Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T75797
(Former ID: TTDS00169)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Prostaglandin F2-alpha receptor (PTGFR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Prostanoid FP receptor; PGF2-alpha receptor; PGF2 alpha receptor; PGF receptor; FP prostanoid receptor; FP prostaglandin receptor
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PTGFR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Abortion [ICD-11: JA00] | |||||
| 2 | Glaucoma [ICD-11: 9C61] | |||||
| 3 | Coronary atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BA80] | |||||
| Function |
The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Initiates luteolysis in the corpus luteum. Isoforms 2 to 7 do not bind PGF2-alpha but are proposed to modulate signaling by participating in variant receptor complexes; heterodimers between isoform 1 and isoform 5 are proposed to be a receptor for prostamides including the synthetic analog bimatoprost. Receptor for prostaglandin F2-alpha (PGF2-alpha).
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
GPCR rhodopsin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MSMNNSKQLVSPAAALLSNTTCQTENRLSVFFSVIFMTVGILSNSLAIAILMKAYQRFRQ
KSKASFLLLASGLVITDFFGHLINGAIAVFVYASDKEWIRFDQSNVLCSIFGICMVFSGL CPLLLGSVMAIERCIGVTKPIFHSTKITSKHVKMMLSGVCLFAVFIALLPILGHRDYKIQ ASRTWCFYNTEDIKDWEDRFYLLLFSFLGLLALGVSLLCNAITGITLLRVKFKSQQHRQG RSHHLEMVIQLLAIMCVSCICWSPFLVTMANIGINGNHSLETCETTLFALRMATWNQILD PWVYILLRKAVLKNLYKLASQCCGVHVISLHIWELSSIKNSLKVAAISESPVAEKSAST Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T35YGY | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 6 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BOL-303259-X | Drug Info | Approved | Open-angle glaucoma | [2] | |
| 2 | Carboprost Tromethamine | Drug Info | Approved | Abortion | [3] | |
| 3 | Dinoprostone | Drug Info | Approved | Medical abortion | [4], [5] | |
| 4 | Latanoprost | Drug Info | Approved | Open-angle glaucoma | [6], [7] | |
| 5 | Tafluprost | Drug Info | Approved | Glaucoma/ocular hypertension | [8], [9], [10], [11] | |
| 6 | Travoprost | Drug Info | Approved | Open-angle glaucoma | [12], [7] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 4 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PGF2ALPHA-IE | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Glaucoma/ocular hypertension | [14] | |
| 2 | PDC-41 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Dysmenorrhea | [16] | |
| 3 | bimatoprost (free acid form) | Drug Info | Clinical trial | Alzheimer disease | [17] | |
| 4 | PGF2alpha | Drug Info | Clinical trial | Solid tumour/cancer | [18] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Agonist | [+] 14 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BOL-303259-X | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 2 | Latanoprost | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 3 | Travoprost | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 4 | bimatoprost (free acid form) | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 5 | PGF2alpha | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 6 | 13,14-dihydro-16-m-chlorophenoxy-w-tetranor-PGF1alpha | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 7 | AL-8810 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 8 | AL12180 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 9 | cloprostenol | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 10 | fluprostenol | Drug Info | [32], [33] | |||
| 11 | M&B 28767 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 12 | PGD2 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 13 | U46619 | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 14 | [3H]PGF2alpha | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 4 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Carboprost Tromethamine | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 2 | Tafluprost | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 3 | PGF2ALPHA-IE | Drug Info | [11], [23] | |||
