Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T29339
(Former ID: TTDI02051)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Retinoic acid-inducible gene-1 (RIG-1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Retinoic acidinducible gene I protein; Retinoic acidinducible gene 1 protein; Retinoic acid-inducible gene I protein; Retinoic acid-inducible gene 1 protein; RLR1; RLR-1; RIGIlike receptor 1; RIGI; RIG1; RIG-I-like receptor 1; RIG-I; Probable ATPdependent RNA helicase DDX58; Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX58; DEAD box protein 58
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
DDX58
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 4 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Hepatitis virus infection [ICD-11: 1E50-1E51] | |||||
| 2 | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||||
| 3 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| 4 | Squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B60-2D01] | |||||
| Function |
Its ligands include: 5'-triphosphorylated ssRNA and dsRNA and short dsRNA (<1 kb in length). In addition to the 5'-triphosphate moiety, blunt-end base pairing at the 5'-end of the RNA is very essential. Overhangs at the non-triphosphorylated end of the dsRNA RNA have no major impact on its activity. A 3'overhang at the 5'triphosphate end decreases and any 5'overhang at the 5' triphosphate end abolishes its activity. Upon ligand binding it associates with mitochondria antiviral signaling protein (MAVS/IPS1) which activates the IKK-related kinases: TBK1 and IKBKE which phosphorylate interferon regulatory factors: IRF3 and