Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T47107
(Former ID: TTDC00015)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Protein kinase C gamma (PRKCG)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
PRKCG; PKCG; PKC-gamma
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PRKCG
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||||
| 2 | Mastocytosis [ICD-11: 2A21] | |||||
| Function |
Calcium-activated, phospholipid-and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays diverse roles in neuronal cells and eye tissues, such as regulation of the neuronal receptors GRIA4/GLUR4 and GRIN1/NMDAR1, modulation of receptors and neuronal functions related to sensitivity to opiates, pain and alcohol, mediation of synaptic function and cell survival after ischemia, and inhibition of gap junction activity after oxidative stress. Binds and phosphorylates GRIA4/GLUR4 glutamate receptor and regulates its function by increasing plasma membrane-associated GRIA4 expression. In primary cerebellar neurons treated with the agonist 3,5-dihyidroxyphenylglycine, functions downstream of the metabotropic glutamate receptor GRM5/MGLUR5 and phosphorylates GRIN1/NMDAR1 receptor which plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. May be involved in the regulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP), but may be not necessary for the process of synaptic plasticity. May be involved in desensitization of mu-type opioid receptor-mediated G-protein activation in the spinal cord, and may be critical for the development and/or maintenance ofmorphine-induced reinforcing effects in the limbic forebrain. May modulate the functionality of mu-type-opioid receptors by participating in a signaling pathway which leads to the phosphorylation anddegradation of opioid receptors. May also contributes to chronic morphine-induced changes in nociceptive processing. Plays a role in neuropathic pain mechanisms and contributes to the maintenance of the allodynia pain produced by peripheral inflammation. Plays an important role in initial sensitivity and tolerance to ethanol, by mediating the behavioral effects of ethanol as well as the effects of this drug on the GABA(A) receptors. During and after cerebral ischemia modulate neurotransmission and cell survival in synaptic membranes, and is involved in insulin-induced inhibition of necrosis, an important mechanism for minimizing ischemic injury. Required for the elimination of multiple climbing fibers during innervation of Purkinje cells in developing cerebellum. Is activated in lens epithelial cells upon hydrogen peroxide treatment, and phosphorylates connexin-43 (GJA1/CX43), resulting in disassembly of GJA1 gap junction plaques and inhibition of gap junction activity which could provide a protective effect against oxidative stress. Phosphorylates p53/TP53 and promotes p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Involved in the phase resetting of the cerebral cortex circadian clock during temporally restricted feeding. Stabilizes the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1 by interfering with its ubiquitination, thus suppressing its degradation, resultingin phase resetting of the cerebral cortex clock.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.13
