Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T23276
(Former ID: TTDR00373)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
PRKM3; P44-MAPK; P44-ERK1; P44 Mitogen-activated protein kinase; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3; Microtubule-associated protein-2 kinase; Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase; MAPK 3; MAP kinase isoform p44; MAP kinase 3; Insulin-stimulated MAP2 kinase; ERT2; ERK-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MAPK3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 4 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| 3 | Arteries/arterioles disorder [ICD-11: BD52] | |||||
| 4 | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||||
| Function |
MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 are the 2 MAPKs which play an important role in the MAPK/ERK cascade. They participate also in a signaling cascade initiated by activated KIT and KITLG/SCF. Depending on the cellular context, the MAPK/ERK cascade mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation through the regulation of transcription, translation, cytoskeletal rearrangements. The MAPK/ERK cascade plays also a role in initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating a number of transcription factors. About 160 substrates have already been discovered for ERKs. Many of these substrates are localized in the nucleus, and seem to participate in the regulation of transcription upon stimulation. However, other substrates are found in the cytosol as well as in other cellular organelles, and those are responsible for processes such as translation, mitosis and apoptosis. Moreover, the MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of the endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC); as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. The substrates include transcription factors (such as ATF2, BCL6, ELK1, ERF, FOS, HSF4 or SPZ1), cytoskeletal elements (such as CANX, CTTN, GJA1, MAP2, MAPT, PXN, SORBS3 or STMN1), regulators of apoptosis (such as BAD, BTG2, CASP9, DAPK1, IER3, MCL1 or PPARG), regulators of translation (such as EIF4EBP1) and a variety of other signaling-related molecules (like ARHGEF2, FRS2 or GRB10). Protein kinases (such as RAF1, RPS6KA1/RSK1, RPS6KA3/RSK2, RPS6KA2/RSK3, RPS6KA6/RSK4, SYK, MKNK1/MNK1, MKNK2/MNK2, RPS6KA5/MSK1, RPS6KA4/MSK2, MAPKAPK3 or MAPKAPK5) and phosphatases (such as DUSP1, DUSP4, DUSP6 or DUSP16) are other substrates which enable the propagation the MAPK/ERK signal to additional cytosolic and nuclear targets, thereby extending the specificity of the cascade. Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.24
