglycerol and fatty acyl CoA as substrates. In contrast to DGAT2 it is not essential for survival. May be involved in VLDL (very low density lipoprotein) assembly. In liver, plays a role in esterifying exogenous fatty acids to glycerol. Functions as the major acyl-CoA retinol acyltransferase (ARAT) in the skin, where it acts to maintain retinoid homeostasis and prevent retinoid toxicity leading to skin and hair disorders.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Acyltransferase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.3.1.20
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MGDRGSSRRRRTGSRPSSHGGGGPAAAEEEVRDAAAGPDVGAAGDAPAPAPNKDGDAGVG
SGHWELRCHRLQDSLFSSDSGFSNYRGILNWCVVMLILSNARLFLENLIKYGILVDPIQV VSLFLKDPYSWPAPCLVIAANVFAVAAFQVEKRLAVGALTEQAGLLLHVANLATILCFPA AVVLLVESITPVGSLLALMAHTILFLKLFSYRDVNSWCRRARAKAASAGKKASSAAAPHT VSYPDNLTYRDLYYFLFAPTLCYELNFPRSPRIRKRFLLRRILEMLFFTQLQVGLIQQWM VPTIQNSMKPFKDMDYSRIIERLLKLAVPNHLIWLIFFYWLFHSCLNAVAELMQFGDREF YRDWWNSESVTYFWQNWNIPVHKWCIRHFYKPMLRRGSSKWMARTGVFLASAFFHEYLVS VPLRMFRLWAFTGMMAQIPLAWFVGRFFQGNYGNAAVWLSLIIGQPIAVLMYVHDYYVLN YEAPAAEA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T20IHC | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Hesperetin | Drug Info | Approved | High blood cholesterol level | [2] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 3 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LCQ908 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Hepatitis C virus infection | [3], [4] | |
| 2 | AZD7687 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Diabetic complication | [5], [6] | |
| 3 | P-7435 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Diabetic complication | [7] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PF-04620110 | Drug Info | Terminated | Type-2 diabetes | [10], [11] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 21 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Hesperetin | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | AZD7687 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 3 | P-7435 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 4 | amidepsines | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 5 | Azole derivative 6 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 6 | Azole derivative 7 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 