Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T57943
(Former ID: TTDR00440)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Caspase-3 (CASP3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Yama protein; SREBP cleavage activity 1; SCA-1; Protein Yama; Cysteine protease CPP32; Caspase 3; CPP32; CPP-32; CASP-3; Apopain
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CASP3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||||
| Function |
At the onset of apoptosis it proteolytically cleaves poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) at a '216-Asp-|-Gly-217' bond. Cleaves and activates sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) between the basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper domain and the membrane attachment domain. Cleaves and activates caspase-6, -7 and -9. Involved in the cleavage of huntingtin. Triggers cell adhesion in sympathetic neurons through RET cleavage. Involved in the activation cascade of caspases responsible for apoptosis execution.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Peptidase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.4.22.56
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MENTENSVDSKSIKNLEPKIIHGSESMDSGISLDNSYKMDYPEMGLCIIINNKNFHKSTG
MTSRSGTDVDAANLRETFRNLKYEVRNKNDLTREEIVELMRDVSKEDHSKRSSFVCVLLS HGEEGIIFGTNGPVDLKKITNFFRGDRCRSLTGKPKLFIIQACRGTELDCGIETDSGVDD DMACHKIPVEADFLYAYSTAPGYYSWRNSKDGSWFIQSLCAMLKQYADKLEFMHILTRVN RKVATEFESFSFDATFHAKKQIPCIVSMLTKELYFYH Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A05213 ; BADD_A05311 ; BADD_A05519 ; BADD_A05675 ; BADD_A08298 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T85U8U | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PAC1 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Anaplastic astrocytoma | [2], [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Activator | [+] 2 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PAC1 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | PETCM | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 15 