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAAAAAQGGGGGEPRRTEGVGPGVPGEVEMVKGQPFDVGPRYTQLQYIGEGAYGMVSSAY
DHVRKTRVAIKKISPFEHQTYCQRTLREIQILLRFRHENVIGIRDILRASTLEAMRDVYI VQDLMETDLYKLLKSQQLSNDHICYFLYQILRGLKYIHSANVLHRDLKPSNLLINTTCDL KICDFGLARIADPEHDHTGFLTEYVATRWYRAPEIMLNSKGYTKSIDIWSVGCILAEMLS NRPIFPGKHYLDQLNHILGILGSPSQEDLNCIINMKARNYLQSLPSKTKVAWAKLFPKSD SKALDLLDRMLTFNPNKRITVEEALAHPYLEQYYDPTDEPVAEEPFTFAMELDDLPKERL KELIFQETARFQPGVLEAP Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A03834 ; BADD_A08298 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T25NSJ | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 4 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BVD-523 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Melanoma | [2] | |
| 2 | ASN007 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [6] | |
| 3 | GDC-0994 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [7] | |
| 4 | VAN-10-4-eluting stent | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Artery stenosis | [8] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 2 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BVD-523 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | GDC-0994 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 3 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ASN007 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 2 | VAN-10-4-eluting stent | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 3 | 6-[(E)-2-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-vinyl]-9H-purine | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: SCH772984 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of human ERK1 in complex with SCH772984 revealing a novel inhibitor-induced binding pocket | PDB:4QTB | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.40 Å | Mutation | No | [13] |
| PDB Sequence |
VPGEVEMVKG
33 QPFDVGPRYT43 QLQYIGEGAY53 GMVSSAYDHV63 RKTRVAIKKI73 SPFEHQTYCQ 83 RTLREIQILL93 RFRHENVIGI103 RDILRASTLE113 AMRDVYIVQD123 LMETDLYKLL 133 KSQQLSNDHI143 CYFLYQILRG153 LKYIHSANVL163 HRDLKPSNLL173 INTTCDLKIC 183 DFGLARIADP193 EHDHTGFLTE203 YVATRWYRAP213 EIMLNSKGYT223 KSIDIWSVGC 233 ILAEMLSNRP243 IFPGKHYLDQ253 LNHILGILGS263 PSQEDLNCII273 NMKARNYLQS 283 LPSKTKVAWA293 KLFPKSDSKA303 LDLLDRMLTF313 NPNKRITVEE323 ALAHPYLEQY 333 YDPTDEPVAE343 EPFTFAMELD353 DLPKERLKEL363 IFQETARFQP373 G |
|||||
|
|
ILE48
3.903
ALA52
3.076
TYR53
3.374
VAL56
4.321
ALA69
3.490
LYS71
2.924
ILE73
3.555
