Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T72168
(Former ID: TTDS00206)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Mineralocorticoid receptor (MR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 2; Mineralocorticoid receptor; MLR; MCR; Inner ear mineralocorticoid receptor; Delta
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
NR3C2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 6 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Adrenocortical insufficiency [ICD-11: 5A74] | |||||
| 2 | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61] | |||||
| 3 | Contraceptive management [ICD-11: QA21] | |||||
| 4 | Heart failure [ICD-11: BD10-BD1Z] | |||||
| 5 | Hypertension [ICD-11: BA00-BA04] | |||||
| 6 | Hypo-osmolality/hyponatraemia [ICD-11: 5C72] | |||||
| Function |
Binds to mineralocorticoid response elements (MRE) and transactivates target genes. The effect of MC is to increase ion and water transport and thus raise extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure and lower potassium levels. Receptor for both mineralocorticoids (MC) such as aldosterone and glucocorticoids (GC) such as corticosterone or cortisol.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Nuclear hormone receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
METKGYHSLPEGLDMERRWGQVSQAVERSSLGPTERTDENNYMEIVNVSCVSGAIPNNST
QGSSKEKQELLPCLQQDNNRPGILTSDIKTELESKELSATVAESMGLYMDSVRDADYSYE QQNQQGSMSPAKIYQNVEQLVKFYKGNGHRPSTLSCVNTPLRSFMSDSGSSVNGGVMRAV VKSPIMCHEKSPSVCSPLNMTSSVCSPAGINSVSSTTASFGSFPVHSPITQGTPLTCSPN VENRGSRSHSPAHASNVGSPLSSPLSSMKSSISSPPSHCSVKSPVSSPNNVTLRSSVSSP ANINNSRCSVSSPSNTNNRSTLSSPAASTVGSICSPVNNAFSYTASGTSAGSSTLRDVVP SPDTQEKGAQEVPFPKTEEVESAISNGVTGQLNIVQYIKPEPDGAFSSSCLGGNSKINSD SSFSVPIKQESTKHSCSGTSFKGNPTVNPFPFMDGSYFSFMDDKDYYSLSGILGPPVPGF DGNCEGSGFPVGIKQEPDDGSYYPEASIPSSAIVGVNSGGQSFHYRIGAQGTISLSRSAR DQSFQHLSSFPPVNTLVESWKSHGDLSSRRSDGYPVLEYIPENVSSSTLRSVSTGSSRPS KICLVCGDEASGCHYGVVTCGSCKVFFKRAVEGQHNYLCAGRNDCIIDKIRRKNCPACRL QKCLQAGMNLGARKSKKLGKLKGIHEEQPQQQQPPPPPPPPQSPEEGTTYIAPAKEPSVN TALVPQLSTISRALTPSPVMVLENIEPEIVYAGYDSSKPDTAENLLSTLNRLAGKQMIQV VKWAKVLPGFKNLPLEDQITLIQYSWMCLSSFALSWRSYKHTNSQFLYFAPDLVFNEEKM HQSAMYELCQGMHQISLQFVRLQLTFEEYTIMKVLLLLSTIPKDGLKSQAAFEEMRTNYI KELRKMVTKCPNNSGQSWQRFYQLTKLLDSMHDLVSDLLEFCFYTFRESHALKVEFPAML VEIISDQLPKVESGNAKPLYFHRK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T64F54 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 6 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Aldosterone | Drug Info | Approved | Hypertension | [5], [6] | |
| 2 | Desoxycorticosterone Acetate | Drug Info | Approved | Discovery agent | [7] | |
| 3 | Eplerenone | Drug Info | Approved | Heart failure | [4], [8] | |
| 4 | Finerenone | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic kidney disease | [9] | |
| 5 | Fludrocortisone | Drug Info | Approved | Cerebral salt-wasting syndrome | [10], [11] | |
| 6 | Spironolactone | Drug Info | Approved | Congestive heart failure | [12], [13] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 7 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BR-4628 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Heart failure | [15] | |
| 2 | LY-2623091 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic kidney disease | [16] | |
| 3 | MT-3995 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic nephropathy | [17] | |
| 4 | Nerenone | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic nephropathy | [18] | |
| 5 | ZK-91587 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Cardiovascular disease | [19] | |
| 6 | KBP-5074 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Hypertension | [20] | |
| 7 | XL550 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-2 diabetes | [21] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PF-03882845 | Drug Info | Terminated | Diabetic nephropathy | [23] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 4 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Agonist | [+] 3 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Aldosterone | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 2 | Fludrocortisone | Drug Info | [1], [27] | |||
