Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T61029
(Former ID: TTDI03596)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Long transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPM6)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 6; Melastatin-related TRP cation channel 6; Channel kinase 2; CHAK2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TRPM6
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Essential ion channel and serine/threonine-protein kinase. Crucial for magnesium homeostasis. Has an important role in epithelial magnesium transport and in the active magnesium absorption in the gut and kidney. Isoforms of the type M6-kinase lack the ion channel region.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Transient receptor potential catioin channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MKEQPVLERLQSQKSWIKGVFDKRECSTIIPSSKNPHRCTPVCQVCQNLIRCYCGRLIGD
HAGIDYSWTISAAKGKESEQWSVEKHTTKSPTDTFGTINFQDGEHTHHAKYIRTSYDTKL DHLLHLMLKEWKMELPKLVISVHGGIQNFTMPSKFKEIFSQGLVKAAETTGAWIITEGIN TGVSKHVGDALKSHSSHSLRKIWTVGIPPWGVIENQRDLIGKDVVCLYQTLDNPLSKLTT LNSMHSHFILSDDGTVGKYGNEMKLRRNLEKYLSLQKIHCRSRQGVPVVGLVVEGGPNVI LSVWETVKDKDPVVVCEGTGRAADLLAFTHKHLADEGMLRPQVKEEIICMIQNTFNFSLK QSKHLFQILMECMVHRDCITIFDADSEEQQDLDLAILTALLKGTNLSASEQLNLAMAWDR VDIAKKHILIYEQHWKPDALEQAMSDALVMDRVDFVKLLIEYGVNLHRFLTIPRLEELYN TKQGPTNTLLHHLVQDVKQHTLLSGYRITLIDIGLVVEYLIGRAYRSNYTRKHFRALYNN LYRKYKHQRHSSGNRNESAESTLHSQFIRTAQPYKFKEKSIVLHKSRKKSKEQNVSDDPE STGFLYPYNDLLVWAVLMKRQKMAMFFWQHGEEATVKAVIACILYRAMAHEAKESHMVDD ASEELKNYSKQFGQLALDLLEKAFKQNERMAMTLLTYELRNWSNSTCLKLAVSGGLRPFV SHTCTQMLLTDMWMGRLKMRKNSWLKIIISIILPPTILTLEFKSKAEMSHVPQSQDFQFM