PRO75
4.605
TYR81
3.222
ARG84
3.581
THR85
3.616
GLU88
3.468
ILE101
4.105
ILE120
4.690
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: 5'-iodotubercidin | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structural dissection of human mitogen-activated kinase ERK1 | PDB:2ZOQ | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.39 Å | Mutation | No | [14] |
| PDB Sequence |
VPGEVEMVKG
33 QPFDVGPRYT43 QLQYIGEGAY53 GMVSSAYDHV63 RKTRVAIKKI73 SPFEHQTYCQ 83 RTLREIQILL93 RFRHENVIGI103 RDILRASTLE113 AMRDVYIVQD123 LMETDLYKLL 133 KSQQLSNDHI143 CYFLYQILRG153 LKYIHSANVL163 HRDLKPSNLL173 INTTCDLKIC 183 DFGLARIADP193 EHDHTGFLTE203 VATRWYRAPE214 IMLNSKGYTK224 SIDIWSVGCI 234 LAEMLSNRPI244 FPGKHYLDQL254 NHILGILGSP264 SQEDLNCIIN274 MKARNYLQSL 284 PSKTKVAWAK294 LFPKSDSKAL304 DLLDRMLTFN314 PNKRITVEEA324 LAHPYLEQYY 334 DPTDEPVAEE344 PFTFAMELDD354 LPKERLKELI364 FQETARFQPG374 V |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oocyte meiosis | hsa04114 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |
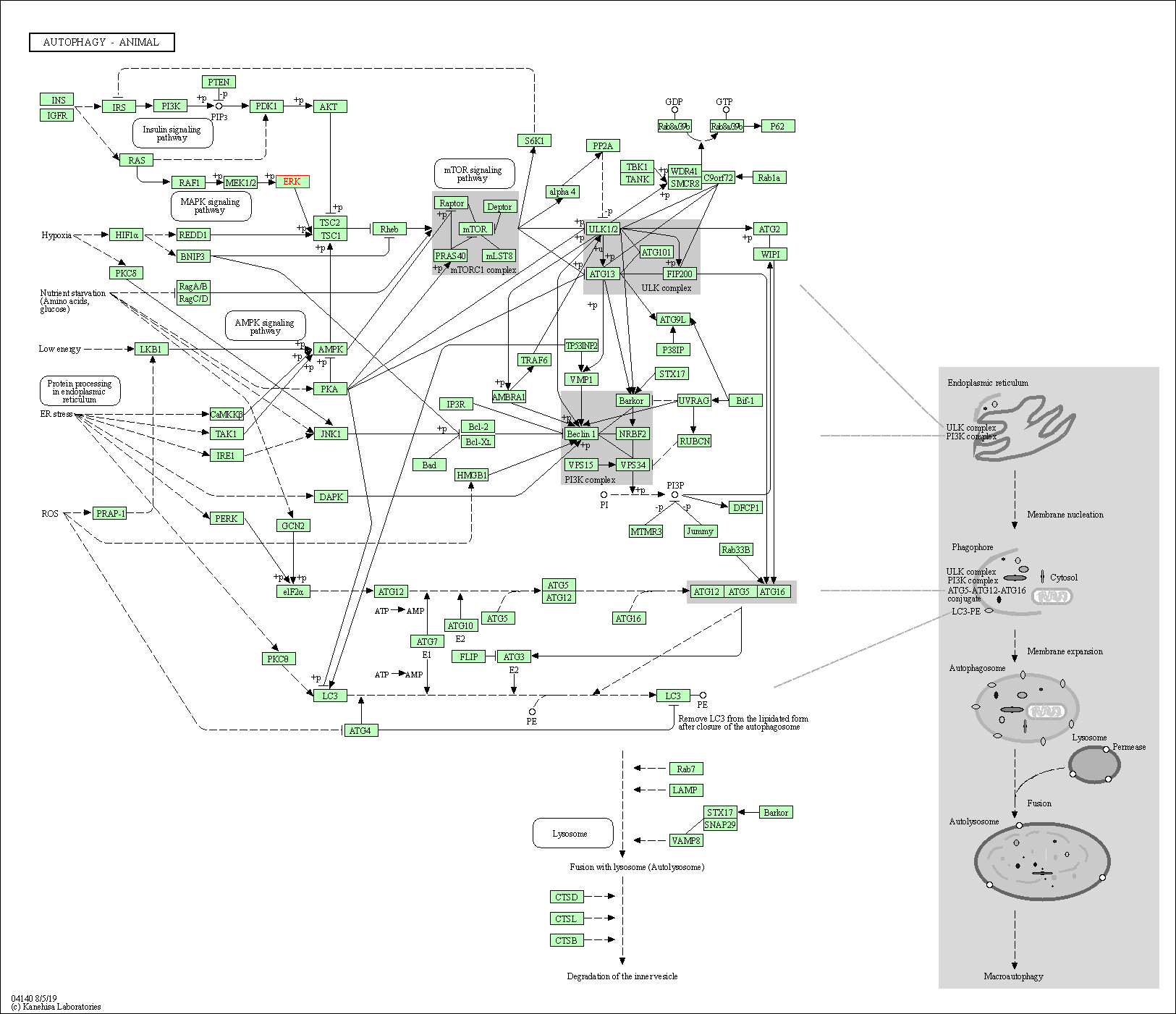
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |
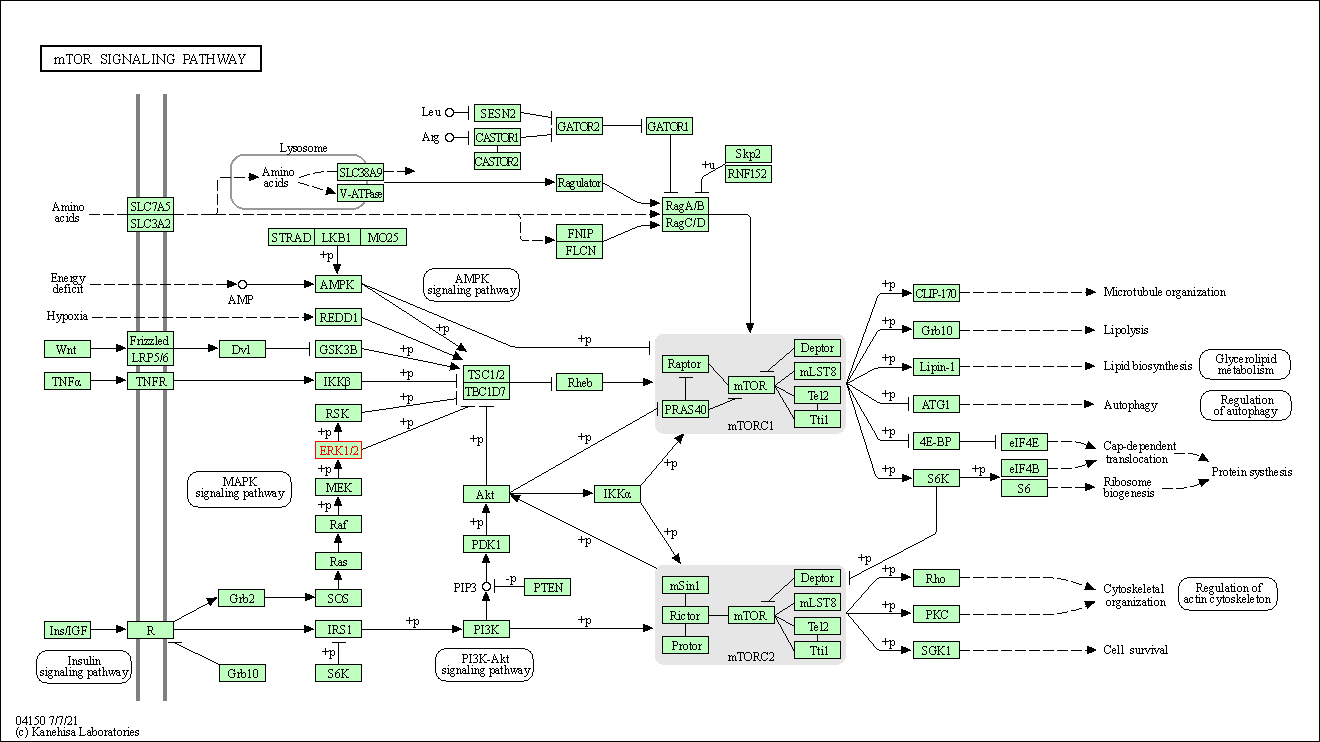
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
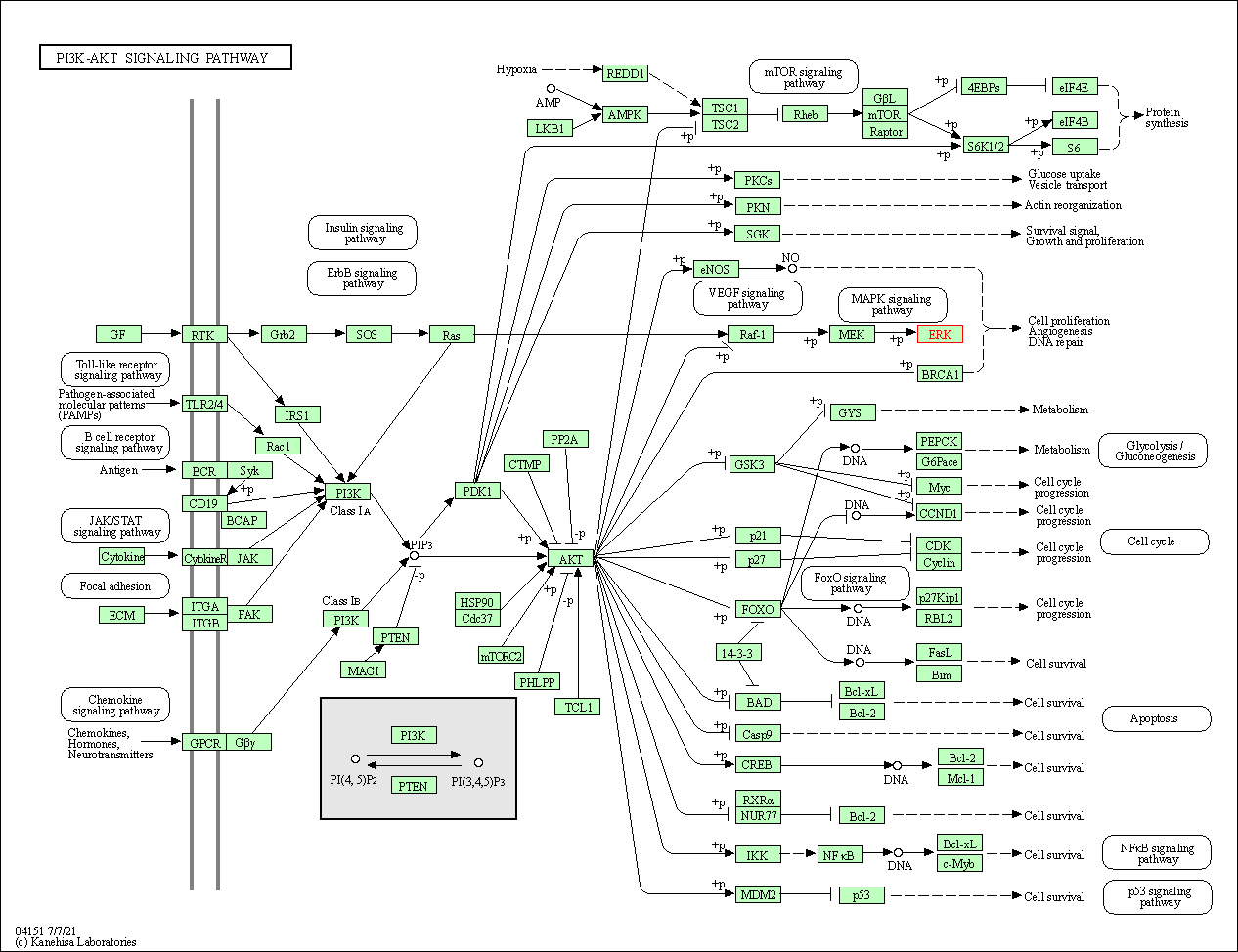
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |