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | 2-(4-fluoro-benzyl)isoquinoline-1,3,4-trione | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 2 | 2-(4-methoxy-benzyl)isoquinoline-1,3,4-trione | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | 2-allylisoquinoline-1,3,4-trione | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 4 | 2-benzylisoquinoline-1,3,4-trione | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 5 | 2-methylisoquinoline-1,3,4-trione | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 6 | 2-phenethylisoquinoline-1,3,4-trione | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 7 | 5-(azepan-1-ylsulfonyl)indoline-2,3-dione | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 8 | 5-(azetidin-1-ylsulfonyl)indoline-2,3-dione | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 9 | 5-(piperidin-1-ylsulfonyl)indoline-2,3-dione | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 10 | 5-(pyrrolidin-1-ylsulfonyl)indoline-2,3-dione | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 11 | Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-CHO | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 12 | Ac-DEVD-CHO | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 13 | AZ10417808 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 14 | M826 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 15 | SJ-8002 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Cysteinesulfonic Acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structures of Caspase-3 with Bound Isoquinoline-1,3,4-trione Derivative Inhibitors | PDB:3DEK | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.40 Å | Mutation | No | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
DNSYKMDYPE
43 MGLCIIINNK53 NFHKSTGMTS63 RSGTDVDAAN73 LRETFRNLKY83 EVRNKNDLTR 93 EEIVELMRDV103 SKEDHSKRSS113 FVCVLLSHGE123 EGIIFGTNGP133 VDLKKITNFF 143 RGDRCRSLTG153 KPKLFIIQAR164 GTELDCGIET174 KIPVDADFLY195 AYSTAPGYYS 205 WRNSKDGSWF215 IQSLCAMLKQ225 YADKLEFMHI235 LTRVNRKVAT245 EFESFSFDAT 255 FHAKKQIPCI265 VSMLTKELYF275 YH