WYYSDQNASSSKESASVKEYDLERGHDEKLDENQHFGLESGHQHLPWTRKVYEFYSAPIV KFWFYTMAYLAFLMLFTYTVLVEMQPQPSVQEWLVSIYIFTNAIEVVREICISEPGKFTQ KVKVWISEYWNLTETVAIGLFSAGFVLRWGDPPFHTAGRLIYCIDIIFWFSRLLDFFAVN QHAGPYVTMIAKMTANMFYIVIIMAIVLLSFGVARKAILSPKEPPSWSLARDIVFEPYWM IYGEVYAGEIDVCSSQPSCPPGSFLTPFLQAVYLFVQYIIMVNLLIAFFNNVYLDMESIS NNLWKYNRYRYIMTYHEKPWLPPPLILLSHVGLLLRRLCCHRAPHDQEEGDVGLKLYLSK EDLKKLHDFEEQCVEKYFHEKMEDVNCSCEERIRVTSERVTEMYFQLKEMNEKVSFIKDS LLSLDSQVGHLQDLSALTVDTLKVLSAVDTLQEDEALLAKRKHSTCKKLPHSWSNVICAE VLGSMEIAGEKKYQYYSMPSSLLRSLAGGRHPPRVQRGALLEITNSKREATNVRNDQERQ ETQSSIVVSGVSPNRQAHSKYGQFLLVPSNLKRVPFSAETVLPLSRPSVPDVLATEQDIQ TEVLVHLTGQTPVVSDWASVDEPKEKHEPIAHLLDGQDKAEQVLPTLSCTPEPMTMSSPL SQAKIMQTGGGYVNWAFSEGDETGVFSIKKKWQTCLPSTCDSDSSRSEQHQKQAQDSSLS DNSTRSAQSSECSEVGPWLQPNTSFWINPLRRYRPFARSHSFRFHKEEKLMKICKIKNLS GSSEIGQGAWVKAKMLTKDRRLSKKKKNTQGLQVPIITVNACSQSDQLNPEPGENSISEE EYSKNWFTVSKFSHTGVEPYIHQKMKTKEIGQCAIQISDYLKQSQEDLSKNSLWNSRSTN LNRNSLLKSSIGVDKISASLKSPQEPHHHYSAIERNNLMRLSQTIPFTPVQLFAGEEITV YRLEESSPLNLDKSMSSWSQRGRAAMIQVLSREEMDGGLRKAMRVVSTWSEDDILKPGQV FIVKSFLPEVVRTWHKIFQESTVLHLCLREIQQQRAAQKLIYTFNQVKPQTIPYTPRFLE VFLIYCHSANQWLTIEKYMTGEFRKYNNNNGDEITPTNTLEELMLAFSHWTYEYTRGELL VLDLQGVGENLTDPSVIKPEVKQSRGMVFGPANLGEDAIRNFIAKHHCNSCCRKLKLPDL KRNDYSPERINSTFGLEIKIESAEEPPARETGRNSPEDDMQL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral absorption | hsa04978 | Affiliated Target |
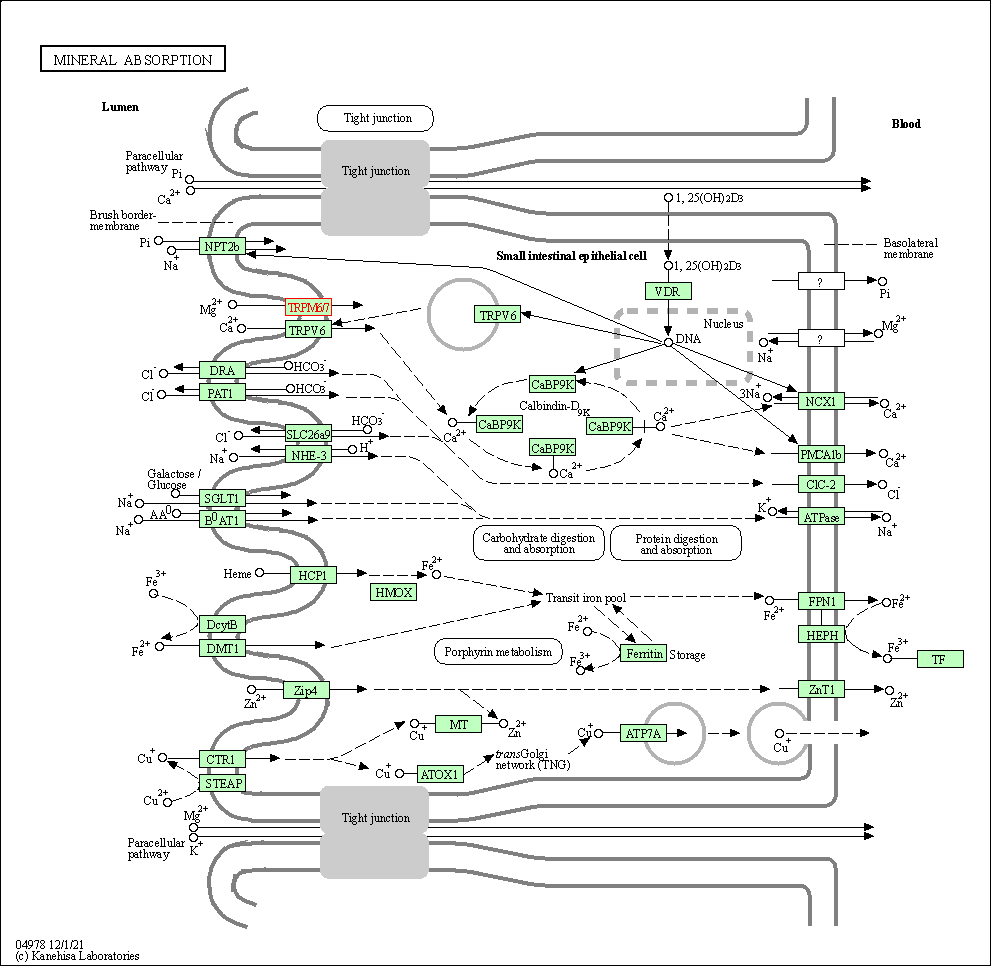
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Functional characterization of homo- and heteromeric channel kinases TRPM6 and TRPM7. J Gen Physiol. 2006 May;127(5):525-37. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