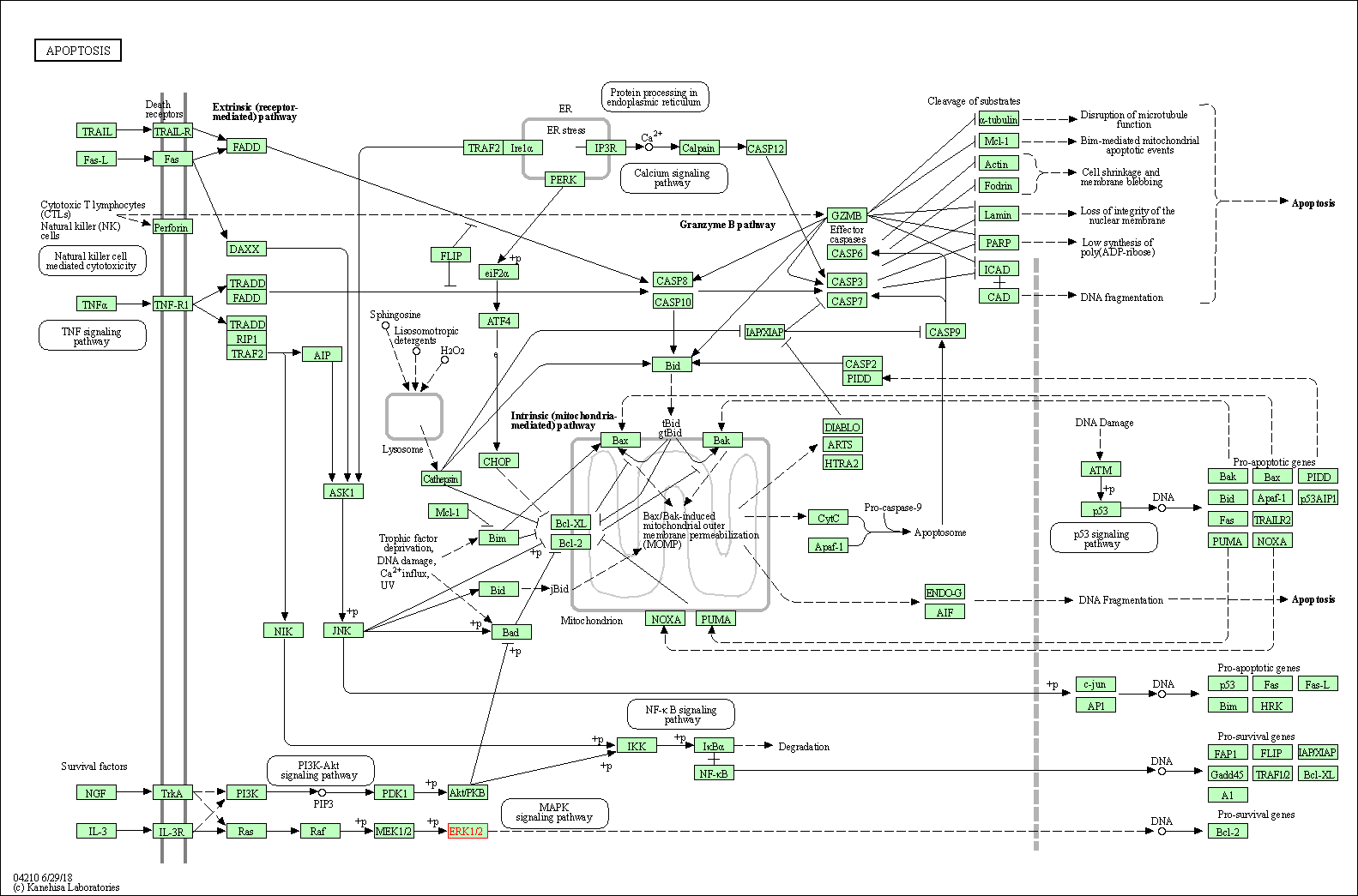
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Axon guidance | hsa04360 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
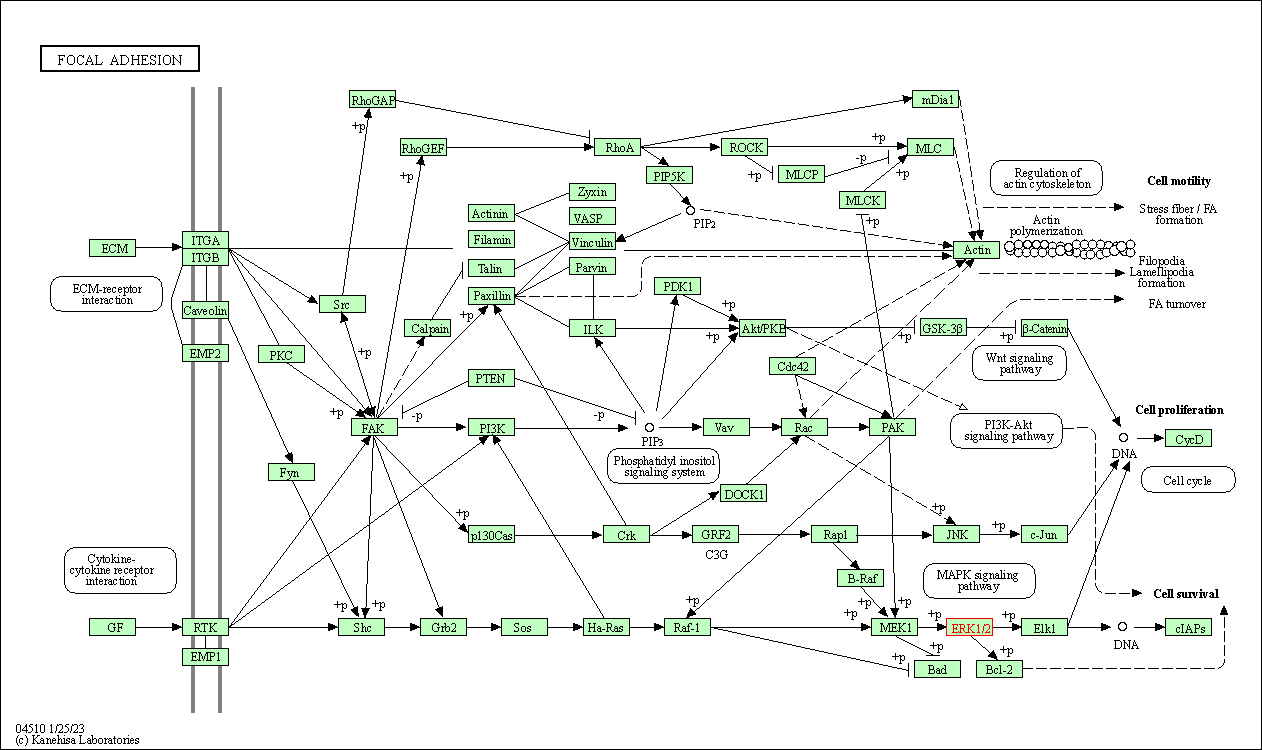
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adherens junction | hsa04520 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Gap junction | hsa04540 | Affiliated Target |
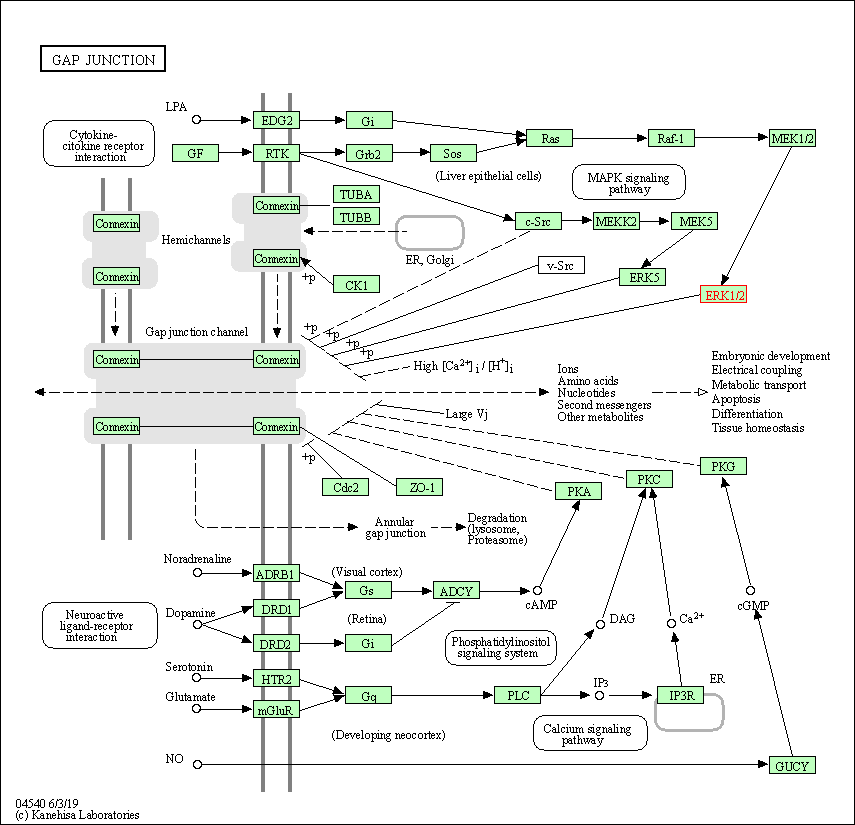
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | Affiliated Target |
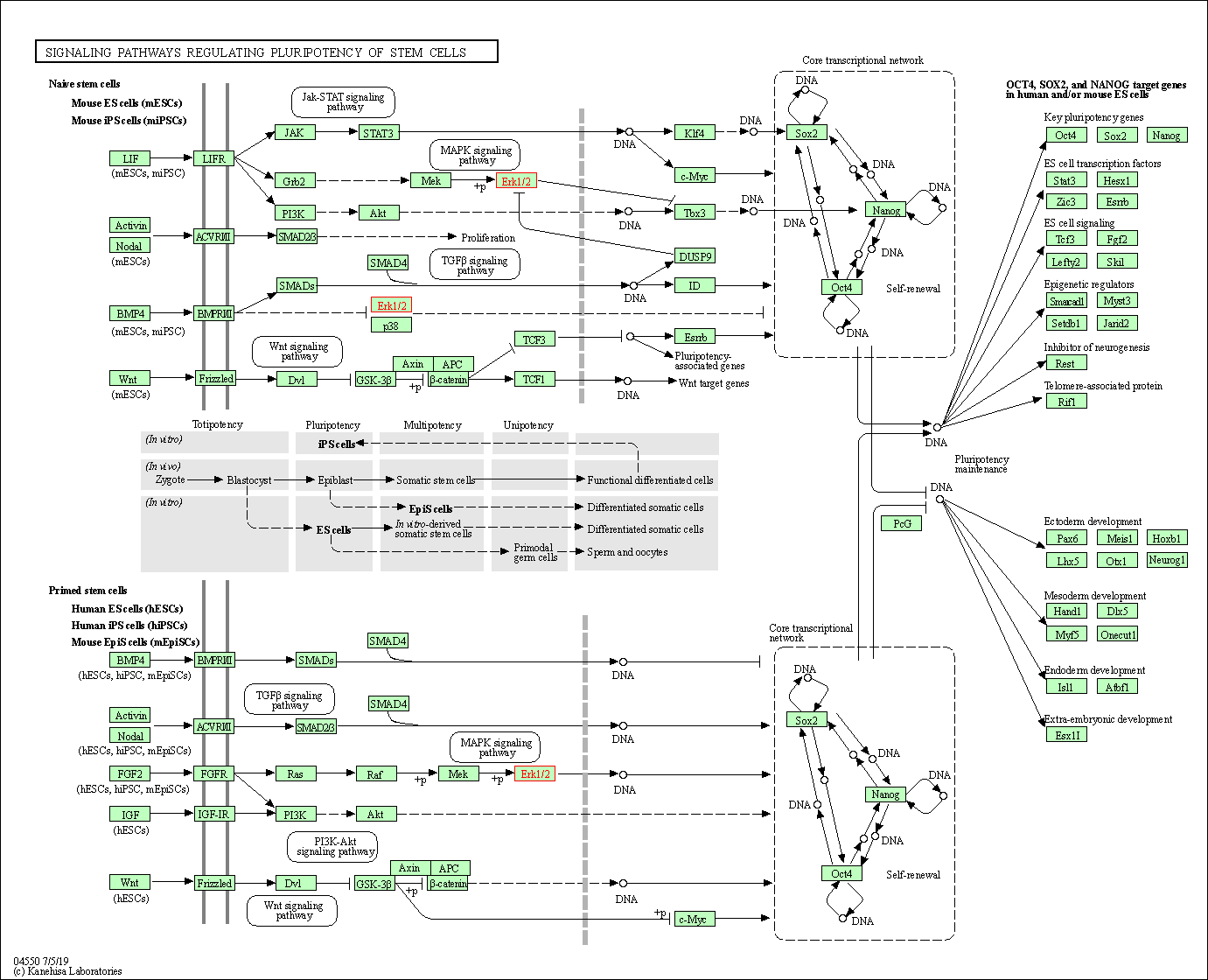
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Platelet activation | hsa04611 | Affiliated Target |
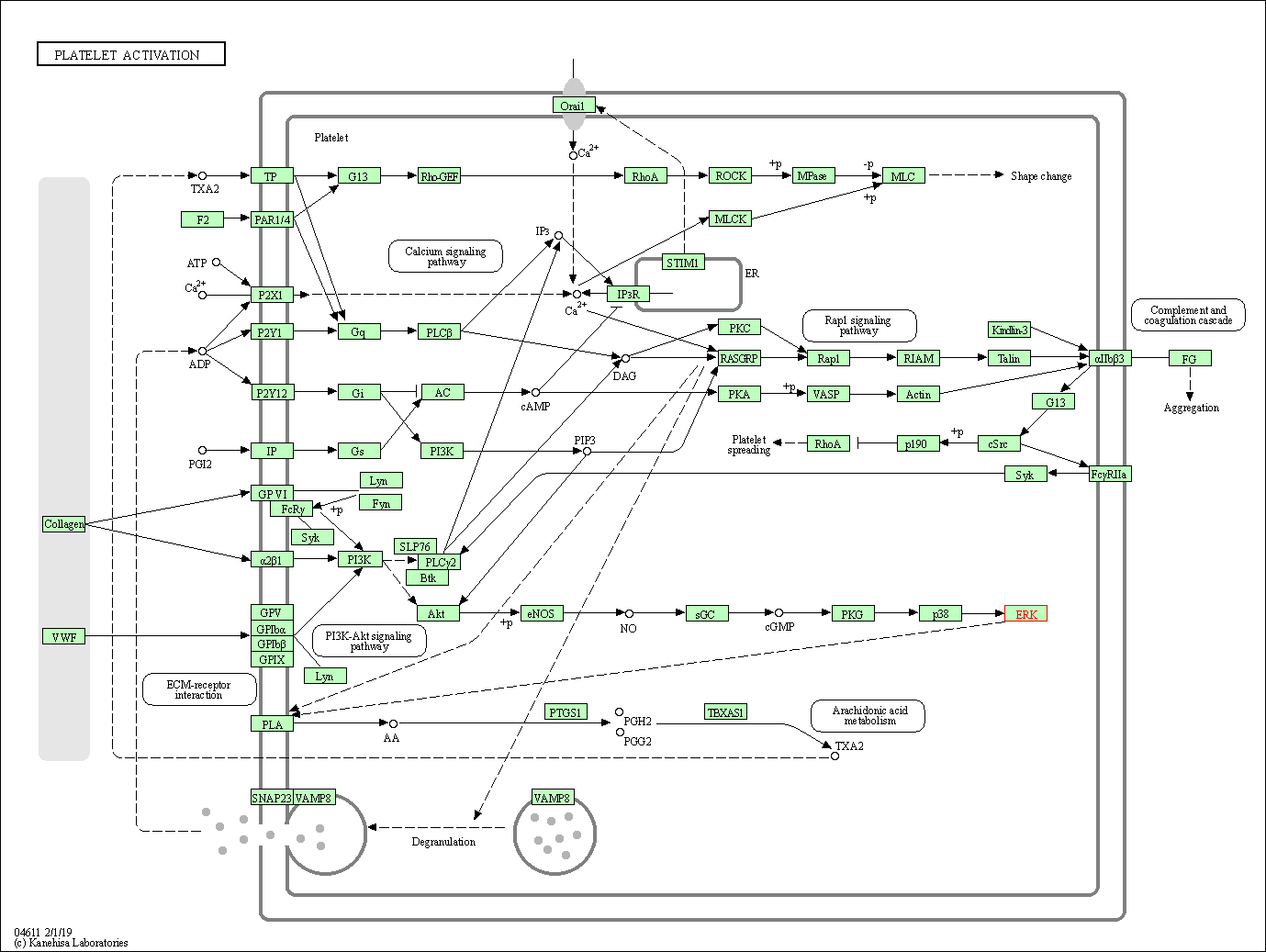
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | hsa04658 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |
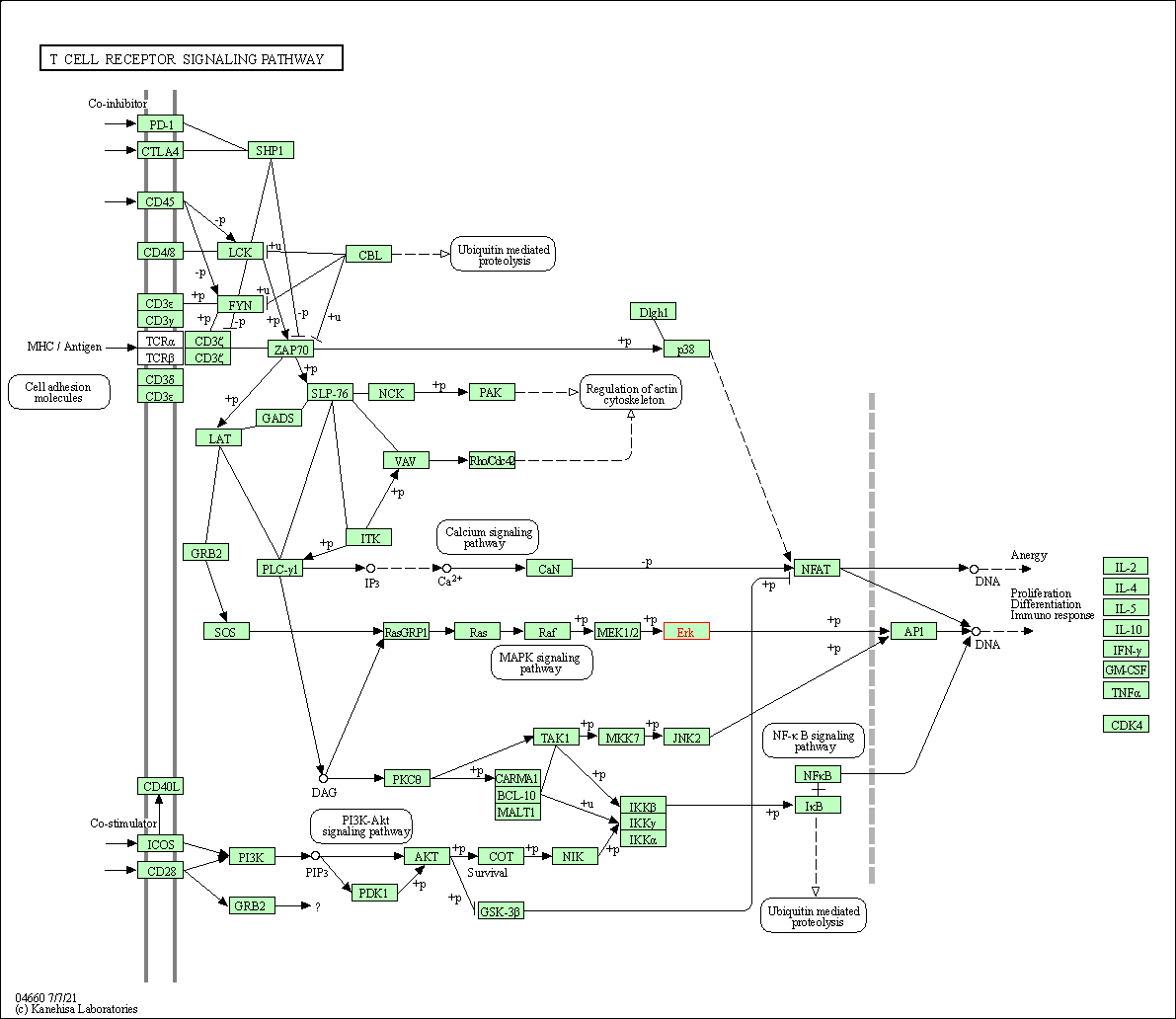
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |
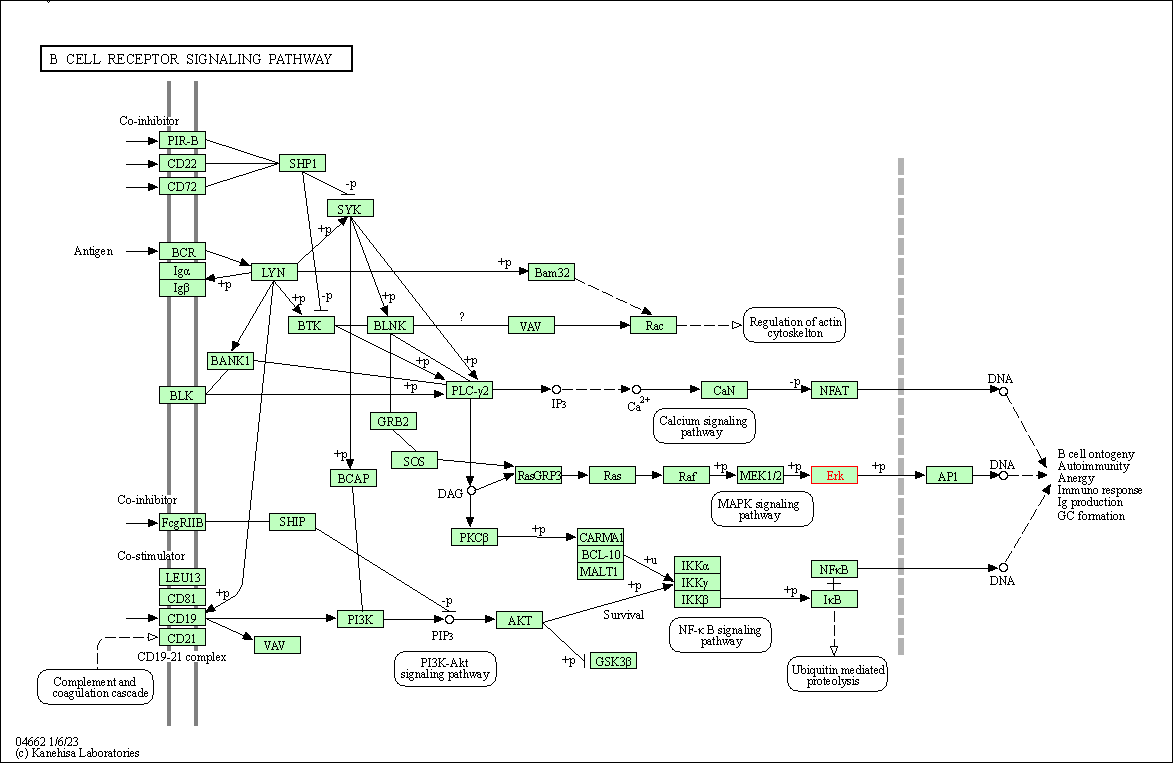
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |
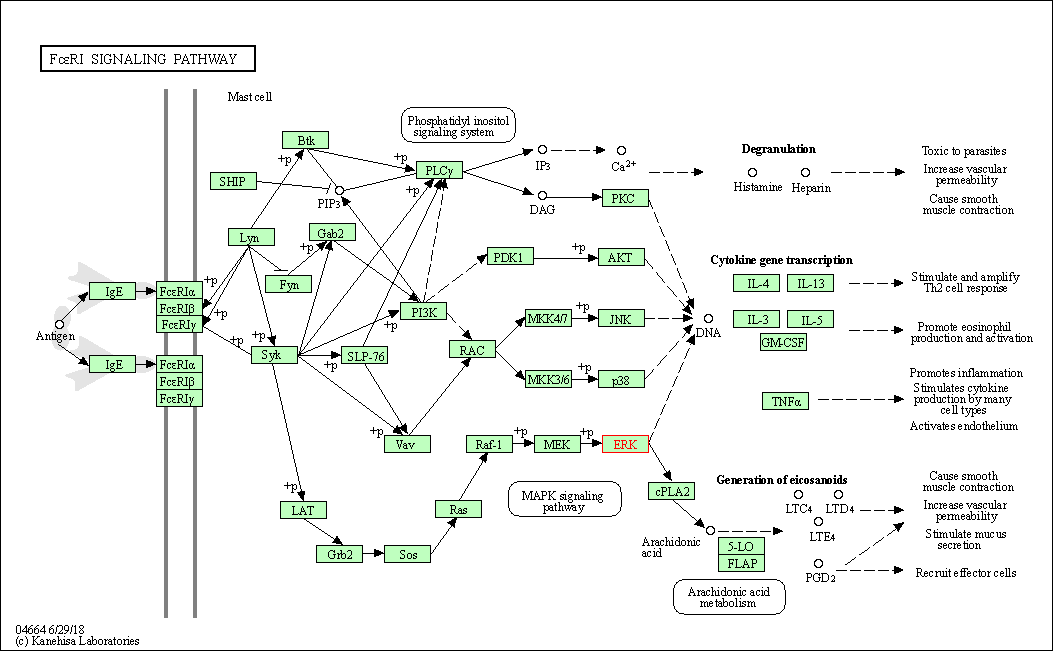
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |
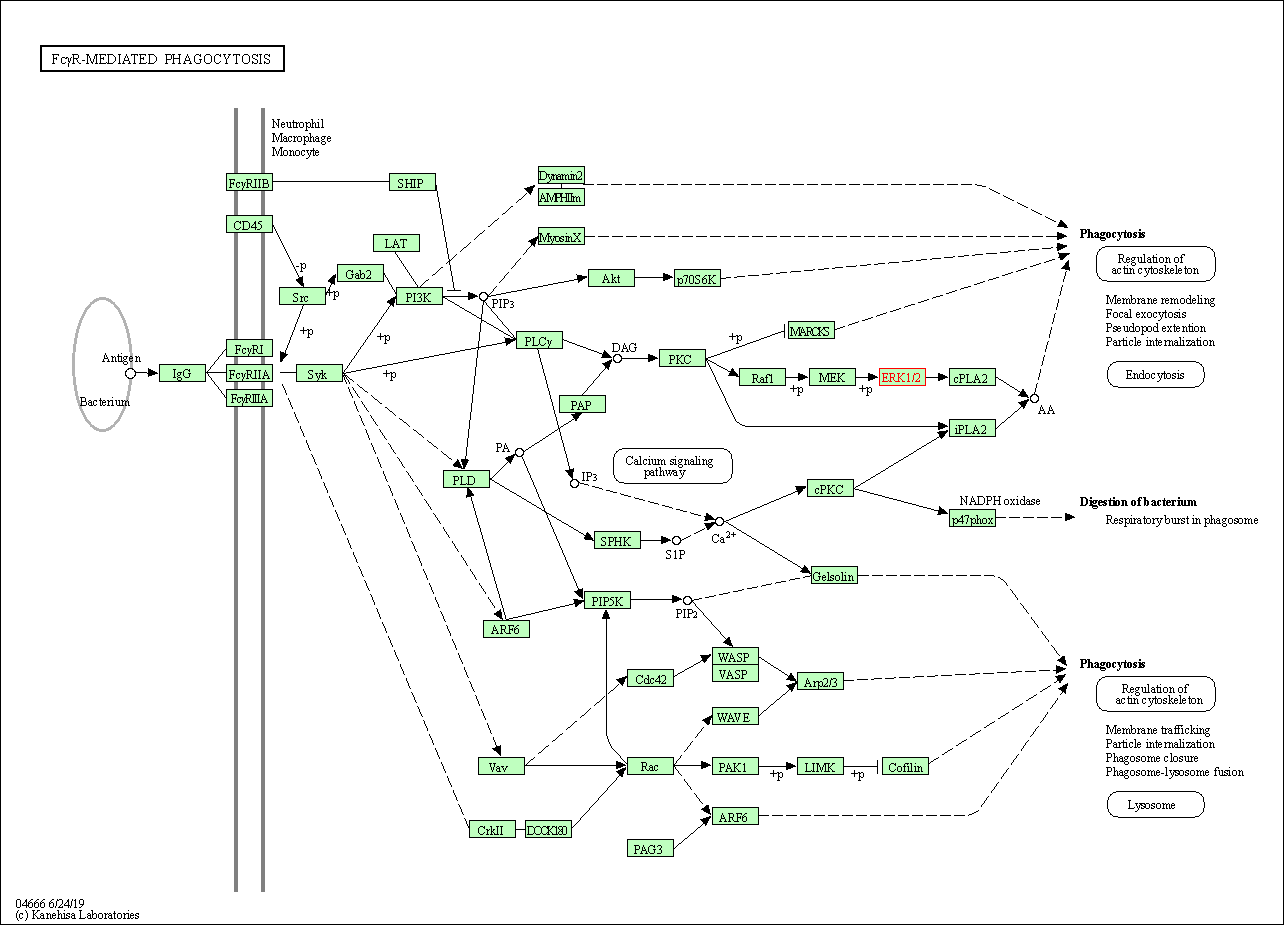