| 3 | deoxycorticosterone | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 4 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Desoxycorticosterone Acetate | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 2 | Eplerenone | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 3 | Spironolactone | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 4 | PF-03882845 | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 14 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Finerenone | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 2 | BR-4628 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 3 | LY-2623091 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 4 | MT-3995 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 5 | Nerenone | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 6 | ZK-91587 | Drug Info | [7], [19] | |||
| 7 | KBP-5074 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 8 | XL550 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 9 | PMID27551786-Compound-106 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 10 | PMID27551786-Compound-138 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 11 | PMID27551786-Compound-II | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 12 | PMID27551786-Compound-III | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 13 | PMID27551786-Compound-IV | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 14 | RU28318 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 7 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | (11-BETA)-11,21-DIHYDROXY-PREGN-4-ENE-3,20-DIONE | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 2 | AL-43 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 3 | B-Octylglucoside | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 4 | CB-1922 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 5 | LG-120838 | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 6 | LGD-5552 | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 7 | WAY-255348 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Eplerenone | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | The structure of MR in complex with eplerenone. | PDB:5MWY | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.75 Å | Mutation | No | [39] |
| PDB Sequence |
YFSPVMVLEN
744 IEPEIVYAGY754 DSSKPDTAEN764 LLSTLNRLAG774 KQMIQVVKWA784 KVLPGFKNLP 794 LEDQITLIQY804 SWMSLSSFAL814 SWRSYKHTNS824 QFLYFAPDLV834 FNEEKMHQSA 844 MYELCQGMHQ854 ISLQFVRLQL864 TFEEYTIMKV874 LLLLSTIPKD884 GLKSQAAFEE 894 MRTNYIKELR904 KMVTGQSWQR920 FYQLTKLLDS930 MHDLVSDLLE940 FCFYTFRESH 950 ALKVEFPAML960 VEIISDQLPK970 VESGNAKPLY980 FHRK
|
|||||
|
|
LEU766
3.706
LEU769
3.550
ASN770
3.492
LEU772
4.108
ALA773
3.665
GLN776
3.127
TRP806
3.746
MET807
3.543
SER810
3.617
SER811
4.222
LEU814
3.474
ARG817
2.735
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Prednisone | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Mineralocorticoid Receptor Double Mutant with Bound Cortisone | PDB:2AAX | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.75 Å | Mutation | Yes | [40] |
| PDB Sequence |
ALVPQLSTIS
731 RALTPSPVMV741 LENIEPEIVY751 AGYDSSKPDT761 AENLLSTLNR771 LAGKQMIQVV 781 KWAKVLPGFK791 NLPLEDQITL801 IQYSWMSLLS811 FALSWRSYKH821 TNSQFLYFAP 831 DLVFNEEKMH841 QSAMYELCQG851 MHQISLQFVR861 LQLTFEEYTI871 MKVLLLLSTI 881 PKDGLKSQAA891 FEEMRTNYIK901 ELRKMVTKCN912 NSGQSWQRFY922 QLTKLLDSMH 932 DLVSDLLEFC942 FYTFRESHAL952 KVEFPAMLVE962 IISDQLPKVE972 SGNAKPLYFH 982 R
|
|||||
|
|
LEU766
3.477
LEU769
2.872
ASN770
3.147
LEU772
3.793
ALA773
3.436
GLN776
3.263
TRP806
4.301
MET807
3.948
LEU810
3.704
SER811
4.204
LEU814
3.910
ARG817
2.707
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | hsa04960 | Affiliated Target |
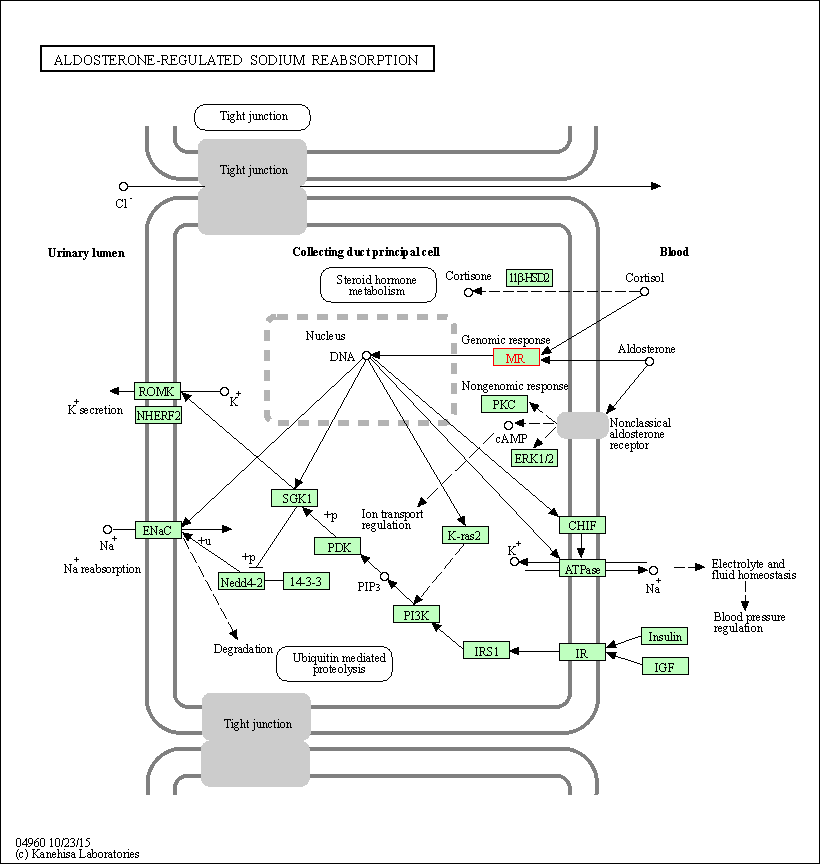
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 1 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Kidney Function | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 1 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ACE Inhibitor Pathway | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Mineralocorticoid receptor-mediated inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in aged humans. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003 Oct;58(10):B900-5. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drug information of Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2874). | |||||
| REF 4 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 5 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2872). | |||||
| REF 6 | Treatment of hypertension with olmesartan medoxomil, alone and in combination with a diuretic: an update. J Hum Hypertens. 2007 Sep;21(9):699-708. | |||||
| REF 7 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 8 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2876). | |||||
| REF 9 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2022. Application Number: 215341. | |||||