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAGLGPGVGDSEGGPRPLFCRKGALRQKVVHEVKSHKFTARFFKQPTFCSHCTDFIWGIG
KQGLQCQVCSFVVHRRCHEFVTFECPGAGKGPQTDDPRNKHKFRLHSYSSPTFCDHCGSL LYGLVHQGMKCSCCEMNVHRRCVRSVPSLCGVDHTERRGRLQLEIRAPTADEIHVTVGEA RNLIPMDPNGLSDPYVKLKLIPDPRNLTKQKTRTVKATLNPVWNETFVFNLKPGDVERRL SVEVWDWDRTSRNDFMGAMSFGVSELLKAPVDGWYKLLNQEEGEYYNVPVADADNCSLLQ KFEACNYPLELYERVRMGPSSSPIPSPSPSPTDPKRCFFGASPGRLHISDFSFLMVLGKG SFGKVMLAERRGSDELYAIKILKKDVIVQDDDVDCTLVEKRVLALGGRGPGGRPHFLTQL HSTFQTPDRLYFVMEYVTGGDLMYHIQQLGKFKEPHAAFYAAEIAIGLFFLHNQGIIYRD LKLDNVMLDAEGHIKITDFGMCKENVFPGTTTRTFCGTPDYIAPEIIAYQPYGKSVDWWS FGVLLYEMLAGQPPFDGEDEEELFQAIMEQTVTYPKSLSREAVAICKGFLTKHPGKRLGS GPDGEPTIRAHGFFRWIDWERLERLEIPPPFRPRPCGRSGENFDKFFTRAAPALTPPDRL VLASIDQADFQGFTYVNPDFVHPDARSPTSPVPVPVM Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T17E95 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Midostaurin | Drug Info | Approved | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 27 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Midostaurin | Drug Info | [1], [3] | |||
| 2 | BALANOL | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | RO-320432 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 4 | (-)-Cercosporamide | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 5 | 2,3,3-Triphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 6 | 2-(4-Hydroxy-phenyl)-3,3-diphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 7 | 3,3-Bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-phenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 8 | 