Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T29130
(Former ID: TTDS00275)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Acute-phase response factor; APRF
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
STAT3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90] | |||||
| Function |
Signal transducer and transcription activator that mediates cellular responses to interleukins, KITLG/SCF, LEP and other growth factors. Once activated, recruits coactivators, such as NCOA1 or MED1, to the promoter region of the target gene. May mediate cellular responses to activated FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Binds to the interleukin-6 (IL-6)-responsive elements identified in the promoters of various acute-phase protein genes. Activated by IL31 through IL31RA. Acts as a regulator of inflammatory response by regulating differentiation of naive CD4(+) T-cells into T-helper Th17 or regulatory T-cells (Treg): deacetylation and oxidation of lysine residues by LOXL3, leads to disrupt STAT3 dimerization and inhibit its transcription activity. Involved in cell cycle regulation by inducing the expression of key genes for the progression from G1 to S phase, such as CCND1. Mediates the effects of LEP on melanocortin production, body energy homeostasis and lactation (By similarity). May play an apoptotic role by transctivating BIRC5 expression under LEP activation. Cytoplasmic STAT3 represses macroautophagy by inhibiting EIF2AK2/PKR activity. Plays a crucial role in basal beta cell functions, such as regulation of insulin secretion (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Transcription factor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAQWNQLQQLDTRYLEQLHQLYSDSFPMELRQFLAPWIESQDWAYAASKESHATLVFHNL
LGEIDQQYSRFLQESNVLYQHNLRRIKQFLQSRYLEKPMEIARIVARCLWEESRLLQTAA TAAQQGGQANHPTAAVVTEKQQMLEQHLQDVRKRVQDLEQKMKVVENLQDDFDFNYKTLK SQGDMQDLNGNNQSVTRQKMQQLEQMLTALDQMRRSIVSELAGLLSAMEYVQKTLTDEEL ADWKRRQQIACIGGPPNICLDRLENWITSLAESQLQTRQQIKKLEELQQKVSYKGDPIVQ HRPMLEERIVELFRNLMKSAFVVERQPCMPMHPDRPLVIKTGVQFTTKVRLLVKFPELNY QLKIKVCIDKDSGDVAALRGSRKFNILGTNTKVMNMEESNNGSLSAEFKHLTLREQRCGN GGRANCDASLIVTEELHLITFETEVYHQGLKIDLETHSLPVVVISNICQMPNAWASILWY