Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T50594
(Former ID: TTDNC00498)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase pim-1 (PIM1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Pim-1 proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase; PIM
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PIM1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Exerts its oncogenic activity through: the regulation of MYC transcriptional activity, the regulation of cell cycle progression and by phosphorylation and inhibition of proapoptotic proteins (BAD, MAP3K5, FOXO3). Phosphorylation of MYC leads to an increase of MYC protein stability and thereby an increase of transcriptional activity. The stabilization of MYC exerted by PIM1 might explain partly the strong synergism between these two oncogenes in tumorigenesis. Mediates survival signaling through phosphorylation of BAD, which induces release of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-X(L)/BCL2L1. Phosphorylation of MAP3K5, an other proapoptotic protein, by PIM1, significantly decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity and inhibits MAP3K5-mediated phosphorylation of JNK and JNK/p38MAPK subsequently reducing caspase-3 activation and cell apoptosis. Stimulates cell cycle progression at the G1-S and G2-M transitions by phosphorylation of CDC25A and CDC25C. Phosphorylation of CDKN1A, a regulator of cell cycle progression at G1, results in the relocation of CDKN1A to the cytoplasm and enhanced CDKN1A protein stability. Promote cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis by down-regulating expression of a regulator of cell cycle progression, CDKN1B, at both transcriptional and post-translational levels. Phosphorylation of CDKN1B,induces 14-3-3-proteins binding, nuclear export and proteasome-dependent degradation. May affect the structure or silencing of chromatin by phosphorylating HP1 gamma/CBX3. Acts also as a regulator of homing and migration of bone marrow cells involving functional interaction with the CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling axis. Proto-oncogene with serine/threonine kinase activity involved in cell survival and cell proliferation and thus providing a selective advantage in tumorigenesis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MLLSKINSLAHLRAAPCNDLHATKLAPGKEKEPLESQYQVGPLLGSGGFGSVYSGIRVSD
NLPVAIKHVEKDRISDWGELPNGTRVPMEVVLLKKVSSGFSGVIRLLDWFERPDSFVLIL ERPEPVQDLFDFITERGALQEELARSFFWQVLEAVRHCHNCGVLHRDIKDENILIDLNRG ELKLIDFGSGALLKDTVYTDFDGTRVYSPPEWIRYHRYHGRSAAVWSLGILLYDMVCGDI PFEHDEEIIRGQVFFRQRVSSECQHLIRWCLALRPSDRPTFEEIQNHPWMQDVLLPQETA EIHLHSLSPGPSK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T37BP1 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CXR-1002 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 6 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CXR-1002 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 2 | Benzothiazine derivative 1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 3 | leucettine L41 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 4 | NCGC00167772-01 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 5 | PMID21982499C14k | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 6 | PMID22136433C20 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine monophosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Kinase Pim1 in Complex with AMP | PDB:1YXU | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.24 Å | Mutation | No | [9] |
| PDB Sequence |
PLESQYQVGP
42 LLGSGGFGSV52 YSGIRVSDNL62 PVAIKHVEKD72 RISDWGELPN82 GTRVPMEVVL 92 LKKVSSGFSG102 VIRLLDWFER112 PDSFVLILER122 PEPVQDLFDF132 ITERGALQEE 142 LARSFFWQVL152 EAVRHCHNCG162 VLHRDIKDEN172 ILIDLNRGEL182 KLIDFGSGAL 192 LKDTVYTDFD202 GTRVYSPPEW212 IRYHRYHGRS222 AAVWSLGILL232 YDMVCGDIPF 242 EHDEEIIRGQ252 VFFRQRVSSE262 CQHLIRWCLA272 LRPSDRPTFE282 EIQNHPWMQD 292 VLLPQETAEI302 HLH