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: (10S)-3,3-dimethyl-8-{[(2S)-2-(phenoxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]sulfonyl}-2,3,4,10-tetrahydropyrimido[1,2-a]indol-10-ol | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | 3,4-Dihydropyrimido(1,2-a)indol-10(2H)-ones as Potent Non-Peptidic Inhibitors of Caspase-3 | PDB:3H0E | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.00 Å | Mutation | No | [13] |
| PDB Sequence |
DNSYKMDYPE
43 MGLCIIINNK53 NFHKSTGMTS63 RSGTDVDAAN73 LRETFRNLKY83 EVRNKNDLTR 93 EEIVELMRDV103 SKEDHSKRSS113 FVCVLLSHGE123 EGIIFGTNGP133 VDLKKITNFF 143 RGDRCRSLTG153 KPKLFIIQAC163 RGTELDCGIE173 DDMACHKIPV189 EADFLYAYST 199 APGYYSWRNS209 KDGSWFIQSL219 CAMLKQYADK229 LEFMHILTRV239 NRKVATEFES 249 FSFDATFHAK259 KQIPCIVSML269 TKELYFY
|
|||||
|
|
MET61
4.228
THR62
4.652
SER120
3.743
HIS121
3.153
GLY122
2.891
GLU123
3.488
PHE128
4.531
ALA162
3.963
CYS163
1.941
GLY165
4.720
THR166
3.537
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
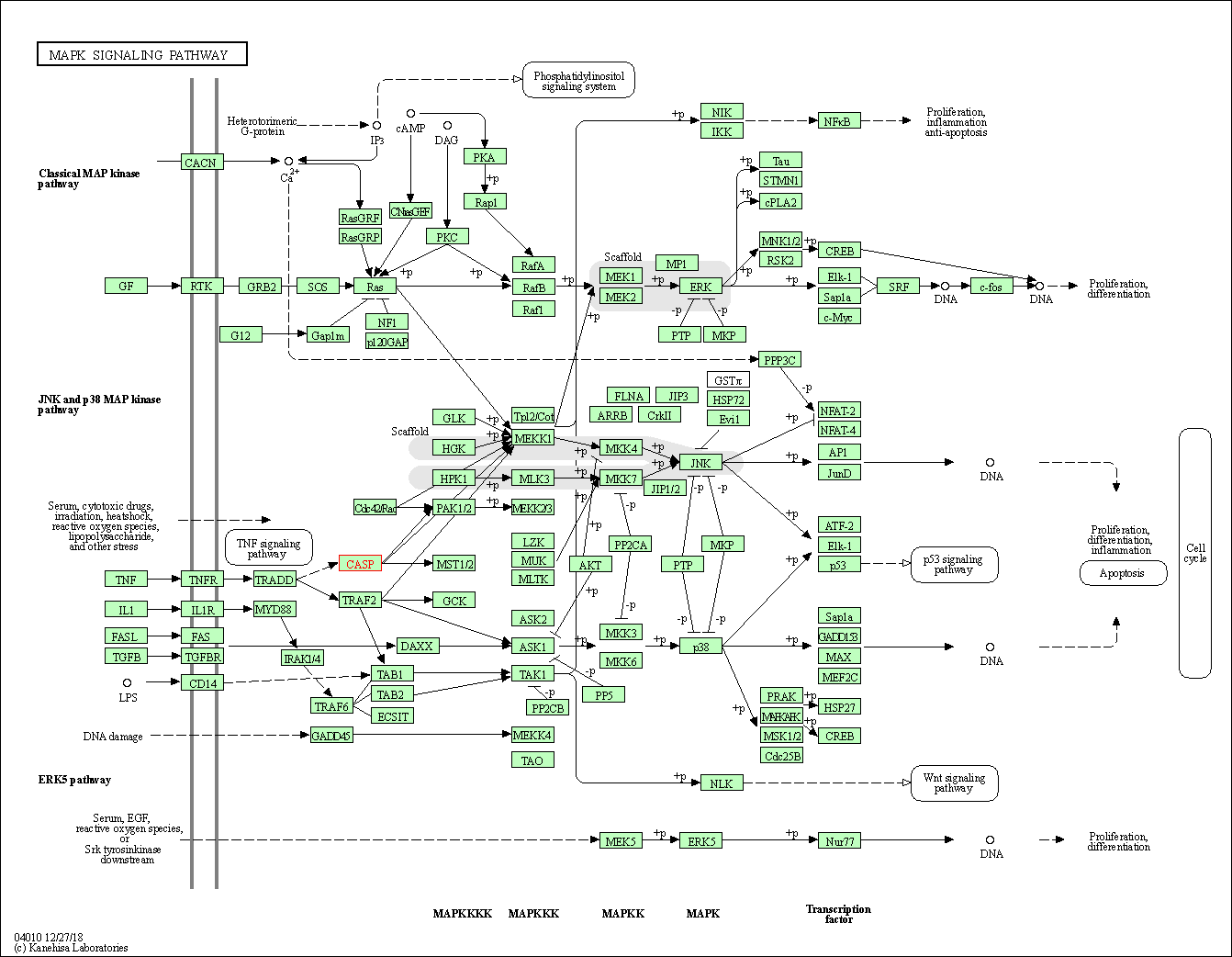