3,3-Bis-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-2-phenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 9 | 3,4-di-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 10 | 3,4-diphenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 11 | 3-(4-Hydroxy-phenyl)-2,3-diphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 12 | 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 13 | 3-(indole-3-yl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 14 | 4-cycloheptyliden(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylphenol | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 15 | 4-cyclopentyliden(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylphenol | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 16 | 4-[1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1-butenyl]phenol | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 17 | 8-Octyl-benzolactam-V9 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 18 | Bisindolylmaleimide-I | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 19 | Go 6983 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 20 | LY-326449 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 21 | Monoctanoin component C | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 22 | PROSTRATIN | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 23 | RO-316233 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 24 | Ro-32-0557 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 25 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophen-4-yl-methanol | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 26 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophene-4,5''-dicarbaldehyde | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 27 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophene-4-carbaldehyde | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: D-serine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the C2 domain of human protein kinase C gamma. | PDB:2UZP | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.00 Å | Mutation | No | [17] |
| PDB Sequence |
MHTERRGRLQ
162 LEIRAPTADE172 IHVTVGEARN182 LIPMDPNGLS192 DPYVKLKLIP202 DPRNLTKQKT 212 RTVKATLNPV222 WNETFVFNLK232 PGDVERRLSV242 EVWDWDRTSR252 NDFMGAMSFG 262 VSELLKAPVD272 GWYKLLNQEE282 GEYYNVPVAD292 A
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Pyridoxal phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the C2 domain of human protein kinase C gamma. | PDB:2UZP | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.00 Å | Mutation | No | [17] |
| PDB Sequence |
MHTERRGRLQ
162 LEIRAPTADE172 IHVTVGEARN182 LIPMDPNGLS192 DPYVKLKLIP202 DPRNLTKQKT 212 RTVKATLNPV222 WNETFVFNLK232 PGDVERRLSV242 EVWDWDRTSR252 NDFMGAMSFG 262 VSELLKAPVD272 GWYKLLNQEE282 GEYYNVPVAD292 A
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | hsa04070 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Gap junction | hsa04540 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | hsa04670 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term potentiation | hsa04720 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glutamatergic synapse | hsa04724 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GABAergic synapse | hsa04727 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | hsa04750 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |