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Quercetin | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of Pim1 with Quercetin | PDB:2O3P | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.24 Å | Mutation | No | [10] |
| PDB Sequence |
PLESQYQVGP
42 LLGSGGFGSV52 YSGIRVSDNL62 PVAIKHVEKD72 RISDWGELPN82 GTRVPMEVVL 92 LKKVSSGFSG102 VIRLLDWFER112 PDSFVLILER122 PEPVQDLFDF132 ITERGALQEE 142 LARSFFWQVL152 EAVRHCHNCG162 VLHRDIKDEN172 ILIDLNRGEL182 KLIDFGSGAL 192 LKDTVYTDFD202 GTRVYSPPEW212 IRYHRYHGRS222 AAVWSLGILL232 YDMVCGDIPF 242 EHDEEIIRGQ252 VFFRQRVSSE262 CQHLIRWCLA272 LRPSDRPTFE282 EIQNHPWMQD 292 VLLPQETAEI302 HLHS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |
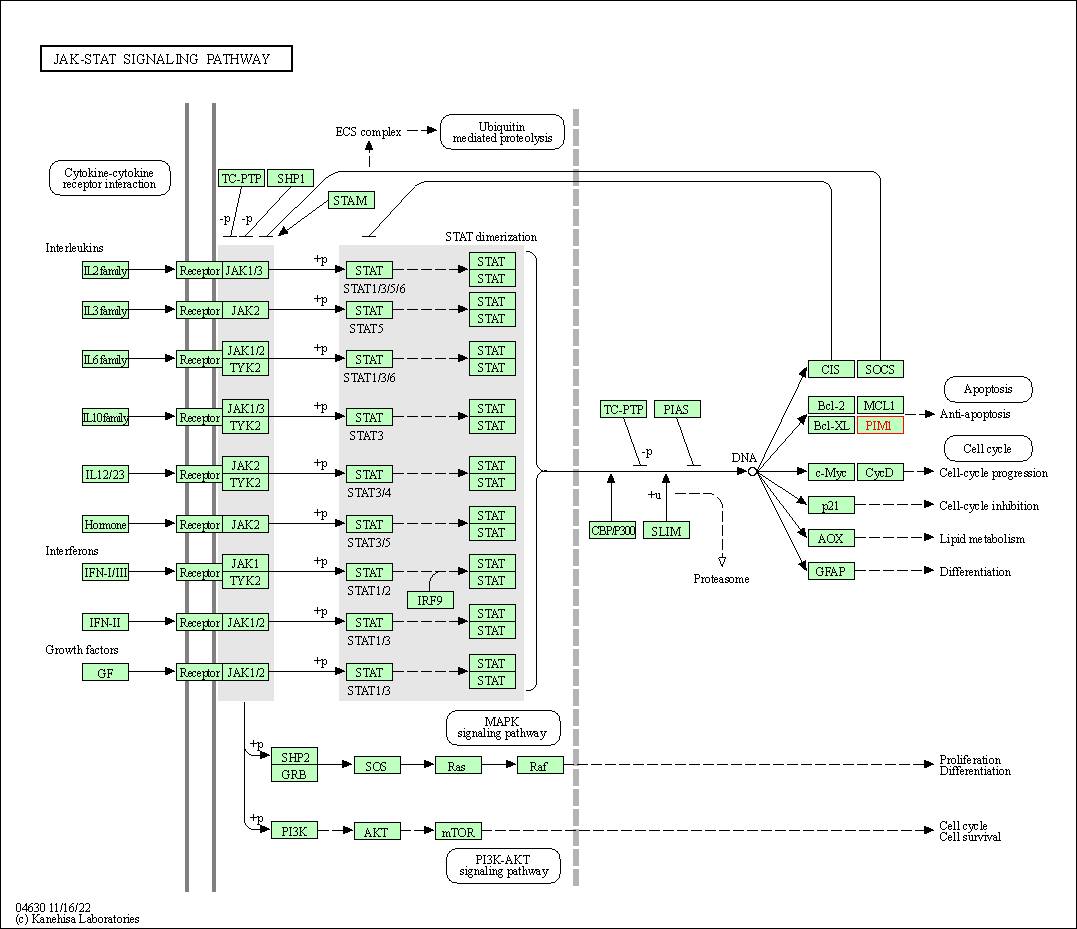
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 1 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 0.00E+00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.18E-01 | Radiality | 1.38E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.07E+02 | Topological coefficient | 1.00E+00 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 3 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | MicroRNAs in cancer | |||||
| 3 | Acute myeloid leukemia | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 5 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL9 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | IL5 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 3 | IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 4 | TGF_beta_Receptor Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 5 | TCR Signaling Pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 6 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | GMCSF-mediated signaling events | |||||
| 2 | Validated targets of C-MYC transcriptional activation | |||||
| 3 | Role of Calcineurin-dependent NFAT signaling in lymphocytes | |||||
| 4 | IL5-mediated signaling events | |||||
| 5 | IL3-mediated signaling events | |||||
| 6 | C-MYB transcription factor network | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 2 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Ectoderm Differentiation | |||||
| 2 | Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2158). | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800034732) | |||||
| REF 4 | 123 Antitumor activity of CXR1002, a novel anti-cancer clinical phase compound that induces ER stress and inhibits PIM kinases: Human tumor xenograft efficacy and in vitro mode of action. EJC Supplements, 2010; 8(7):45-46. | |||||
| REF 5 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy: a patent review (2009 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(9):953-70. | |||||
| REF 6 | Leucettines, a class of potent inhibitors of cdc2-like kinases and dual specificity, tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinases derived from the marine sponge leucettamine B: modulation of alternative pre-RNA splicing. J Med Chem. 2011 Jun 23;54(12):4172-86. | |||||
| REF 7 | 7-(4H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-yl)benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridines: a novel class of Pim kinase inhibitors with potent cell antiproliferative activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Nov 15;21(22):6687-92. | |||||
| REF 8 | 7,8-dichloro-1-oxo-beta-carbolines as a versatile scaffold for the development of potent and selective kinase inhibitors with unusual binding modes. J Med Chem. 2012 Jan 12;55(1):403-13. | |||||
| REF 9 | Crystal structures of proto-oncogene kinase Pim1: a target of aberrant somatic hypermutations in diffuse large cell lymphoma. J Mol Biol. 2005 Apr 22;348(1):183-93. | |||||
| REF 10 | Characterization of a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of the PIM1 kinase. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Jan;6(1):163-72. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