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term potentiation | hsa04720 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glutamatergic synapse | hsa04724 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Melanogenesis | hsa04916 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |
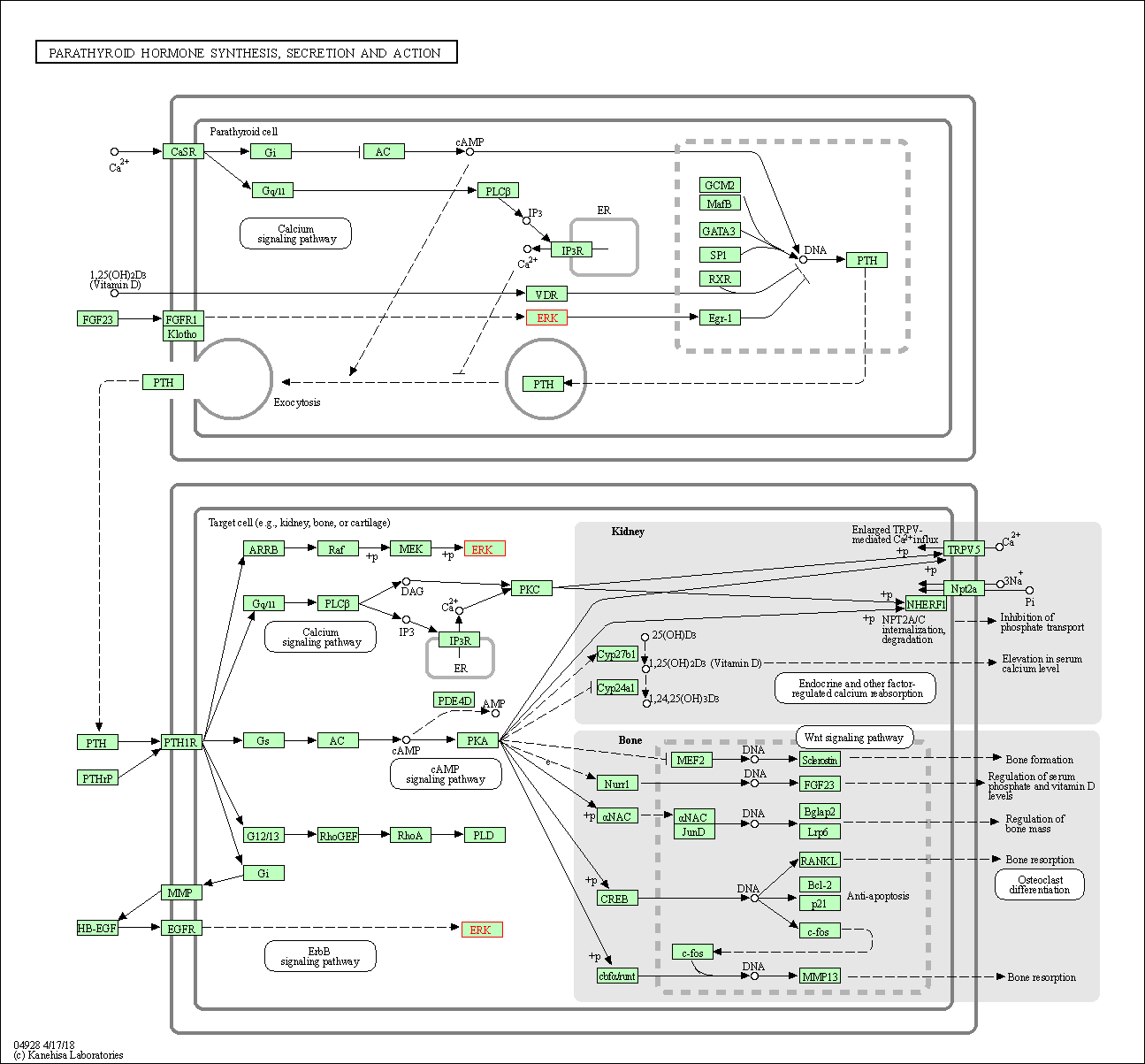
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |
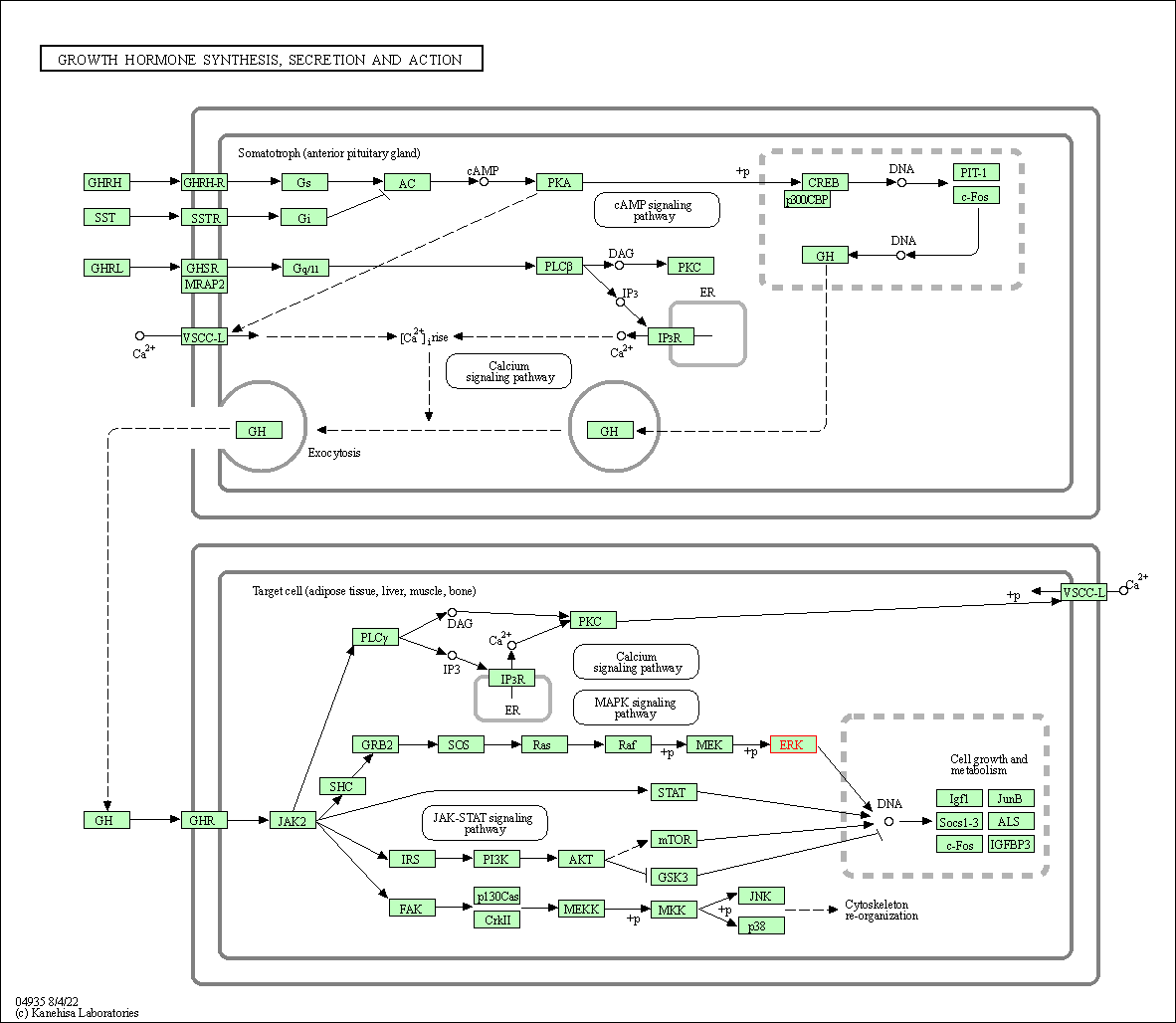
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | hsa04960 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 97 | Degree centrality | 1.04E-02 | Betweenness centrality | 1.41E-02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.82E-01 | Radiality | 1.48E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 9.71E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.34E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.62E-02 | Eccentricity | 10 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | DOI: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2015-4693 | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03417739) A Phase II Study of BVD-523 in Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04198818) A Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of HH2710 in Patient With Advanced Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03520075) Study of ASTX029 in Subjects With Advanced Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04418167) JSI-1187-01 Monotherapy and in Combination With Dabrafenib for Advanced Solid Tumors With MAPK Pathway Mutations. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01875705) A Dose-Escalation Study of GDC-0994 in Patients With Locally Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Drug-Eluting Stent for High Risk Patients. University of Strathclyde Glasgow. 2015 | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04022863) Ovarium Cancer Detection by TEP's and ctDNA. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ERK Mutations Confer Resistance to Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Inhibitors | |||||
| REF 11 | WO patent application no. 2013,1850,32, Nanotherapeutics for drug targeting. | |||||
| REF 12 | Synthesis and biological testing of purine derivatives as potential ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2005 Feb 10;48(3):710-22. | |||||
| REF 13 | A unique inhibitor binding site in ERK1/2 is associated with slow binding kinetics. Nat Chem Biol. 2014 Oct;10(10):853-60. | |||||
| REF 14 | Crystal structure of human mono-phosphorylated ERK1 at Tyr204. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Dec 26;377(4):1123-7. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

