Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T63083
(Former ID: TTDR00922)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 (RAD51)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
hRAD51; RECA; RAD51A; RAD51 homolog A; HsRAD51
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
RAD51
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A86] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Plays an important role in homologous strand exchange, a key step in DNA repair through homologous recombination (HR). Binds to single and double-stranded DNA and exhibits DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Catalyzes the recognition of homology and strand exchange between homologous DNA partners to form a joint molecule between a processed DNA break and the repair template. Binds to single-stranded DNA in an ATP-dependent manner to form nucleoprotein filaments which are essential for the homology search and strand exchange. Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing BRCA2 and RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. Plays a role in regulating mitochondrial DNA copy number under conditions of oxidative stress in the presence of RAD51C and XRCC3. Also involved in interstrand cross-link repair.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAMQMQLEANADTSVEEESFGPQPISRLEQCGINANDVKKLEEAGFHTVEAVAYAPKKEL
INIKGISEAKADKILAEAAKLVPMGFTTATEFHQRRSEIIQITTGSKELDKLLQGGIETG SITEMFGEFRTGKTQICHTLAVTCQLPIDRGGGEGKAMYIDTEGTFRPERLLAVAERYGL SGSDVLDNVAYARAFNTDHQTQLLYQASAMMVESRYALLIVDSATALYRTDYSGRGELSA RQMHLARFLRMLLRLADEFGVAVVITNQVVAQVDGAAMFAADPKKPIGGNIIAHASTTRL YLRKGRGETRICKIYDSPCLPEAEAMFAINADGVGDAKD Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T82S9G | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of a human RAD51-ATP filament. | PDB:5NWL | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.93 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
GPQPISRLEQ
30 CGINANDVKK40 LEEAGFHTVE50 AVAYAPKKEL60 INIKGISEAK70 ADKILAEAAK 80 LVPMGFTTAT90 EFHQRRSEII100 QITTGSKELD110 KLLQGGIETG120 SITEMFGEFR 130 TGKTQICHTL140 AVTCQLPIDR150 GGGEGKAMYI160 DTEGTFRPER170 LLAVAERYGL 180 SGSDVLDNVA190 YARAFNTDHQ200 TQLLYQASAM210 MVESRYALLI220 VDSATALYRT 230 DYSGRGELSA240 RQMHLARFLR250 MLLRLADEFG260 VAVVITNQVV270 GNIIAHASTT 298 RLYLRKGRGE308 TRICKIYDSP318 CLPEAEAMFA328 INADGVGDAK338 D |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: AMP-PNP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human RAD51 post-synaptic complexes mutant (V273P, D274G) | PDB:7C9A | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.43 Å | Mutation | Yes | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
PQPISRLEQC