7 | Benzamide derivative 19 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 8 | Carbamide derivative 3 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 9 | Lactam derivative 1 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 10 | Lactam derivative 2 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 11 | Lactam derivative 3 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 12 | Lactam derivative 4 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 13 | Lactam derivative 5 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 14 | PMID25470667-Compound-AZD3988 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 15 | PMID25470667-Compound-BAY744113 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 16 | PMID25470667-Compound-Figure4-1A | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 17 | Pyrazine carboxamide derivative 1 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 18 | Pyridine-carboximide derivative 1 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 19 | Pyridine-carboximide derivative 2 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 20 | T863 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 21 | PF-04620110 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LCQ908 | Drug Info | [12], [13] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Oleoyl-CoA | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 1 in complex with oleoyl-CoA | PDB:6VP0 | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.10 Å | Mutation | No | [15] |
| PDB Sequence |
WELRCHRLQD
73 SLFSSDSGFS83 NYRGILNWCV93 VMLILSNARL103 FLENLIKYGI113 LVDPIQVVSL 123 FLKDPYSWPA133 PCLVIAANVF143 AVAAFQVEKR153 LAVGALTEQA163 GLLLHVANLA 173 TILCFPAAVV183 LLVESITPVG193 SLLALMAHTI203 LFLKLFSYRD213 VNSWCRRARA 223 KHTVSYPDNL247 TYRDLYYFLF257 APTLCYELNF267 PRSPRIRKRF277 LLRRILEMLF 287 FTQLQVGLIQ297 QWMVPTIQNS307 MKPFKDMDYS317 RIIERLLKLA327 VPNHLIWLIF 337 FYWLFHSCLN347 AVAELMQFGD357 REFYRDWWNS367 ESVTYFWQNW377 NIPVHKWCIR 387 HFYKPMLRRG397 SSKWMARTGV407 FLASAFFHEY417 LVSVPLRMFR427 LWAFTGMMAQ 437 IPLAWFVGRF447 FQGNYGNAAV457 WLSLIIGQPI467 AVLMYVHDYY477 VLNY |
|||||
|
|
MET199
4.281
TRP334
3.516
LEU335
4.384
PHE337
4.208
PHE338
3.339
LEU341
4.233
PHE342
4.147
TRP364
3.973
THR371
3.839
PHE373
3.748
TRP374
2.875
GLN375
3.167
TRP377
2.429
ASN378