NMLTNNPKNVNFFTKPPIGTWDQVAEVLSWQFSSTTKRGLSIEQLTTLAEKLLGPGVNYS GCQITWAKFCKENMAGKGFSFWVWLDNIIDLVKKYILALWNEGYIMGFISKERERAILST KPPGTFLLRFSESSKEGGVTFTWVEKDISGKTQIQSVEPYTKQQLNNMSFAEIIMGYKIM DATNILVSPLVYLYPDIPKEEAFGKYCRPESQEHPEADPGSAAPYLKTKFICVTPTTCSN TIDLPMSPRTLDSLMQFGNNGEGAEPSAGGQFESLTFDMELTSECATSPM Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A00142 ; BADD_A02356 ; BADD_A03237 ; BADD_A05675 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T96OOK | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Acitretin | Drug Info | Approved | Psoriasis vulgaris | [2], [3] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 9 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Napabucasin | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Pancreatic cancer | [4] | |
| 2 | Golotimod | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Immune System disease | [5] | |
| 3 | Atiprimod | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Multiple myeloma | [7] | |
| 4 | GLG-801 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia | [4] | |
| 5 | IMX-110 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [4] | |
| 6 | OPB-31121 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | [8] | |
| 7 | WP-1066 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Recurrent glioblastoma | [4] | |
| 8 | OPB-51602 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [12] | |
| 9 | TAK-114 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Ulcerative colitis | [13] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 47 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Acitretin | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Napabucasin | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | Golotimod | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 4 | Atiprimod | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 5 | GLG-801 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 6 | IMX-110 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 7 | OPB-31121 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 8 | WP-1066 | Drug Info | [4], [16] | |||