| REF 10 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2873). | |||||
| REF 11 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 010060. | |||||
| REF 12 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2875). | |||||
| REF 13 | Emerging drugs for complications of end-stage liver disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Mar;13(1):159-74. | |||||
| REF 14 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04595370) A Phase 2b, Randomised, Double-Blind, Active Controlled, Multi Centre Study to Evaluate the Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability of Oral AZD9977 and Dapagliflozin Treatment in Patients With Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 15 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800027127) | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02194465) A Study of LY2623091 in Participants With High Blood Pressure. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 17 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01756703) A Study to Evaluate Pharmacodynamics, Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of MT-3995 in Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Subjects With Albuminuria. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 18 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 19 | ZK91587: a novel synthetic antimineralocorticoid displays high affinity for corticosterone (type I) receptors in the rat hippocampus. Life Sci. 1988;43(19):1537-43. | |||||
| REF 20 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 21 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Exelixis (2011). | |||||
| REF 22 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2023. Adis Insight | |||||
| REF 23 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Pfizer (2011). | |||||
| REF 24 | Stimulation of testosterone production in rat Leydig cells by aldosterone is mineralocorticoid receptor mediated. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005 Nov 24;243(1-2):35-42. | |||||
| REF 25 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||||
| REF 26 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 27 | Addison's disease. BMJ. 2009 Jul 2;339:b2385. | |||||
| REF 28 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 626). | |||||
| REF 29 | Nonsteroidal antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015 Sep;24(5):417-24. | |||||
| REF 30 | Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: a patent evaluation of US20150284376A1.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016 Sep 14:1-4. | |||||
| REF 31 | Discovery of (3S,3aR)-2-(3-chloro-4-cyanophenyl)-3-cyclopentyl-3,3a,4,5-tetrahydro-2H-benzo[g] indazole-7-carboxylic acid (PF-3882845), an orally efficacious mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist for hypertension and nephropathy.J Med Chem.2010 Aug 26;53(16):5979-6002. | |||||
| REF 32 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 33 | Nonsteroidal selective glucocorticoid modulators: the effect of C-10 substitution on receptor selectivity and functional potency of 5-allyl-2,5-dih... J Med Chem. 2003 Mar 13;46(6):1016-30. | |||||
| REF 34 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 35 | Pharmacological and functional characterization of human mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor ligands. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct 15;247(2):145-54. | |||||
| REF 36 | 5-Benzylidene 1,2-dihydrochromeno[3,4-f]quinolines, a novel class of nonsteroidal human progesterone receptor agonists. J Med Chem. 1998 Oct 22;41(22):4354-9. | |||||
| REF 37 | Antiinflammatory glucocorticoid receptor ligand with reduced side effects exhibits an altered protein-protein interaction profile. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 4;104(49):19244-9. | |||||
| REF 38 | Design, synthesis, and SAR of new pyrrole-oxindole progesterone receptor modulators leading to 5-(7-fluoro-3,3-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-... J Med Chem. 2008 Mar 27;51(6):1861-73. | |||||
| REF 39 | Preclinical pharmacology of AZD9977: A novel mineralocorticoid receptor modulator separating organ protection from effects on electrolyte excretion. PLoS One. 2018 Feb 23;13(2):e0193380. | |||||
| REF 40 | A ligand-mediated hydrogen bond network required for the activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 2;280(35):31283-93. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