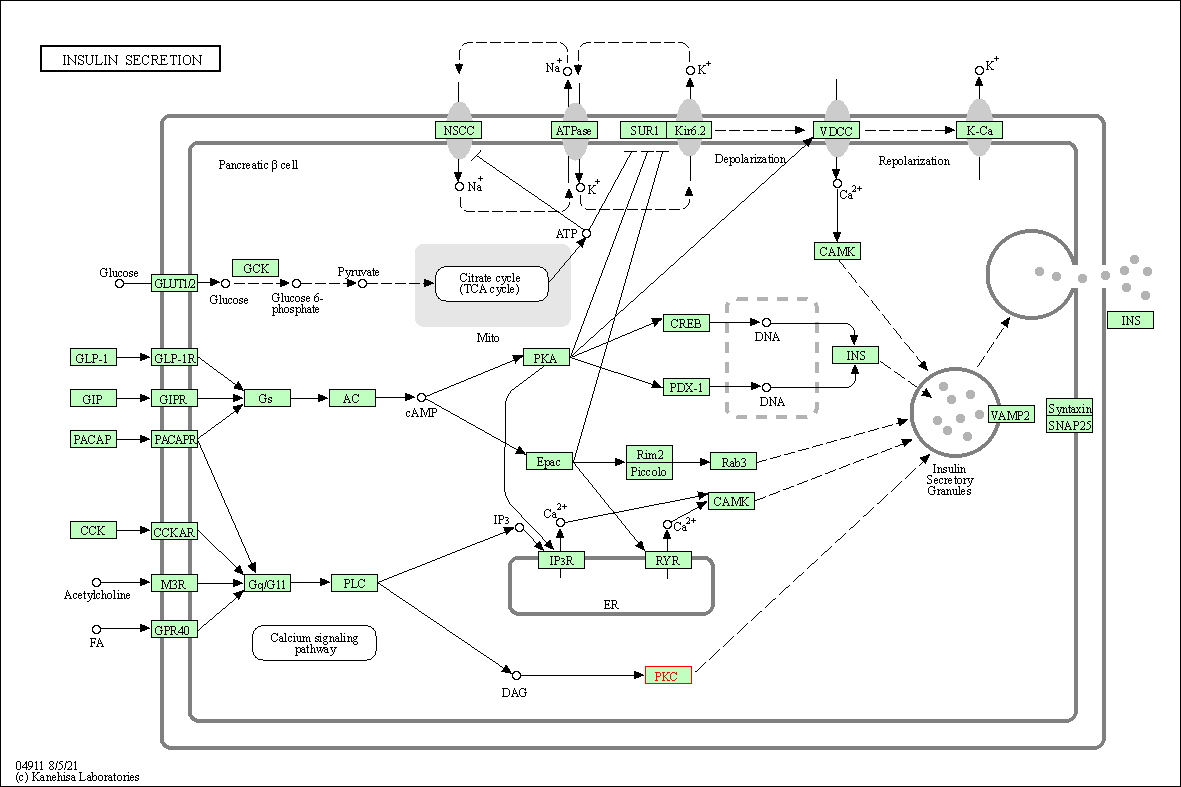
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Melanogenesis | hsa04916 | Affiliated Target |
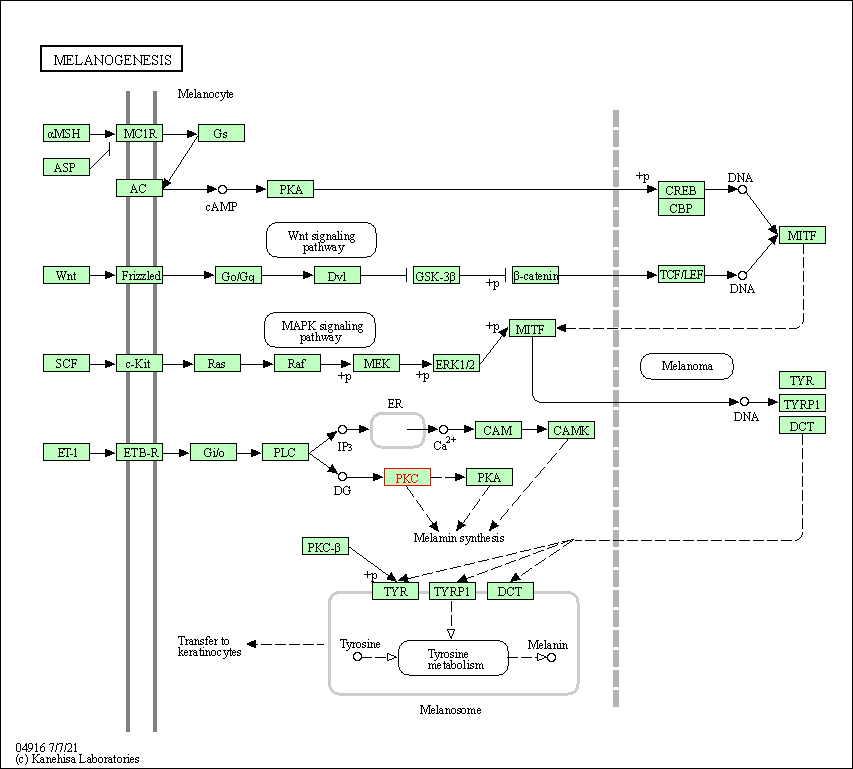
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone synthesis | hsa04918 | Affiliated Target |
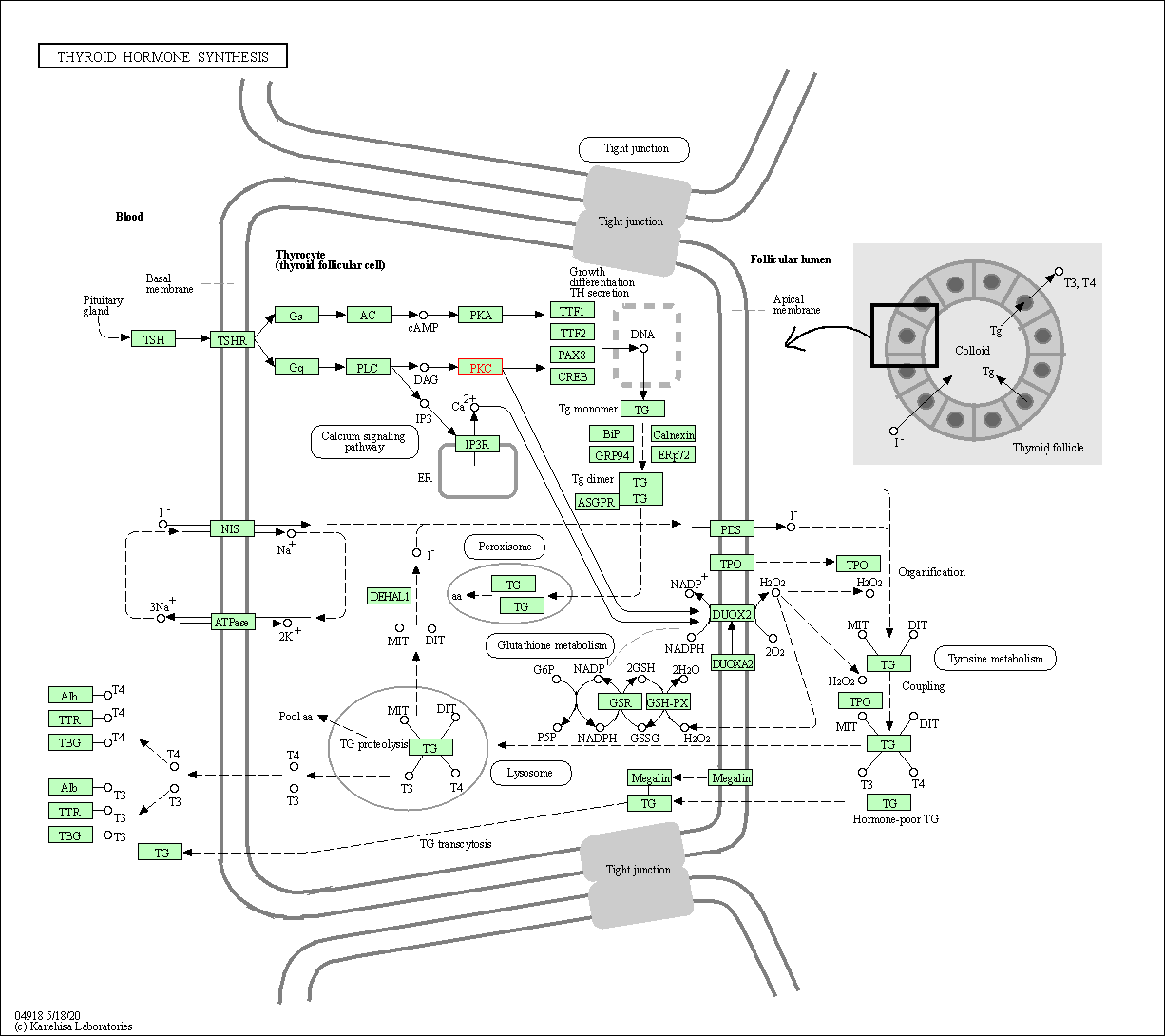
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |
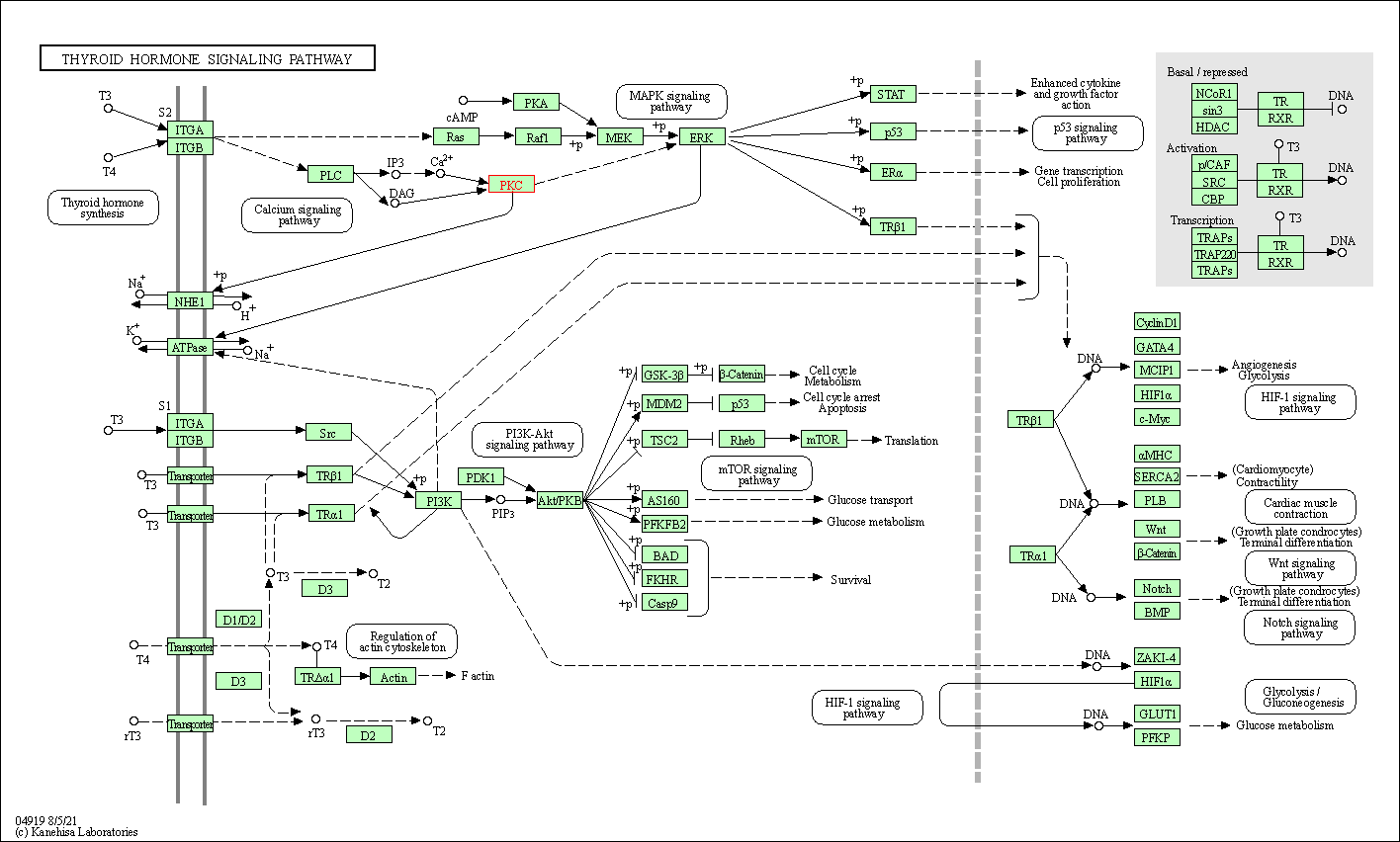
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |
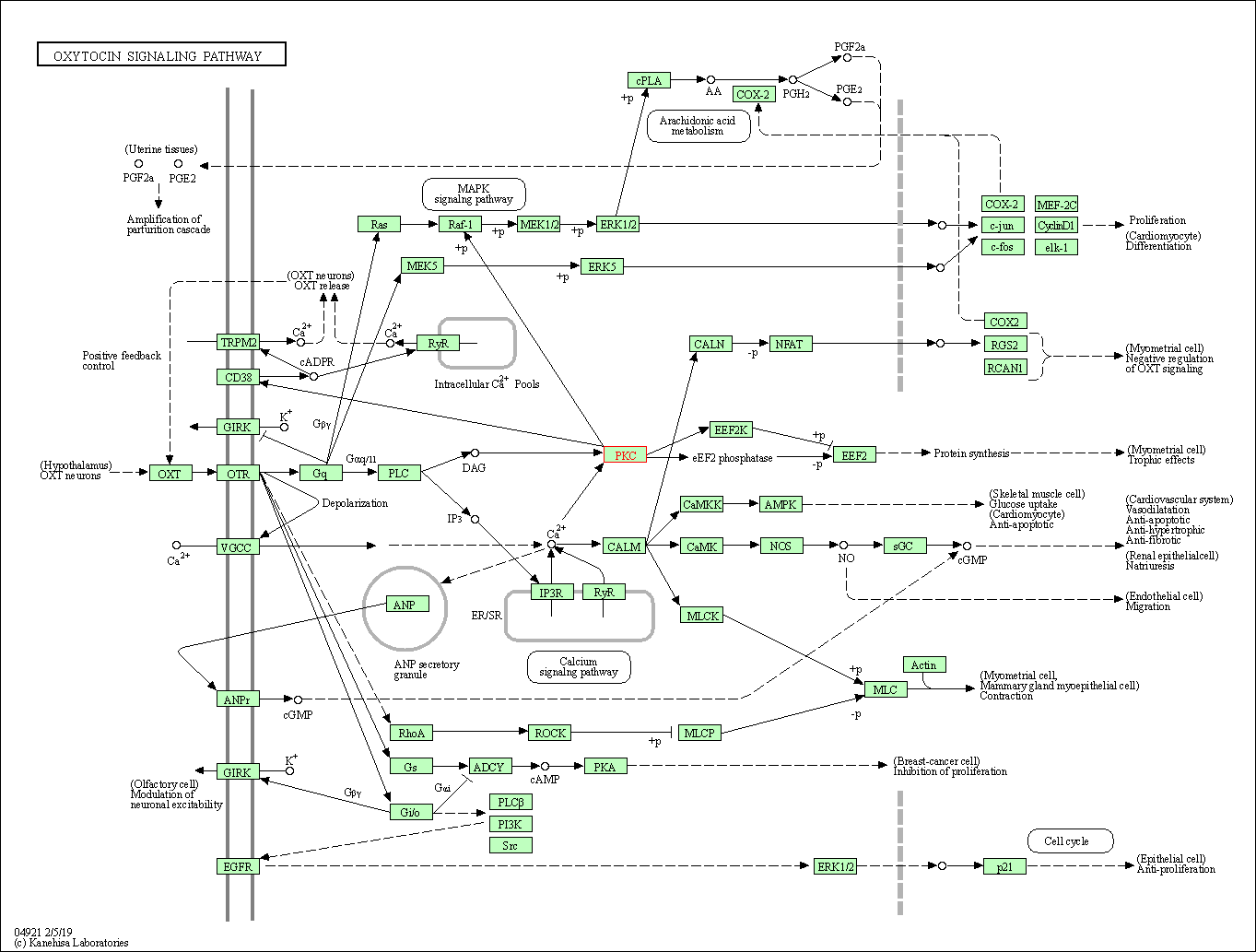
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | hsa04925 | Affiliated Target |
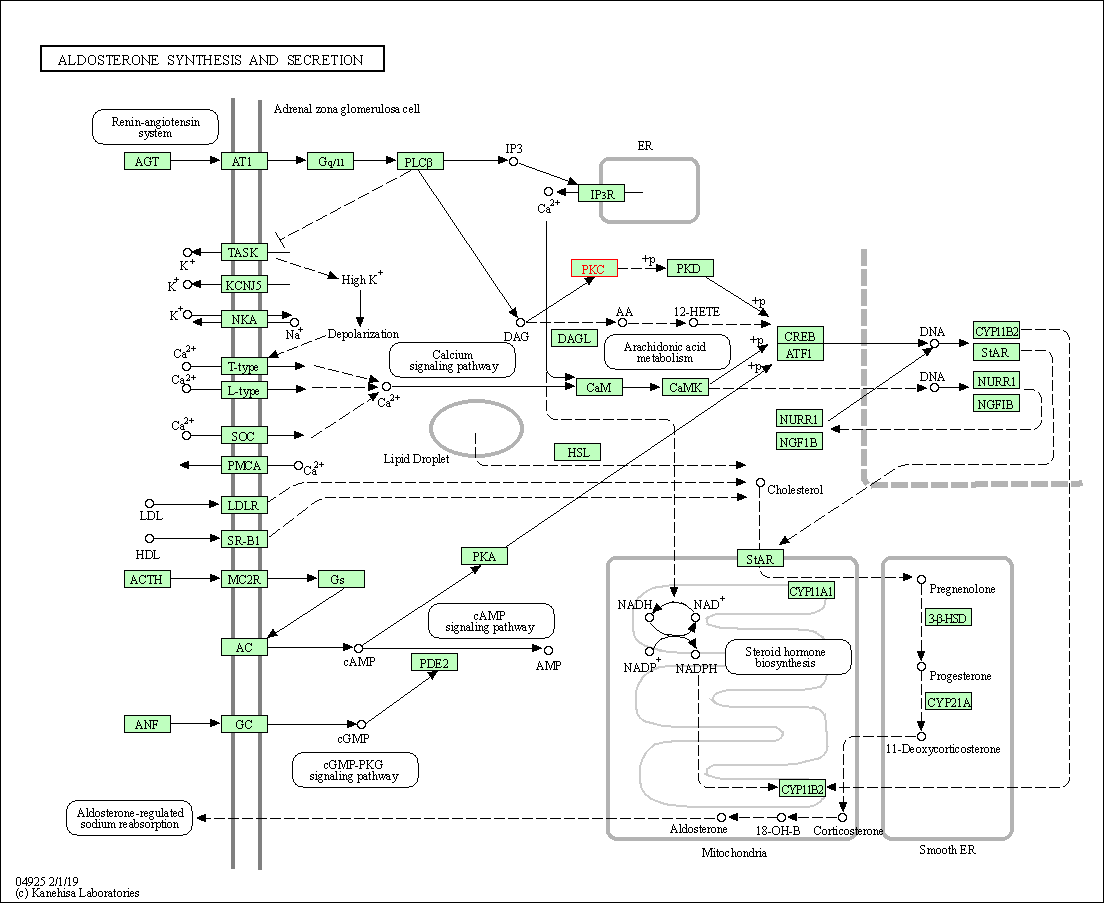
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |
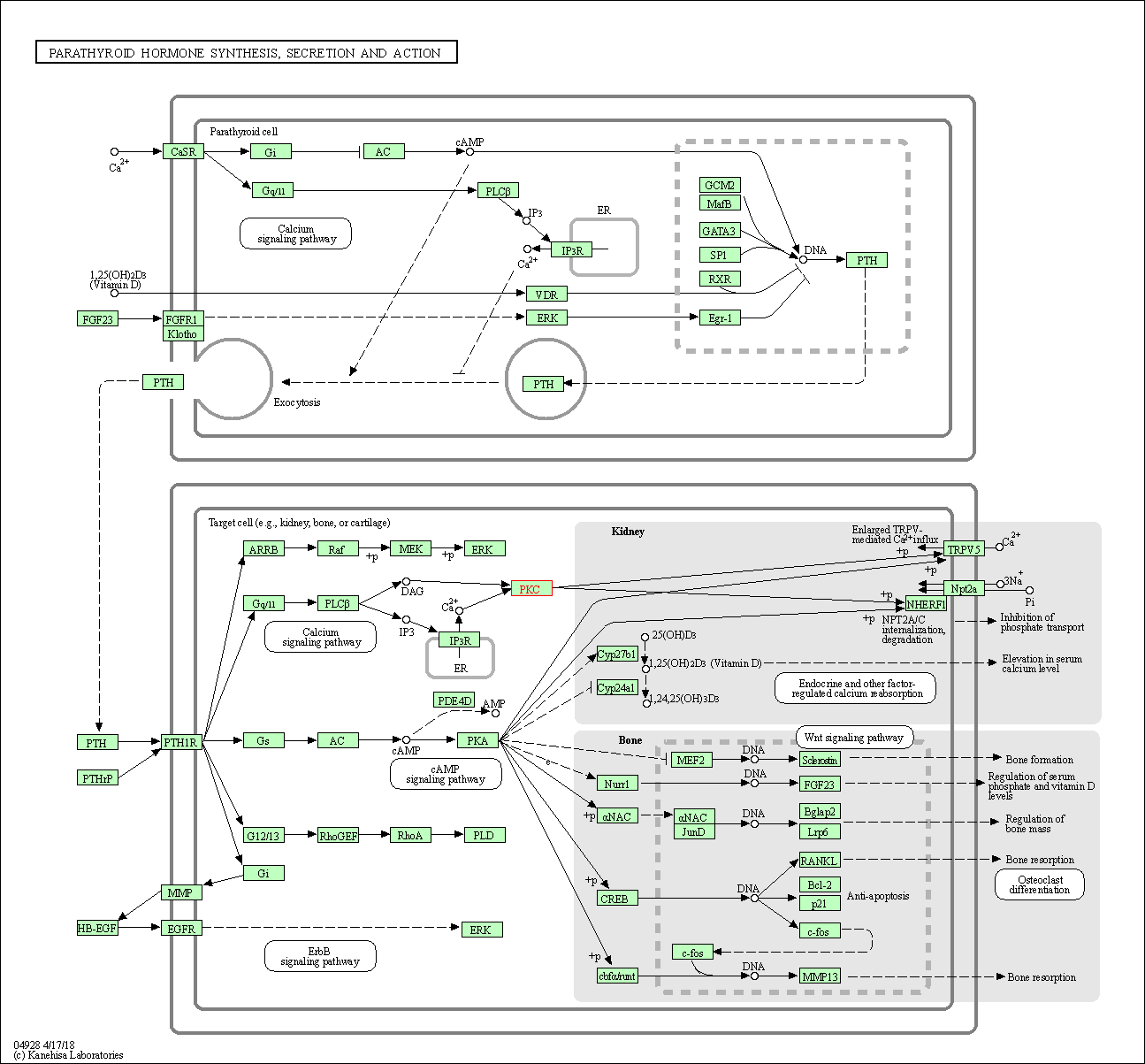
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |
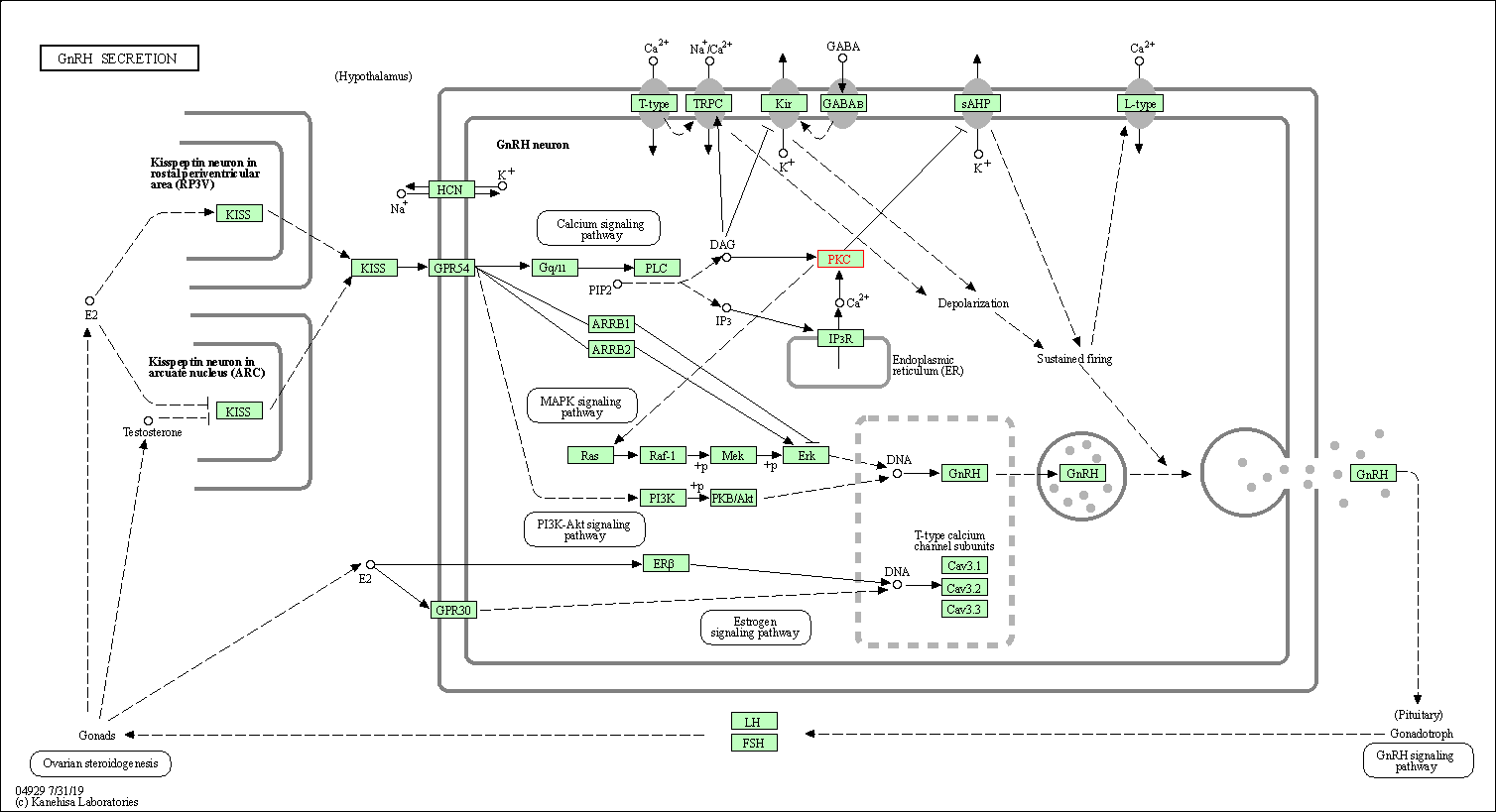
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | hsa04960 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption | hsa04961 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Salivary secretion | hsa04970 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Gastric acid secretion | hsa04971 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Pancreatic secretion | hsa04972 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 3 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 3.55E-09 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.78E-01 | Radiality | 1.29E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 