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | Affiliated Target |
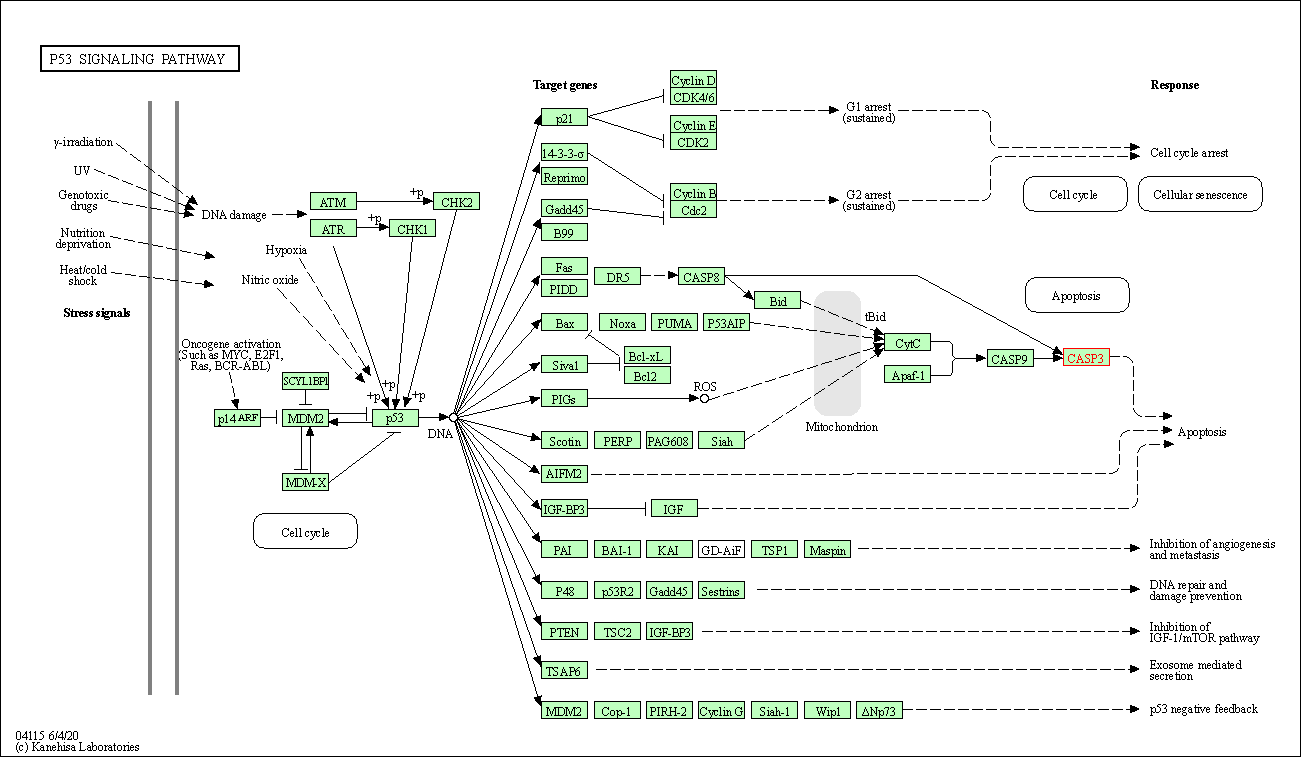
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |
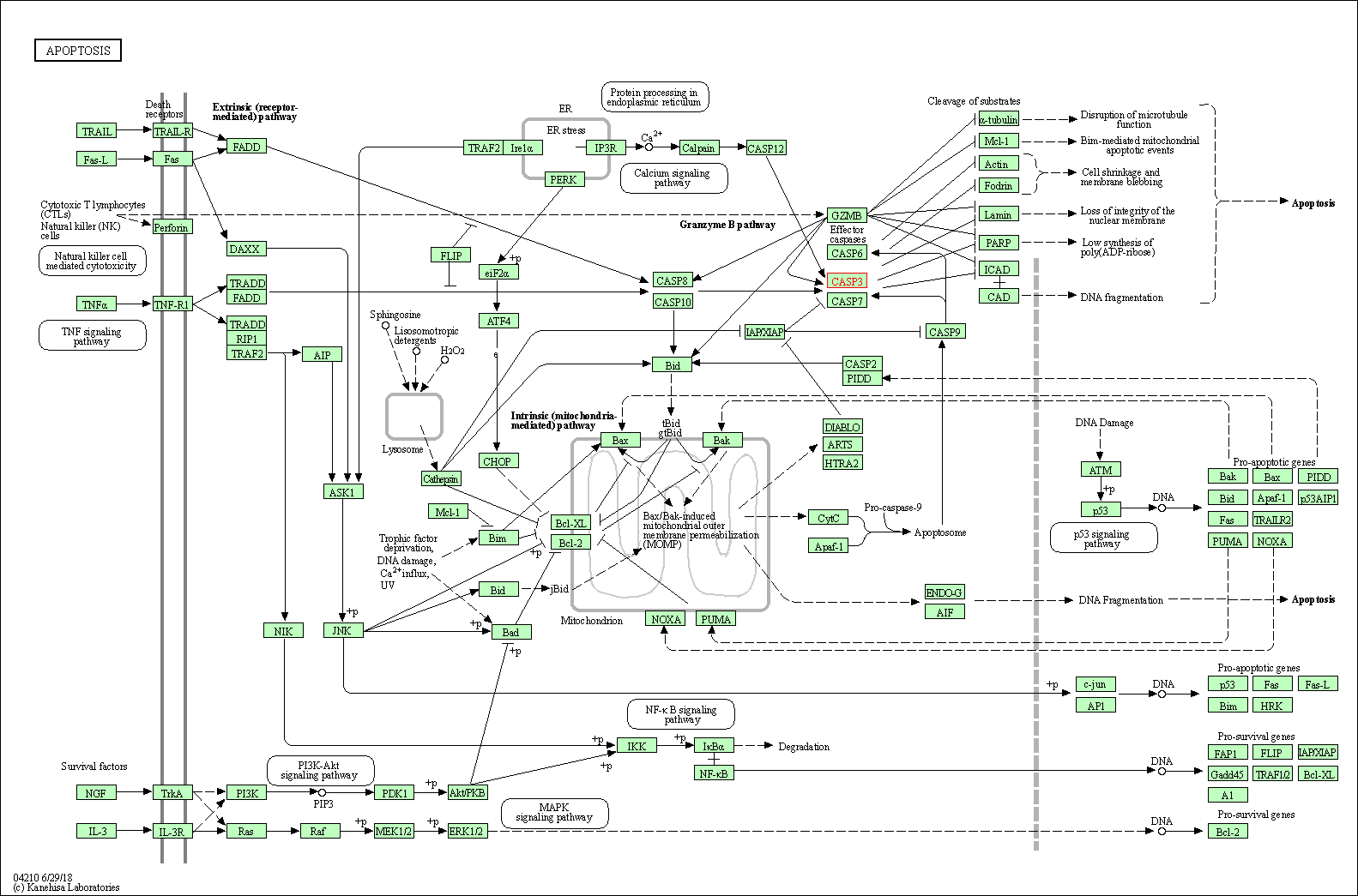
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis - multiple species | hsa04215 | Affiliated Target |
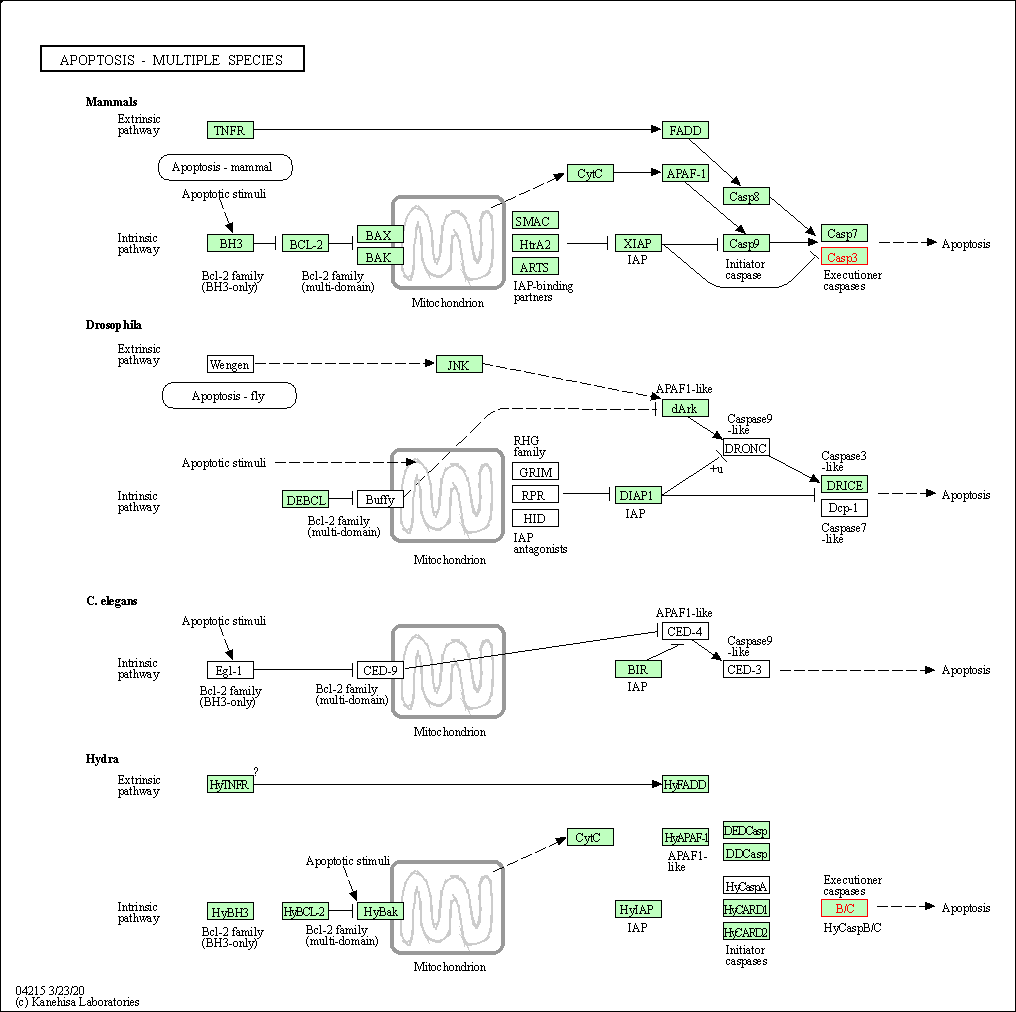
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | hsa04623 | Affiliated Target |
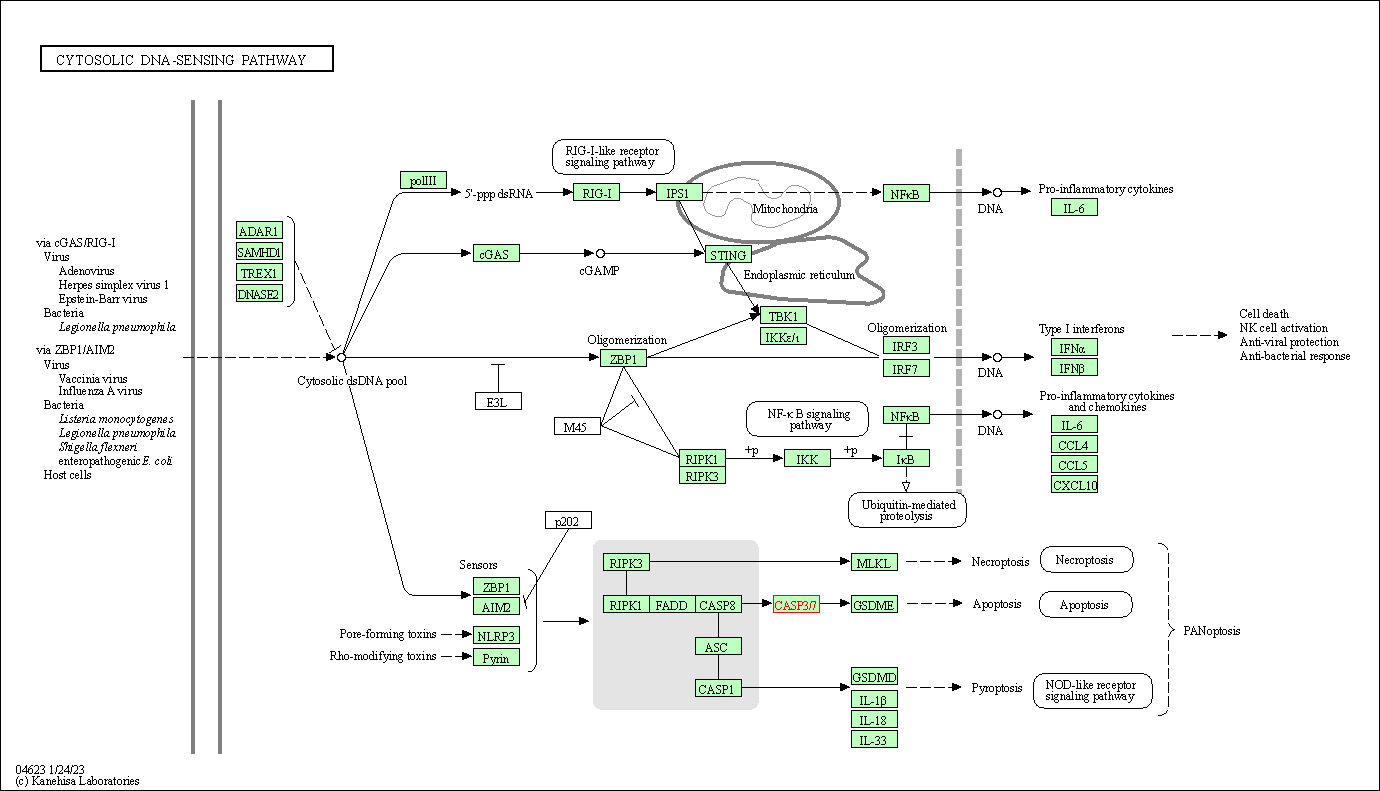
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |
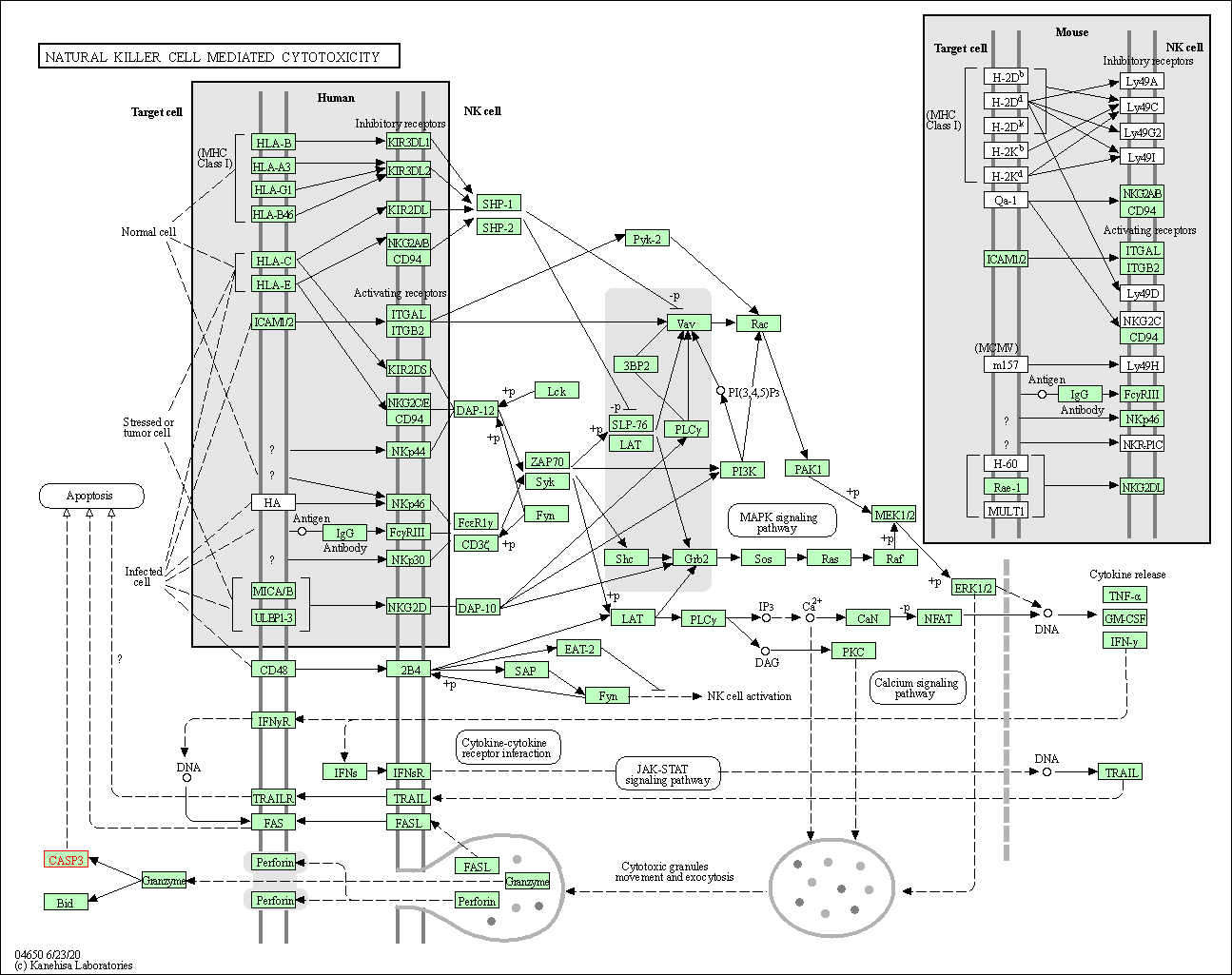
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |
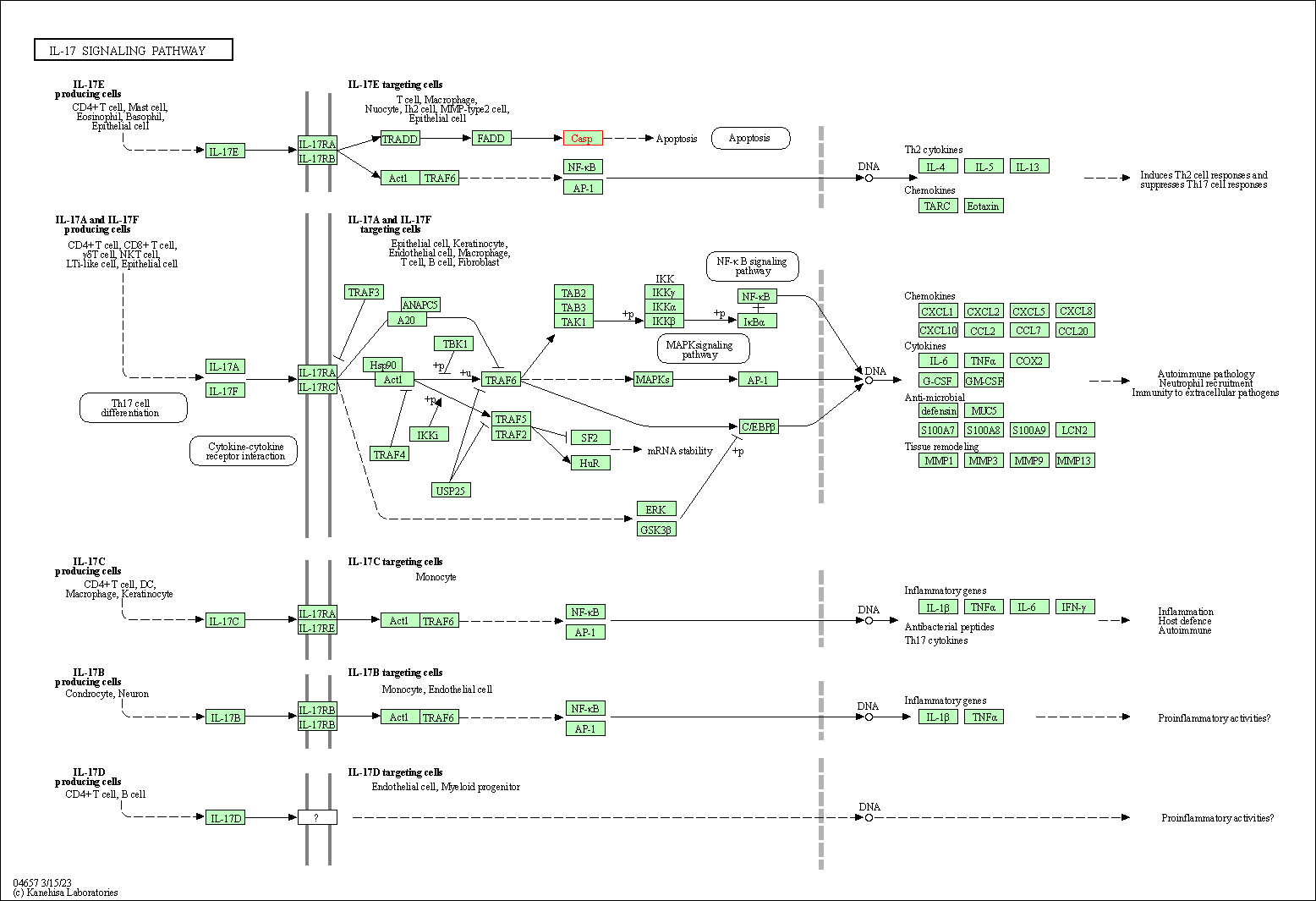
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |
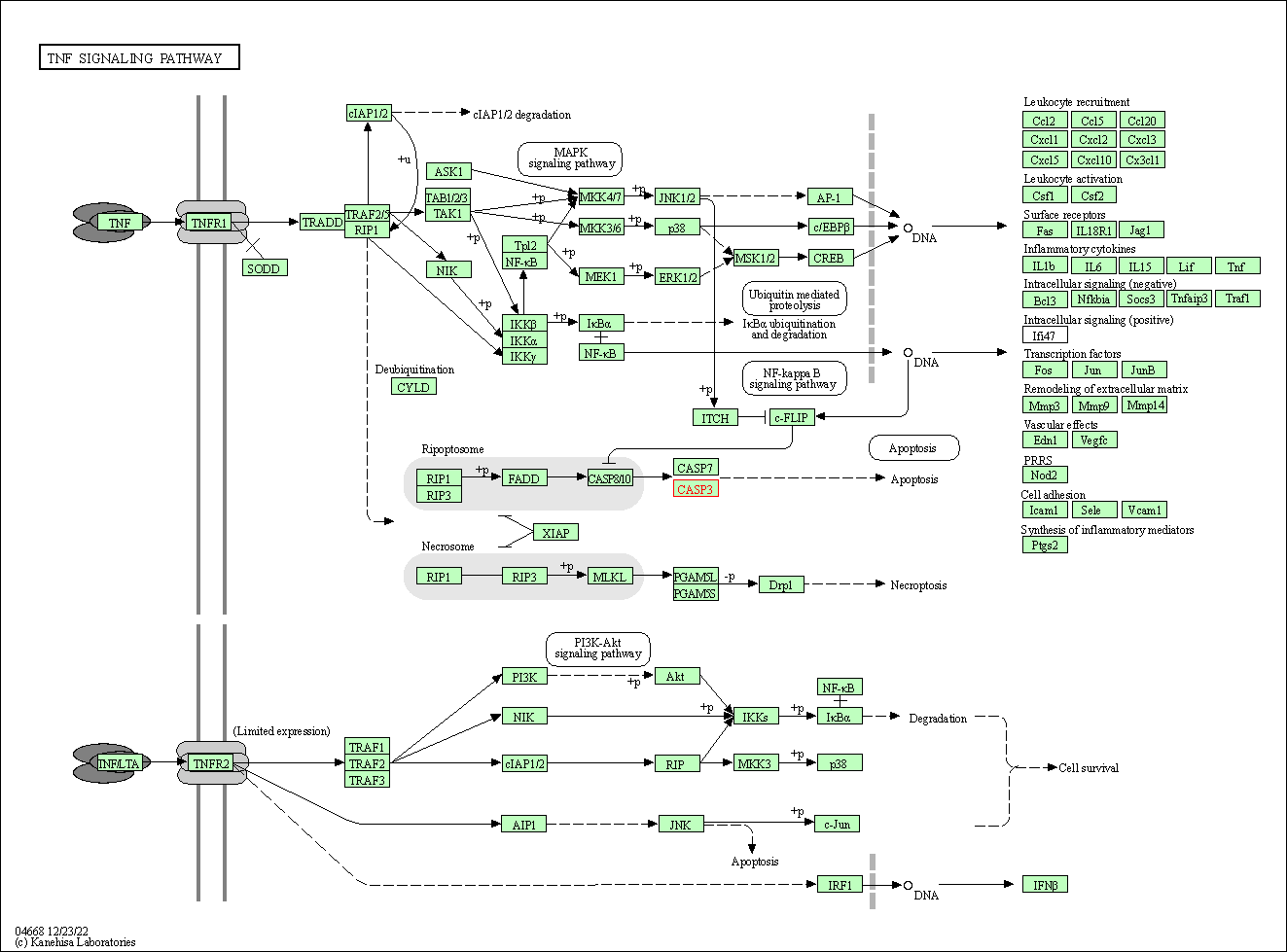
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 49 | Degree centrality | 5.26E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 4.58E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.60E-01 | Radiality | 1.45E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 