| 9 | OPB-51602 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 10 | Curcumin analog 2 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 11 | Flavonoid derivative 3 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 12 | Flavonoid derivative 5 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 13 | Gold-complexed thiosaccharide derivative 1 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 14 | Gold-complexed thiosaccharide derivative 2 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 15 | Gold-complexed thiosaccharide derivative 3 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 16 | Oxazole derivative 1 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 17 | Peptide analog 7 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 18 | Peptidomimetic analog 1 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 19 | Peptidomimetic analog 2 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 20 | Peptidomimetic analog 3 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 21 | Platinum IV complexe 1 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 22 | PMID26394986-Compound-10 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 23 | PMID26394986-Compound-11 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 24 | PMID26394986-Compound-12 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 25 | PMID26394986-Compound-20 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 26 | PMID26394986-Compound-21 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 27 | PMID26394986-Compound-22 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 28 | PMID26394986-Compound-42 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 29 | PMID26394986-Compound-43 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 30 | PMID26394986-Compound-44 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 31 | PMID26394986-Compound-50 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 32 | PMID26394986-Compound-51 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 33 | PMID26394986-Compound-52 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 34 | Pyrazole derivative 62 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 35 | Pyrazole derivative 63 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 36 | Pyrazole derivative 64 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 37 | Pyrazole derivative 65 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 38 | Pyrazole derivative 66 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 39 | Quinoline carboxamide derivative 1 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 40 | Quinoline carboxamide derivative 2 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 41 | Quinoline carboxamide derivative 3 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 42 | Salicylic acid derivative 1 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 43 | Salicylic acid derivative 3 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 44 | Salicylic acid derivative 4 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 45 | Salicylic acid derivative 5 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 46 | Salicylic acid derivative 6 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 47 | GNF-PF-1399 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TAK-114 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: 5'-iodotubercidin | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of ERK2 complexed with allosteric and ATP-competitive inhibitors. | PDB:5AX3 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.98 Å | Mutation | No | [20] |
| PDB Sequence |
LVKKYILALW
358 NE
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: ((2-(((5S,8S,10aR)-3-acetyl-8-(((S)-5-amino-1-(benzhydrylamino)-1,5-dioxopentan-2-yl)carbamoyl)-6-oxodecahydropyrrolo[1,2-a][1,5]diazocin-5-yl)carbamoyl)-1H-indol-5-yl)difluoromethyl)phosphonic acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Stat3 Core in complex with compound SD36 | PDB:6NJS | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.70 Å | Mutation | No | [21] |
| PDB Sequence |
VVTEKQQMLE
145 QHLQDVRKRV155 QDLEQKMKVV165 ENLQDDFDFN175 YKTLKNQSVT196 RQKMQQLEQM 206 LTALDQMRRS216 IVSELAGLLS226 AMEYVQKTLT236 DEELADWKRR246 QQIACIGGPP 256 NICLDRLENW266 ITSLAESQLQ276 TRQQIKKLEE286 LQQKVSYKGD296 PIVQHRPMLE 306 ERIVELFRNL316 MKSAFVVERQ326 PCMPMHPDRP336 LVIKTGVQFT346 TKVRLLVKFP 356 ELNYQLKIKV366 CIDKDRGSRK383 FNILGTNTKV393 MNMEESNNGS403 LSAEFKHLTL 413 REQRCLIVTE434 ELHLITFETE444 VYHQGLKIDL454 ETHSLPVVVI464 SNICQMPNAW 474 ASILWYNMLT484 NNPKNVNFFT494 KPPIGTWDQV504 AEVLSWQFSS514 TTKRGLSIEQ 524 LTTLAEKLLG534 PGVNYSGCQI544 TWAKFCKENM554 AGKGFSFWVW564 LDNIIDLVKK 574 YILALWNEGY584 IMGFISKERE594 RAILSTKPPG604 TFLLRFSESS614 KEGGVTFTWV 624 EKDISGKTQI634 QSVEPYTKQQ644 LNNMSFAEII654 MGYKIMDATN664 ILVSPLVYLY 674 PDIPKEEAFG684 KYC