4.031
VAL381
4.024
HIS382
2.339
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Phosphatidylserine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 1 in complex with oleoyl-CoA | PDB:6VP0 | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.10 Å | Mutation | No | [15] |
| PDB Sequence |
WELRCHRLQD
73 SLFSSDSGFS83 NYRGILNWCV93 VMLILSNARL103 FLENLIKYGI113 LVDPIQVVSL 123 FLKDPYSWPA133 PCLVIAANVF143 AVAAFQVEKR153 LAVGALTEQA163 GLLLHVANLA 173 TILCFPAAVV183 LLVESITPVG193 SLLALMAHTI203 LFLKLFSYRD213 VNSWCRRARA 223 KHTVSYPDNL247 TYRDLYYFLF257 APTLCYELNF267 PRSPRIRKRF277 LLRRILEMLF 287 FTQLQVGLIQ297 QWMVPTIQNS307 MKPFKDMDYS317 RIIERLLKLA327 VPNHLIWLIF 337 FYWLFHSCLN347 AVAELMQFGD357 REFYRDWWNS367 ESVTYFWQNW377 NIPVHKWCIR 387 HFYKPMLRRG397 SSKWMARTGV407 FLASAFFHEY417 LVSVPLRMFR427 LWAFTGMMAQ 437 IPLAWFVGRF447 FQGNYGNAAV457 WLSLIIGQPI467 AVLMYVHDYY477 VLNY |
|||||
|
|
TRP299
3.833
PHE311
4.179
LYS312
4.162
ASP313
3.849
MET314
2.842
ASP315
4.924
TYR316
3.387
ILE319
4.050
ILE320
4.480
LEU323
4.217
LEU324
3.144
LYS325
3.412
ALA327
3.894
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerolipid metabolism | hsa00561 | Affiliated Target |
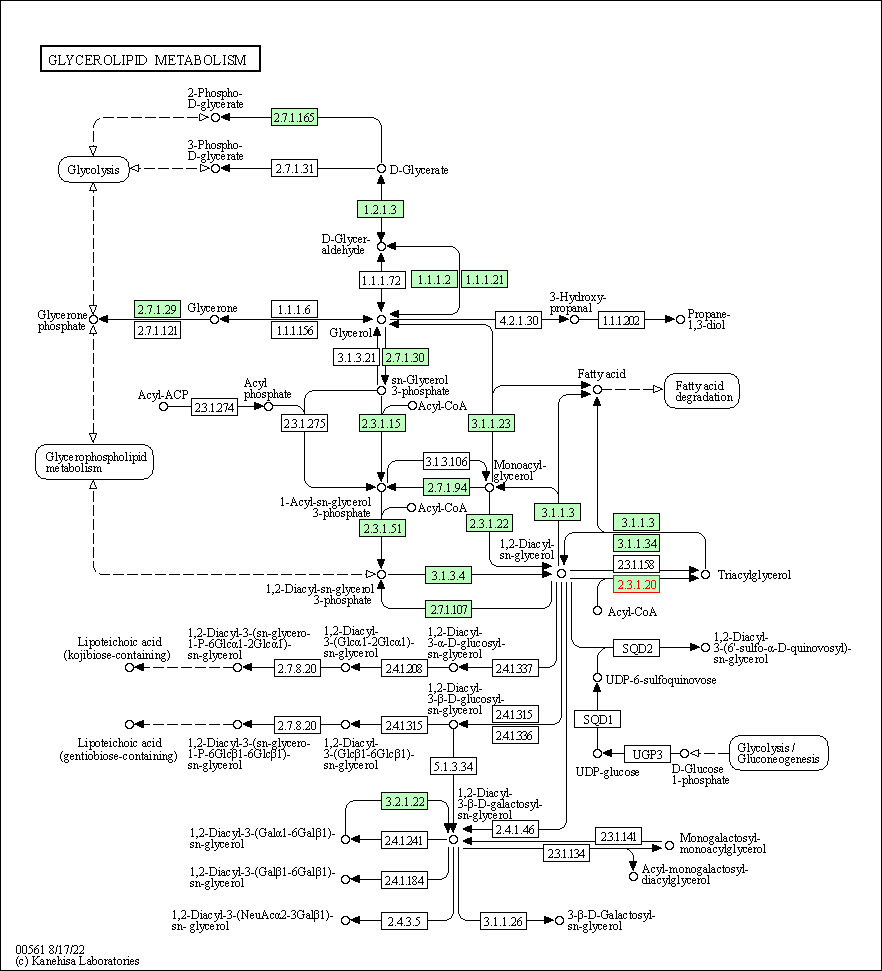
|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retinol metabolism | hsa00830 | Affiliated Target |
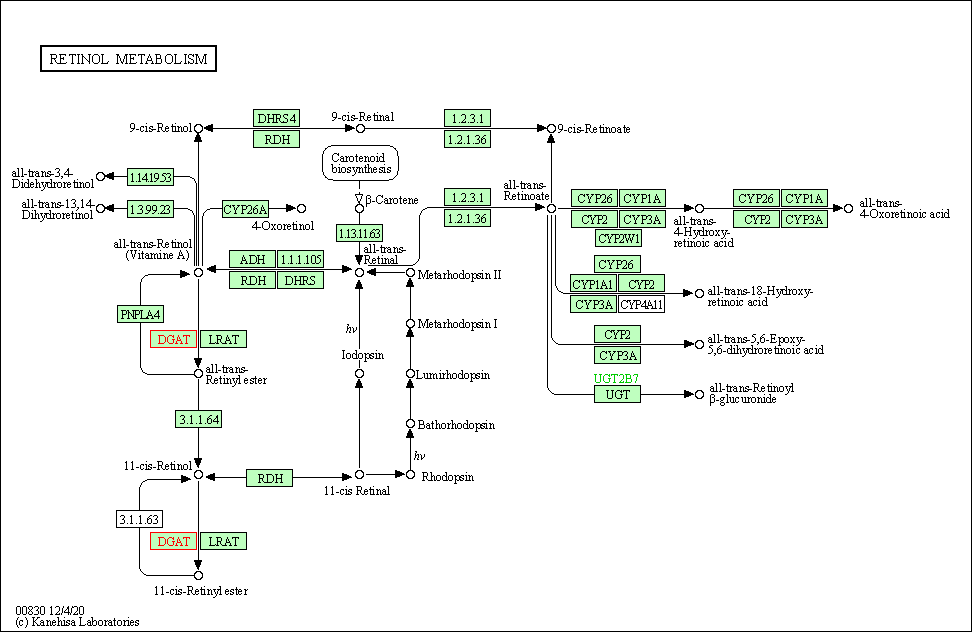
|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fat digestion and absorption | hsa04975 | Affiliated Target |
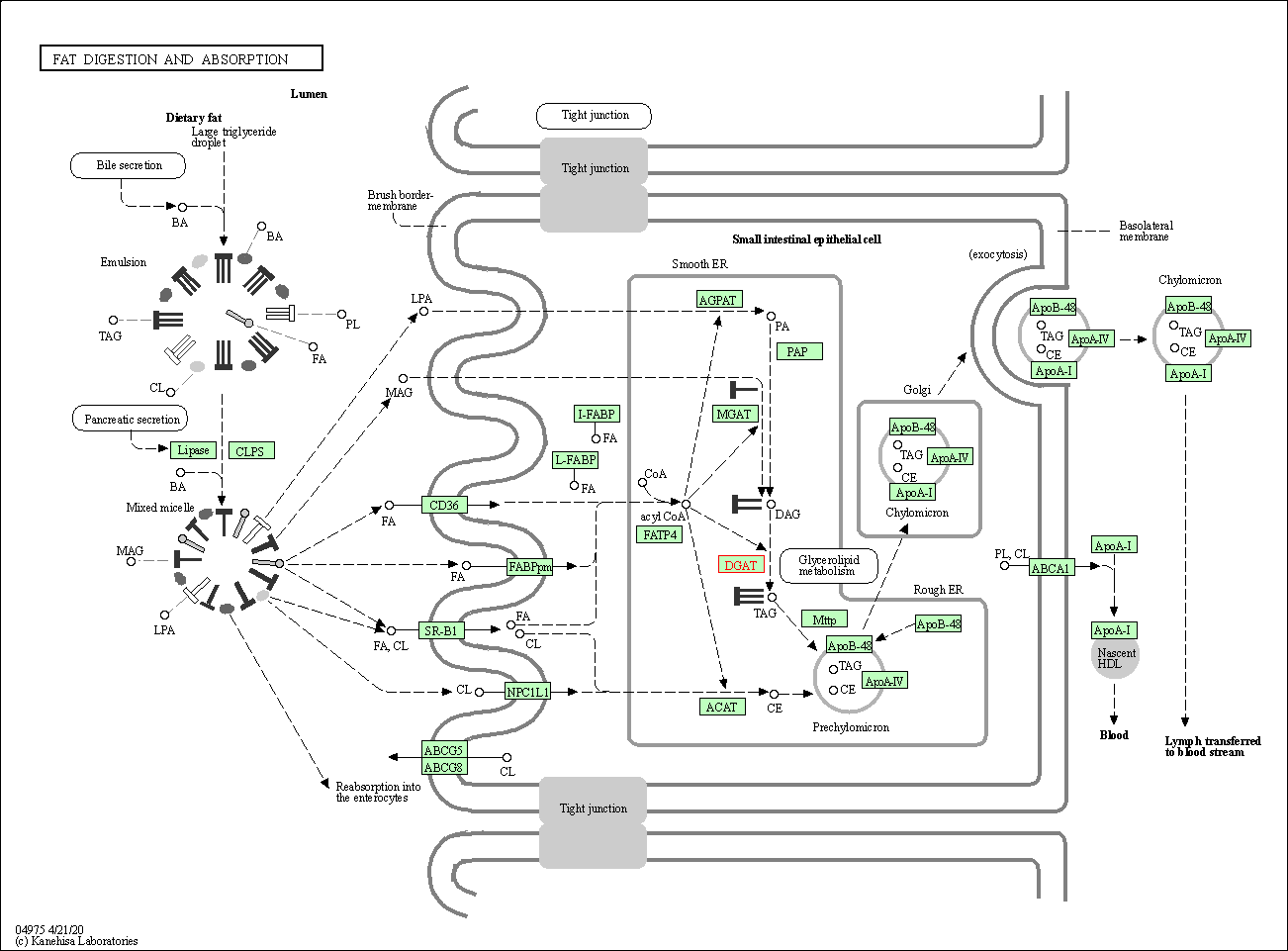
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 4 | Degree centrality | 4.30E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 4.30E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.42E-01 | Radiality | 1.16E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.00E+00 | Topological coefficient | 3.33E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 1 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Triacylglycerol biosynthesis | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glycerolipid metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Retinol metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 4 | Fat digestion and absorption | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Retinol Metabolism | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Acyl chain remodeling of DAG and TAG | |||||