IRF7 which in turn activate transcription of antiviral immunological genes, including interferons (IFNs); IFN-alpha and IFN-beta. Detects both positive and negative strand RNA viruses including members of the families Paramyxoviridae: Human respiratory syncytial virus and measles virus (MeV), Rhabdoviridae: vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), Orthomyxoviridae: influenza A and B virus, Flaviviridae: Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), dengue virus (DENV) and west Nile virus (WNV). It also detects rotavirus and reovirus. Also involved in antiviral signaling in response to viruses containing a dsDNA genome such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Detects dsRNA produced from non-self dsDNA by RNA polymerase III, such as Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs (EBERs). May play important roles in granulocyte production and differentiation, bacterial phagocytosis and in the regulation of cell migration. Innate immune receptor which acts as a cytoplasmic sensor of viral nucleic acids and plays a major role in sensing viral infection and in the activation of a cascade of antiviral responses including the induction of type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Acid anhydride hydrolase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.6.4.13
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MTTEQRRSLQAFQDYIRKTLDPTYILSYMAPWFREEEVQYIQAEKNNKGPMEAATLFLKF
LLELQEEGWFRGFLDALDHAGYSGLYEAIESWDFKKIEKLEEYRLLLKRLQPEFKTRIIP TDIISDLSECLINQECEEILQICSTKGMMAGAEKLVECLLRSDKENWPKTLKLALEKERN KFSELWIVEKGIKDVETEDLEDKMETSDIQIFYQEDPECQNLSENSCPPSEVSDTNLYSP FKPRNYQLELALPAMKGKNTIICAPTGCGKTFVSLLICEHHLKKFPQGQKGKVVFFANQI PVYEQQKSVFSKYFERHGYRVTGISGATAENVPVEQIVENNDIIILTPQILVNNLKKGTI PSLSIFTLMIFDECHNTSKQHPYNMIMFNYLDQKLGGSSGPLPQVIGLTASVGVGDAKNT DEALDYICKLCASLDASVIATVKHNLEELEQVVYKPQKFFRKVESRISDKFKYIIAQLMR DTESLAKRICKDLENLSQIQNREFGTQKYEQWIVTVQKACMVFQMPDKDEESRICKALFL YTSHLRKYNDALIISEHARMKDALDYLKDFFSNVRAAGFDEIEQDLTQRFEEKLQELESV SRDPSNENPKLEDLCFILQEEYHLNPETITILFVKTRALVDALKNWIEGNPKLSFLKPGI LTGRGKTNQNTGMTLPAQKCILDAFKASGDHNILIATSVADEGIDIAQCNLVILYEYVGN VIKMIQTRGRGRARGSKCFLLTSNAGVIEKEQINMYKEKMMNDSILRLQTWDEAVFREKI LHIQTHEKFIRDSQEKPKPVPDKENKKLLCRKCKALACYTADVRVIEECHYTVLGDAFKE CFVSRPHPKPKQFSSFEKRAKIFCARQNCSHDWGIHVKYKTFEIPVIKIESFVVEDIATG VQTLYSKWKDFHFEKIPFDPAEMSK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | SB-9200 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hepatitis B virus infection | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | SB-9200 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |
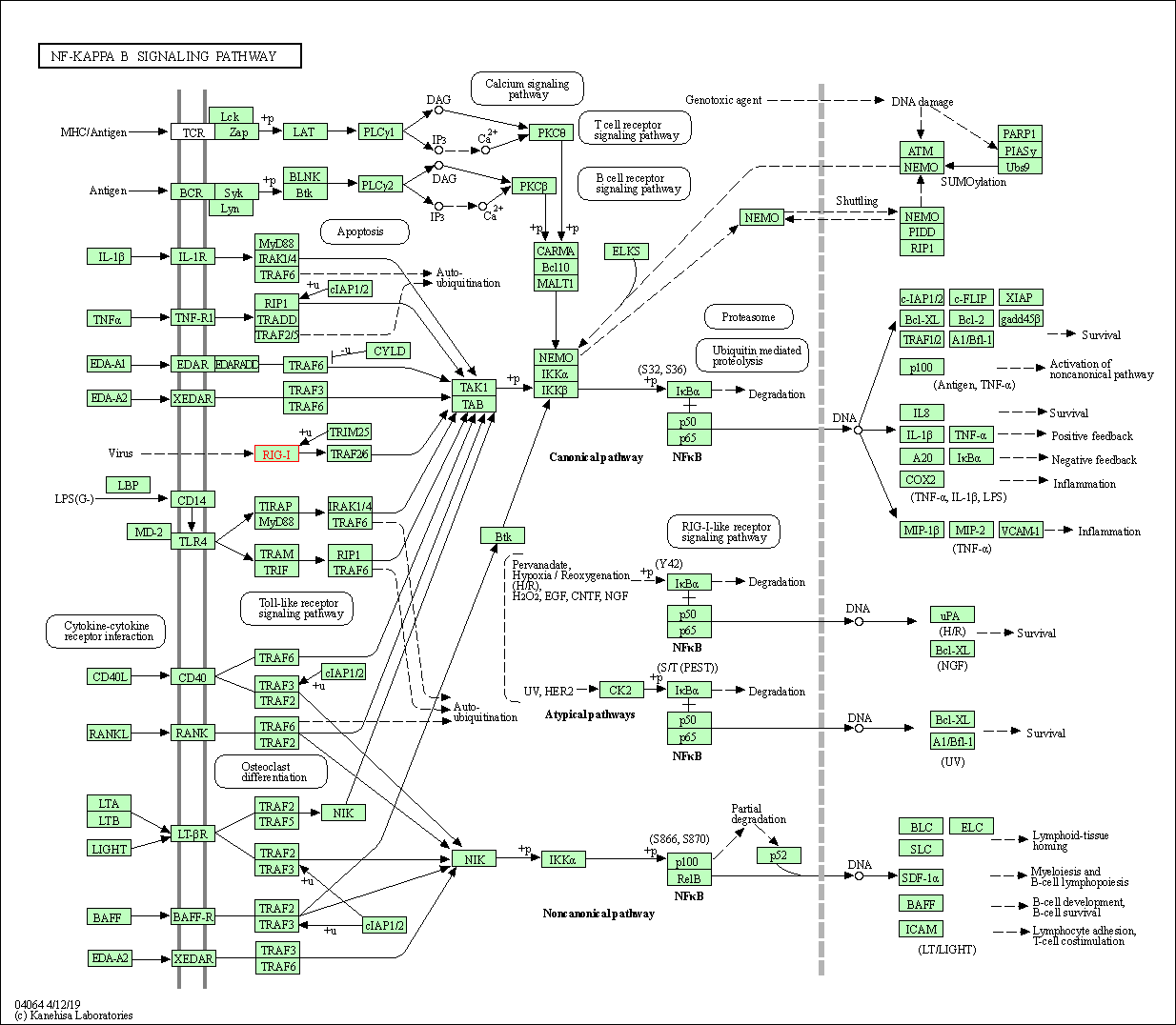
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | Affiliated Target |
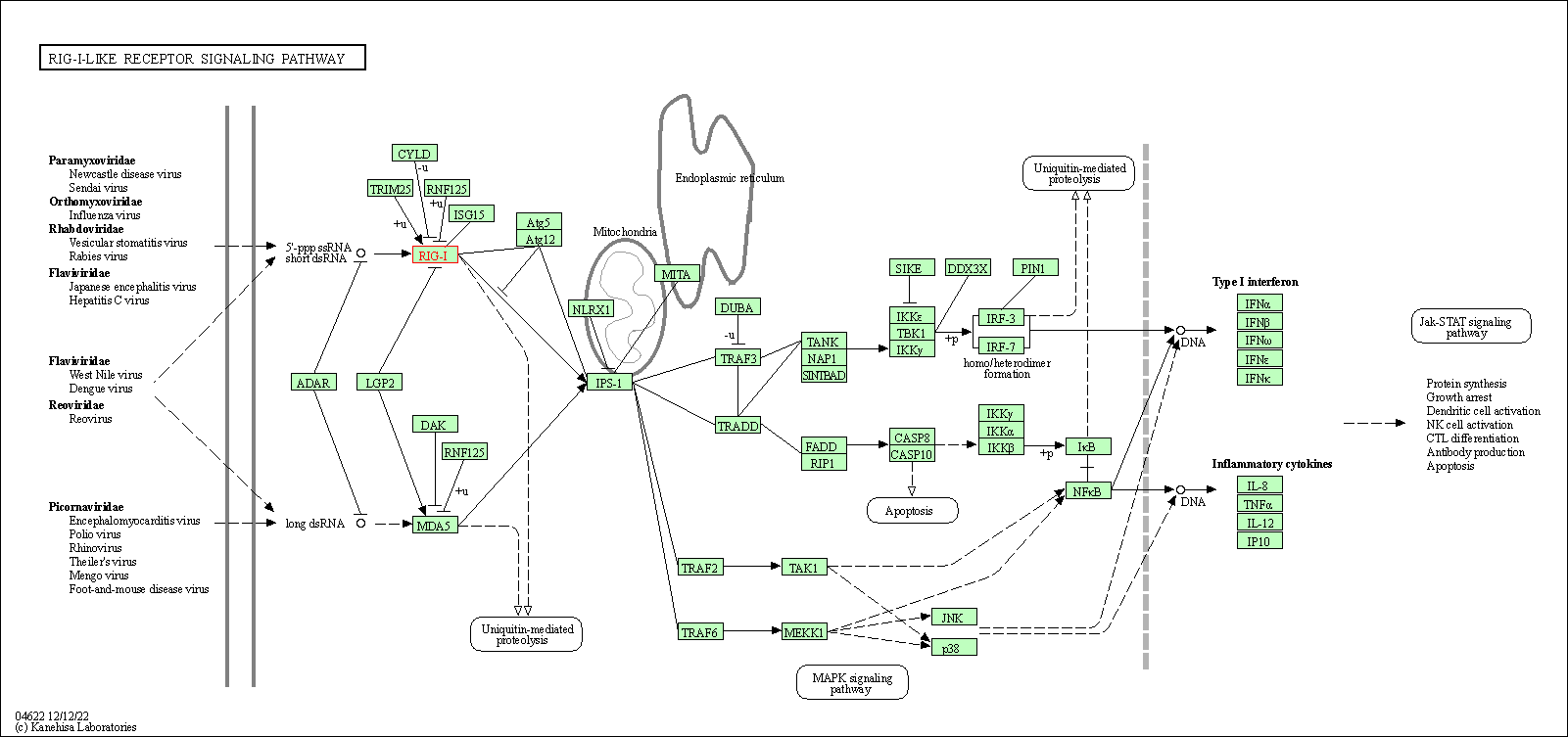
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | hsa04623 | Affiliated Target |
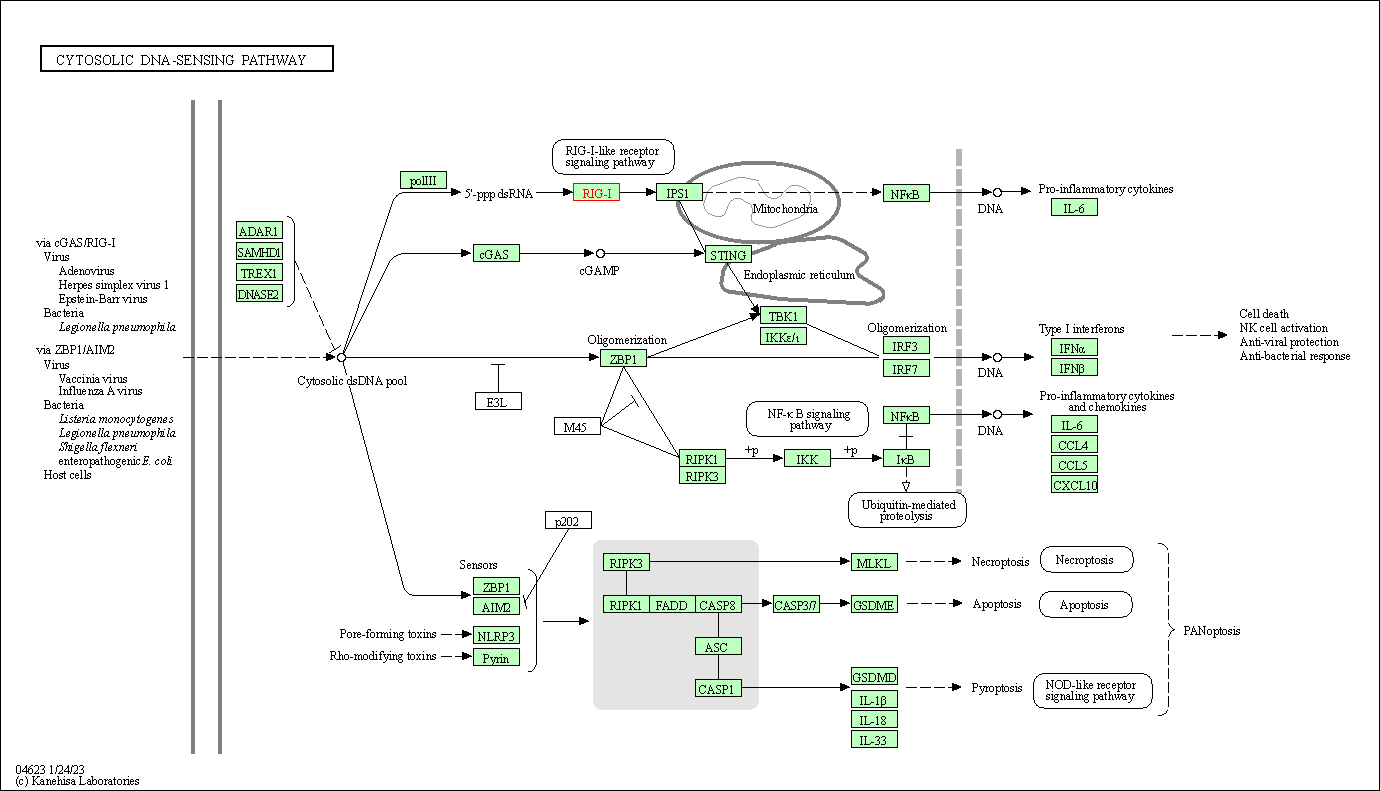
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 27 | Degree centrality | 2.90E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.44E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.32E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.37E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.76E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.71E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 9 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | |||||
| 4 | Hepatitis C | |||||
| 5 | Hepatitis B | |||||
| 6 | Measles | |||||
| 7 | Influenza A | |||||
| 8 | Herpes simplex infection | |||||
| 9 | Epstein-Barr virus infection | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 6 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ISG15 antiviral mechanism | |||||
| 2 | TRAF3-dependent IRF activation pathway | |||||
| 3 | TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation | |||||
| 4 | TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation | |||||
| 5 | NF-kB activation through FADD/RIP-1 pathway mediated by caspase-8 and -10 | |||||
| 6 | Negative regulators of RIG-I/MDA5 signaling | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 1 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | RIG-I/MDA5 mediated induction of IFN-alpha/beta pathways | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Company reprot (Spring Bank Pharmaceuticals) (drug: SB 9200) | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02751996) A Study Evaluating the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Antiviral Efficacy of SB 9200 in Subjects Infected With Chronic HBV (ACHIEVE). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03739138) Intratumoral/Intralesional Administration of MK-4621/JetPEI With or Without Pembrolizumab in Participants With Advanced/Metastatic or Recurrent Solid Tumors (MK-4621-002). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03291002) Study of Intratumoral CV8102 in cMEL, cSCC, hnSCC, and ACC. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