8.16E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.30E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.89E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Small-molecule activation of procaspase-3 to caspase-3 as a personalized anticancer strategy. Nat Chem Biol. 2006 Oct;2(10):543-50. | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 4 | Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of isoquinoline-1,3,4-trione derivatives as potent caspase-3 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2006 Mar 9;49(5):1613-23. | |||||
| REF 5 | Design, synthesis, and discovery of novel non-peptide inhibitor of Caspase-3 using ligand based and structure based virtual screening approach. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Aug 15;17(16):6040-7. | |||||
| REF 6 | Design and synthesis of a potent and selective peptidomimetic inhibitor of caspase-3. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 16;47(26):6455-8. | |||||
| REF 7 | Synthesis and evaluation of vinyl sulfones as caspase-3 inhibitors. A structure-activity study. Eur J Med Chem. 2010 Sep;45(9):3858-63. | |||||
| REF 8 | Novel small molecule inhibitors of caspase-3 block cellular and biochemical features of apoptosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Jan;304(1):433-40. | |||||
| REF 9 | Novel pyrazinone mono-amides as potent and reversible caspase-3 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Feb 15;15(4):1173-80. | |||||
| REF 10 | Distinctive roles of PHAP proteins and prothymosin-alpha in a death regulatory pathway. Science. 2003 Jan 10;299(5604):223-6. | |||||
| REF 11 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1619). | |||||
| REF 12 | Isoquinoline-1,3,4-trione derivatives inactivate caspase-3 by generation of reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 31;283(44):30205-15. | |||||
| REF 13 | 3,4-Dihydropyrimido(1,2-a)indol-10(2H)-ones as potent non-peptidic inhibitors of caspase-3. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Nov 15;17(22):7755-68. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