6.67E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.83E+01 | Topological coefficient | 6.79E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | A comparison of physicochemical property profiles of marketed oral drugs and orally bioavailable anti-cancer protein kinase inhibitors in clinical development. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(14):1408-22. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2018 | |||||
| REF 3 | CBL exon 8/9 mutants activate the FLT3 pathway and cluster in core binding factor/11q deletion acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome subt... Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Apr 1;15(7):2238-47. | |||||
| REF 4 | Evaluation of differential hypoxic cytotoxicity and electrochemical studies of nitro 5-deazaflavins, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 5(18):2155-2160 (1995). | |||||
| REF 5 | Bisindolylmaleimide inhibitors of protein kinase C. Further conformational restriction of a tertiary amine side chain, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 4(11):1303-1308 (1994). | |||||
| REF 6 | (-)-Cercosporamide derivatives as novel antihyperglycemic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Feb 1;19(3):724-6. | |||||
| REF 7 | Multivariate analysis by the minimum spanning tree method of the structural determinants of diphenylethylenes and triphenylacrylonitriles implicate... J Med Chem. 1992 Feb 7;35(3):573-83. | |||||
| REF 8 | Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 3,4-diarylmaleimides as angiogenesis inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2006 Feb 23;49(4):1271-81. | |||||
| REF 9 | Design and synthesis of 8-octyl-benzolactam-V9, a selective activator for protein kinase C epsilon and eta. J Med Chem. 2006 May 4;49(9):2681-8. | |||||
| REF 10 | Protein kinase C epsilon regulates gamma-aminobutyrate type A receptor sensitivity to ethanol and benzodiazepines through phosphorylation of gamma2... J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 9;282(45):33052-63. | |||||
| REF 11 | Inhibition of protein kinase C mu by various inhibitors. Differentiation from protein kinase c isoenzymes. FEBS Lett. 1996 Aug 26;392(2):77-80. | |||||
| REF 12 | (S)-13-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-10,11,14,15-tetrahydro-4,9:16, 21-dimetheno-1H, 13H-dibenzo[e,k]pyrrolo[3,4-h][1,4,13]oxadiazacyclohexadecene-1,3(2H... J Med Chem. 1996 Jul 5;39(14):2664-71. | |||||
| REF 13 | Synthesis and characterization of the second cysteine-rich region of mouse skin PKCGh, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 6(4):353-356 (1996). | |||||
| REF 14 | A nonpromoting phorbol from the samoan medicinal plant Homalanthus nutans inhibits cell killing by HIV-1. J Med Chem. 1992 May 29;35(11):1978-86. | |||||
| REF 15 | Inhibitors of protein kinase C. 1. 2,3-Bisarylmaleimides. J Med Chem. 1992 Jan;35(1):177-84. | |||||
| REF 16 | Novel protein kinase C inhibitors: synthesis and PKC inhibition of beta-substituted polythiophene derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999 Aug 2;9(15):2279-82. | |||||
| REF 17 | Crystal Structure of C2 Domain of Protein Kinase C Gamma | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