|
|||||
|
|
ARG609
2.799
PHE610
4.693
SER611
2.690
GLU612
2.821
SER613
2.701
SER614
4.384
THR620
3.619
TRP623
4.079
GLN635
3.903
SER636
2.790
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |
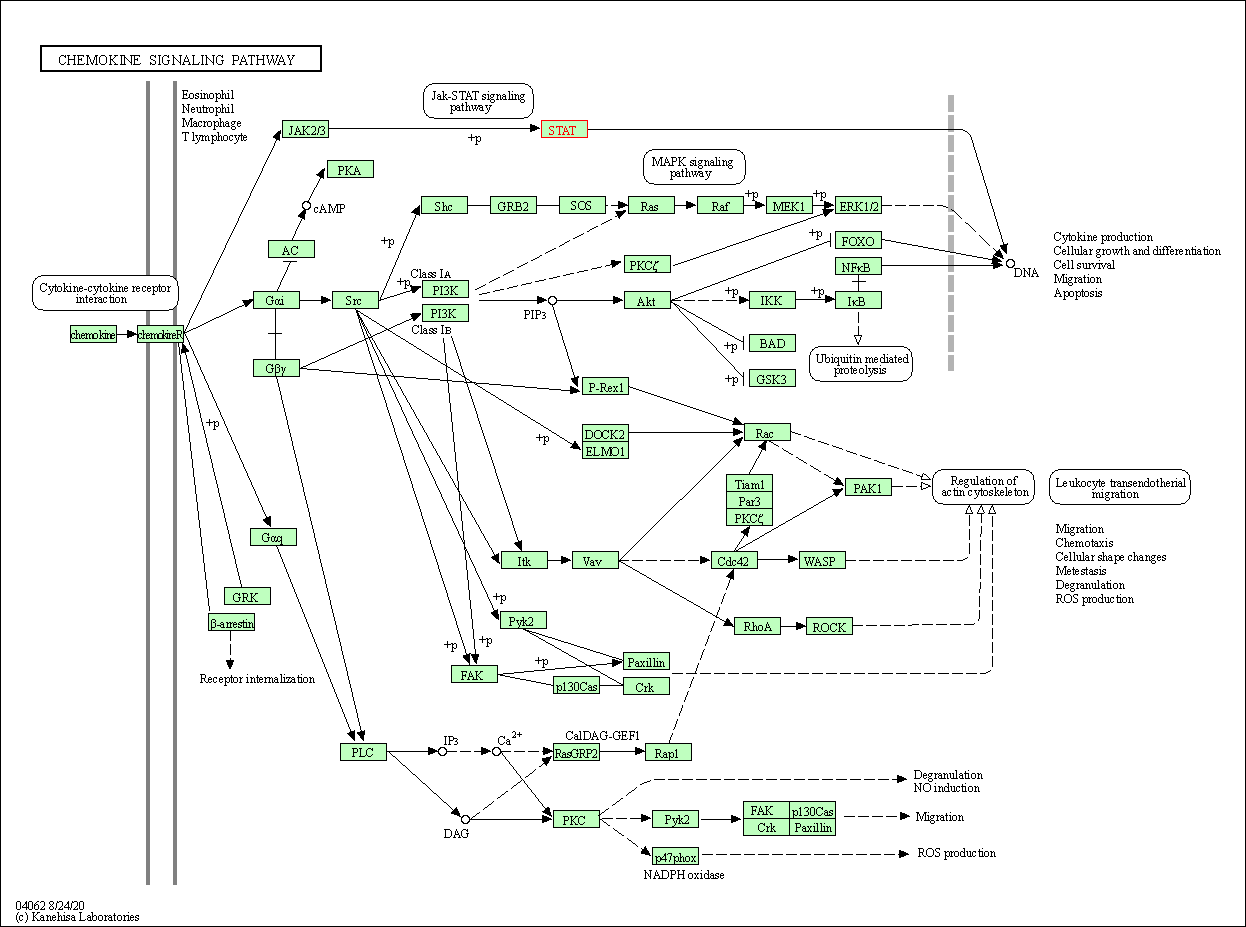
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |
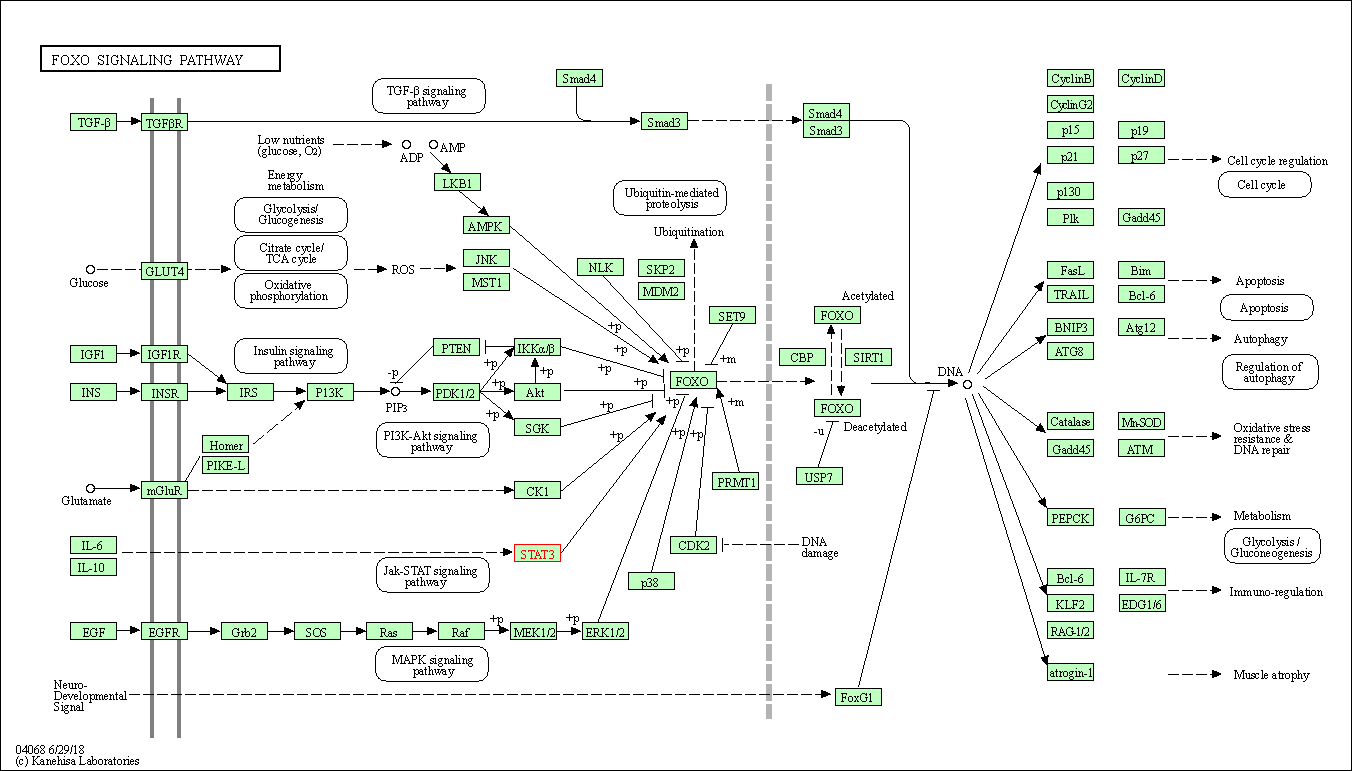
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | Affiliated Target |
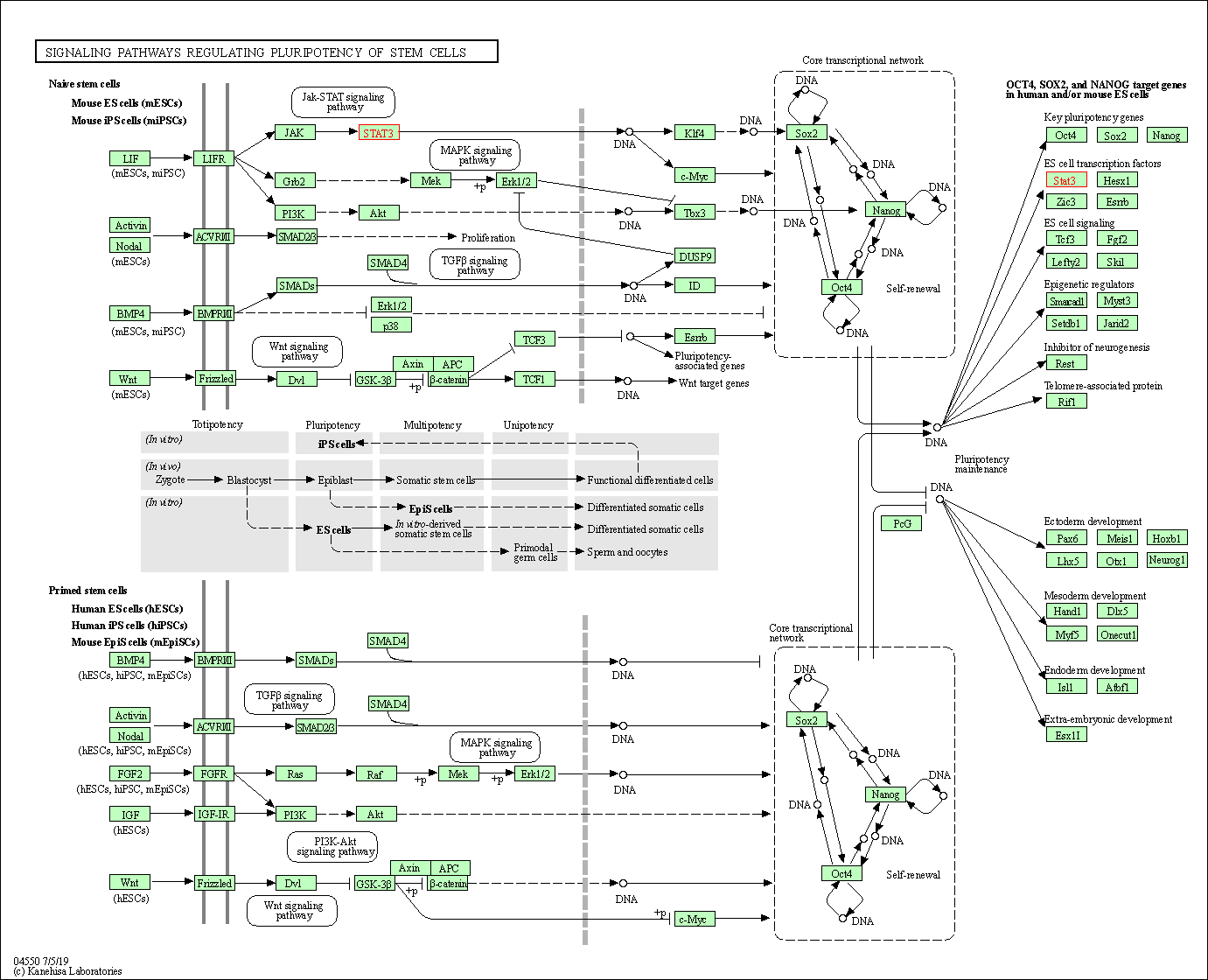
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |
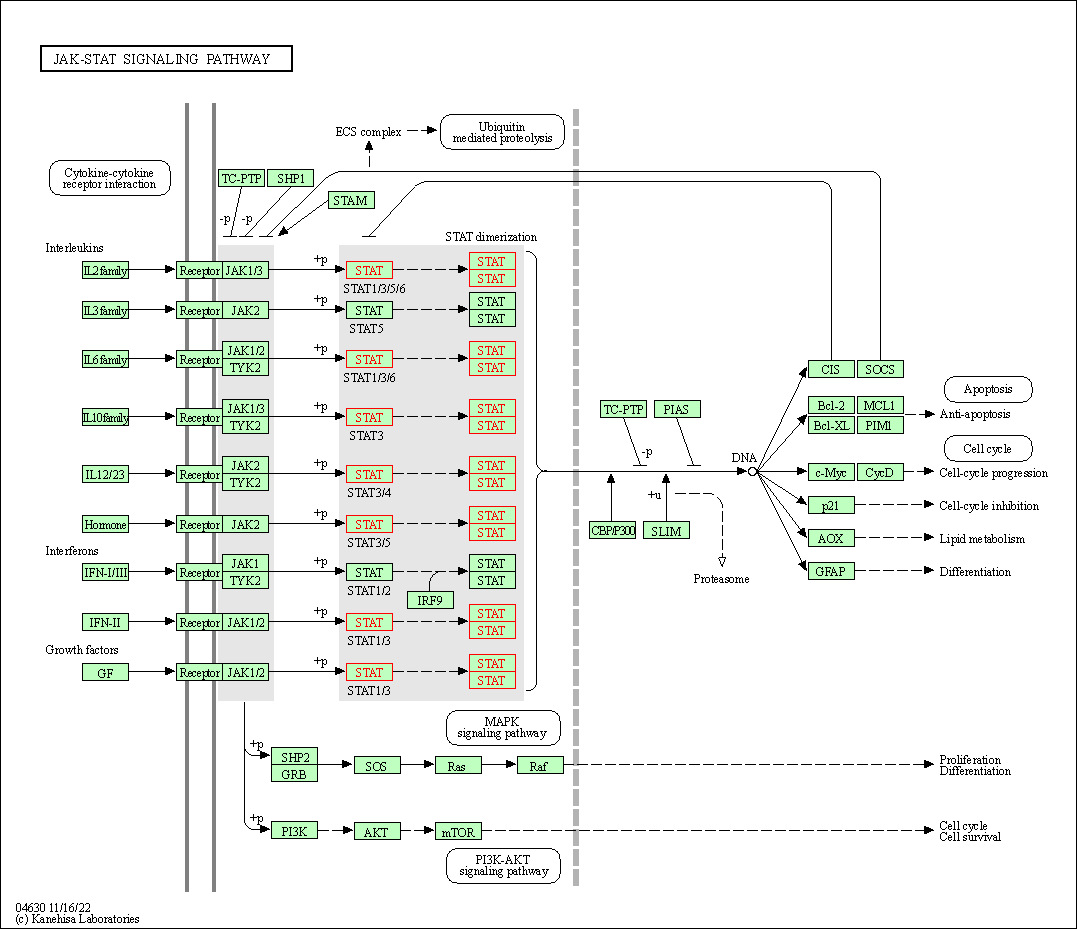
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 128 | Degree centrality | 1.38E-02 | Betweenness centrality | 2.30E-02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.81E-01 | Radiality | 1.47E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 7.81E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.91E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.30E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Effects of acitretin on the expression of signaling pathway-related genes in epidermal squamous-cell carcinoma cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2006 Jan;28(1):21-4. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7598). | |||||
| REF 3 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 4 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00756951) Dose Ranging Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of SCV-07 for the Delay to Onset of Severe Oral Mucositis in Patients Receiving Chemoradiation Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04474470) A Study to Evaluate NT219 Alone and in Combination With ERBITUX (Cetuximab) in Adults With Advanced Solid Tumors and Head and Neck Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | Emerging therapies for multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):99-127. | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01406574) Phase I/II Study of OPB-31121 in Patients With Progressive Hepatocellular Carcinoma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04702503) Study of WP1220 for the Treatment of Adult Subjects With Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma (CTCL). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02250170) Safety and Biomarker of OPB-111077 in Subjects With Advanced Solid Tumor. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03416816) A Study of DSP-0337 in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors to Determine the Safety and the Pharmacokinetic Profile. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02058017) OPB-51602 in Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Prior to Definitive Chemoradiotherapy. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Gastroenterology. | |||||
| REF 14 | National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary (drug id 617379). | |||||
| REF 15 | OPB-31121, a novel small molecular inhibitor, disrupts the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and exhibits an antitumor activity in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013 Jul 10;335(1):145-52. | |||||
| REF 16 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 17 | Phase I and biomarker study of OPB-51602, a novel signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid malignancies. Ann Oncol. 2015 May;26(5):998-1005. | |||||
| REF 18 | A STAT inhibitor patent review: progress since 2011.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(12):1397-421. | |||||
| REF 19 | In silico identification and biochemical evaluation of novel inhibitors of NRH:quinone oxidoreductase 2 (NQO2). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Dec 15;20(24):7331-6. | |||||
| REF 20 | Identification of allosteric ERK2 inhibitors through in silico biased screening and competitive binding assay. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Feb 1;26(3):955-958. | |||||
| REF 21 | A Potent and Selective Small-Molecule Degrader of STAT3 Achieves Complete Tumor Regression In?Vivo. Cancer Cell. 2019 Nov 11;36(5):498-511.e17. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