31 GINANDVKKL41 EEAGFHTVEA51 VAYAPKKELI61 NIKGISEAKA71 DKILAEAAKL 81 VPMGFTTATE91 FHQRRSEIIQ101 ITTGSKELDK111 LLQGGIETGS121 ITEMFGEFRT 131 GKTQICHTLA141 VTCQLPIDRG151 GGEGKAMYID161 TEGTFRPERL171 LAVAERYGLS 181 GSDVLDNVAY191 ARAFNTDHQT201 QLLYQASAMM211 VESRYALLIV221 DSATALYRTD 231 YSGRGELSAR241 QMHLARFLRM251 LLRLADEFGV261 AVVITNQVVA271 QPGGAADPKK 285 PIGGNIIAHA295 STTRLYLRKG305 RGETRICKIY315 DSPCLPEAEA325 MFAINADGVG 335 D
|
|||||
|
|
PHE129
2.838
ARG130
3.650
THR131
3.353
GLY132
3.171
LYS133
2.645
THR134
2.675
GLN135
3.811
GLU163
3.897
ARG170
3.320
ALA293
3.782
HIS294
3.405
SER296
4.088
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homologous recombination | hsa03440 | Affiliated Target |
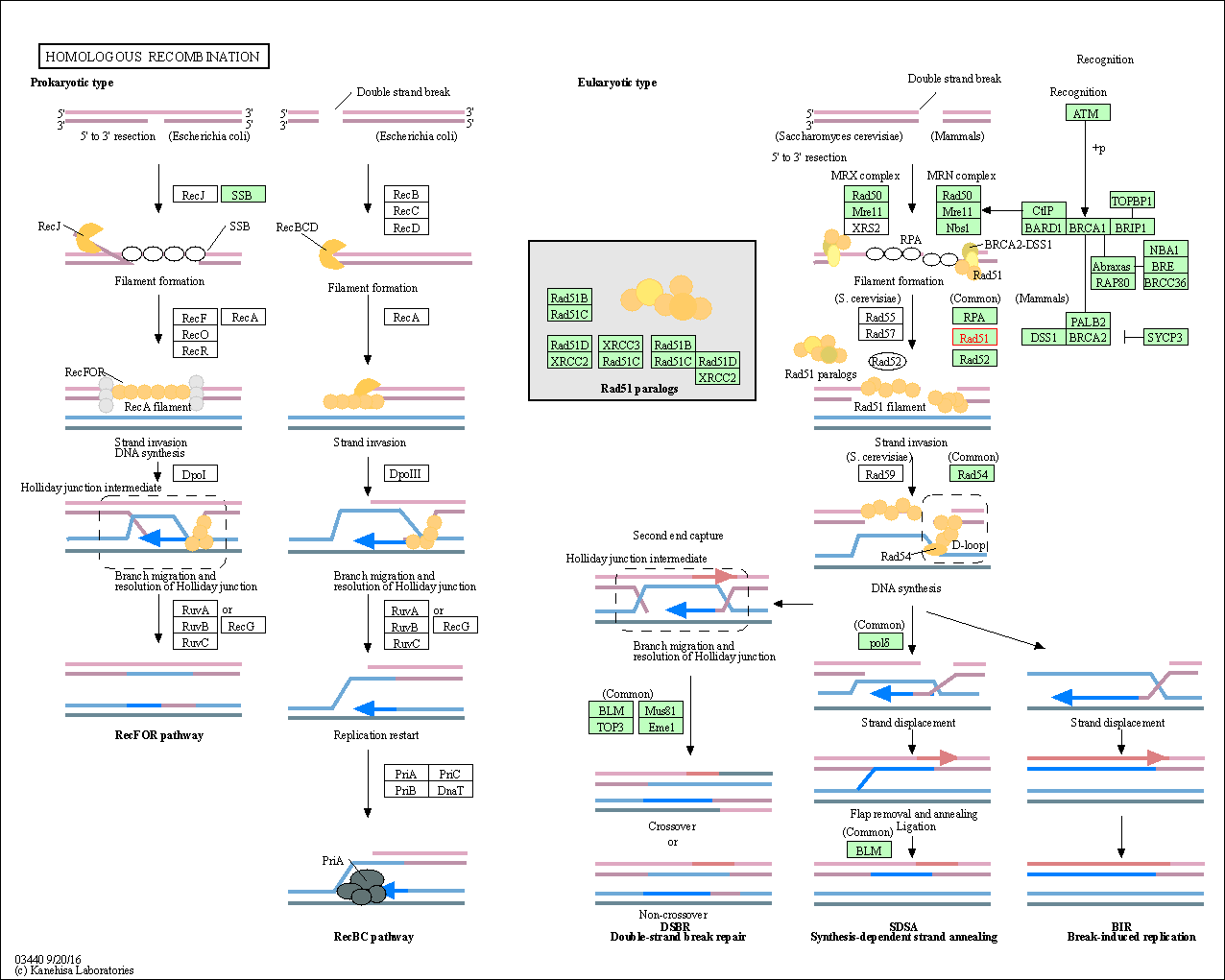
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Replication and repair | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fanconi anemia pathway | hsa03460 | Affiliated Target |
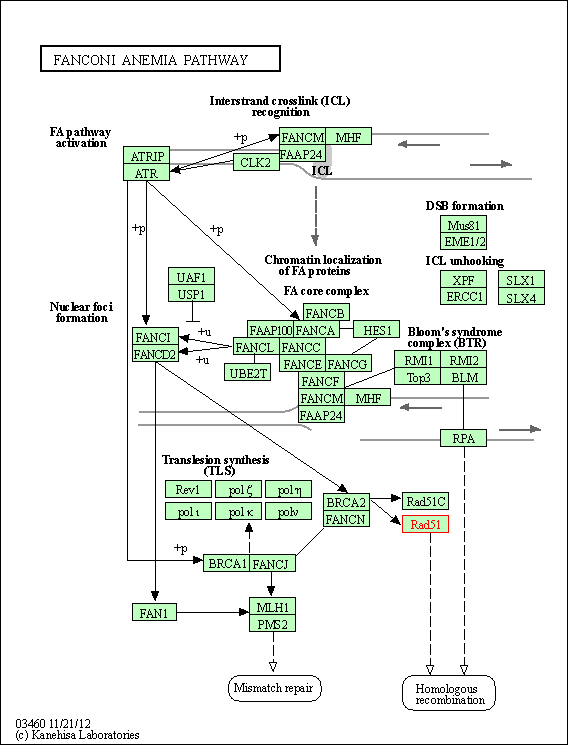
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Replication and repair | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Homologous recombination | |||||
| 2 | Fanconi anemia pathway | |||||
| 3 | Pathways in cancer | |||||
| 4 | Pancreatic cancer | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 3 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | p73 transcription factor network | |||||
| 2 | ATR signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | BARD1 signaling events | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 4 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) | |||||
| 2 | HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) | |||||
| 3 | Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange | |||||
| 4 | Meiotic recombination | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 8 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | DNA Damage Response | |||||
| 2 | Meiotic Recombination | |||||
| 3 | ATM Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 4 | Integrated Pancreatic Cancer Pathway | |||||
| 5 | Integrated Breast Cancer Pathway | |||||
| 6 | Homologous recombination | |||||
| 7 | Double-Strand Break Repair | |||||
| 8 | miRNA Regulation of DNA Damage Response | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03997968) A Phase 1/2 Study of CYT-0851, an Oral RAD51 Inhibitor, in B-Cell Malignancies and Advanced Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Two distinct conformational states define the interaction of human RAD51-ATP with single-stranded DNA. EMBO J. 2018 Apr 3;37(7):e98162. | |||||
| REF 4 | Identification of fidelity-governing factors in human recombinases DMC1 and RAD51 from cryo-EM structures. Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 14;12(1):115. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