| 2 | Triglyceride Biosynthesis | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 5 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Vitamin A and Carotenoid Metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Statin Pathway | |||||
| 3 | Triacylglyceride Synthesis | |||||
| 4 | Glycerophospholipid biosynthesis | |||||
| 5 | Fatty acid, triacylglycerol, and ketone body metabolism | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | In vitro inhibition of diacylglycerol acyltransferase by prenylflavonoids from Sophora flavescens. Planta Med. 2004 Mar;70(3):258-60. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drug information of Hesperetin, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7830). | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01514461) A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo Controlled Study to Assess Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability of LCQ908 in Subjects With Familial Chylomicronemia Syndrome. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7827). | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of AstraZeneca (2011). | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01764425) Clinical Trial to Study the Safety Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, Food Effect & Pharmacodynamics of a New Compound P7435 in Healthy, Overweight and/or Obese Subjects. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026874) | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800035670) | |||||
| REF 10 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7829). | |||||
| REF 11 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Pfizer (2011). | |||||
| REF 12 | DGAT1 inhibitors as anti-obesity and anti-diabetic agents. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2010 Jul;13(4):489-96. | |||||
| REF 13 | Acyltransferase inhibitors: a patent review (2010-present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 Feb;25(2):145-58. | |||||
| REF 14 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800033014) | |||||
| REF 15 | Structure and mechanism of human diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase?1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):329-332. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