| 4 | NCX-125 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 4 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Dinoprostone | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 2 | PDC-41 | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 3 | AS604872 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 4 | PDC-31 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |
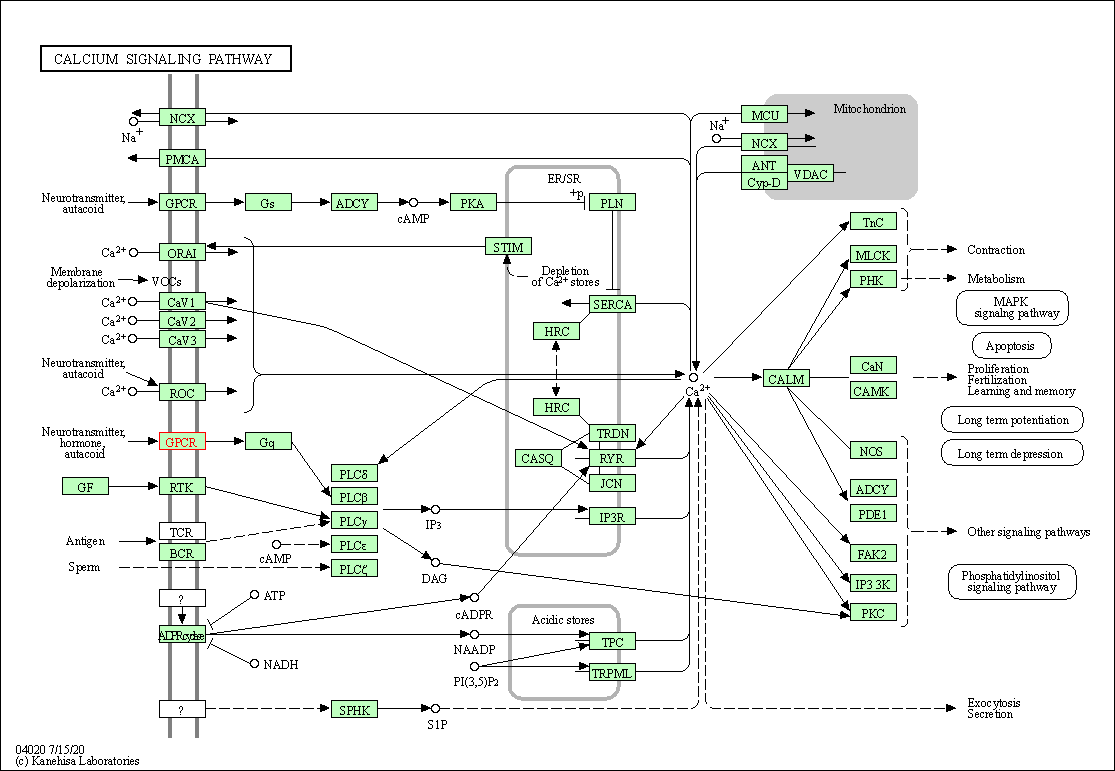
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 2 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Calcium signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Prostanoid ligand receptors | |||||
| 2 | G alpha (q) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 7 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Prostaglandin Synthesis and Regulation | |||||
| 2 | GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||||
| 3 | Gastrin-CREB signalling pathway via PKC and MAPK | |||||
| 4 | Small Ligand GPCRs | |||||
| 5 | GPCR ligand binding | |||||
| 6 | GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| 7 | GPCRs, Other | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Prostaglandin subtype-selective and non-selective IOP-lowering comparison in monkeys. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Feb;25(1):1-8. | |||||
| REF 2 | Evaluation of the Effect of Latanoprostene Bunod Ophthalmic Solution, 0.024% in Lowering Intraocular Pressure over 24 in Healthy Japanese Subjects.Adv Ther. 2015 Nov;32(11):1128-39. | |||||
| REF 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 017989. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 1916). | |||||
| REF 5 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 020411. | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 1961). | |||||
| REF 7 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 8 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7451). | |||||
| REF 9 | Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Feb;12(2):87-90. | |||||
| REF 10 | Pasireotide and octreotide stimulate distinct patterns of sst2A somatostatin receptor phosphorylation. Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Feb;24(2):436-46. | |||||
| REF 11 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 12 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7102). | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01126073) A Double Blind, Randomized Study to Compare Influence of Niacin/Laropiprant on Functional and Morphological Characteristics of Arterial Wall and Parameters of Inflammation in Subjects With Coronary Heart Disease Already Treated With a Statin in Miran Sebestjen, University Medical Centre Ljubljana. | |||||
| REF 14 | The effect of prostaglandin F2 alpha-1-isopropylester (PGF2 alpha-IE) on uveoscleral outflow. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;312:429-36. | |||||
| REF 15 | IOP-Lowering Effect of ONO-9054, A Novel Dual Agonist of Prostanoid EP3 and FP Receptors, in Monkeys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Apr;56(4):2547-52. | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01250587) Dose-Finding Study of PDC31 in Patients With Primary Dysmenorrhea. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 17 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 1959). | |||||
| REF 18 | Stereocontrolled organocatalytic synthesis of prostaglandin PGF2alpha in seven steps. Nature. 2012 Sep 13;489(7415):278-81. | |||||
| REF 19 | Ocular hypotensive activity of BOL-303259-X, a nitric oxide donating prostaglandin F2alpha agonist, in preclinical models. Exp Eye Res. 2011 Sep;93(3):250-5. | |||||
| REF 20 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||||
| REF 21 | Evaluation of WO 2012/177618 A1 and US-2014/0179750 A1: novel small molecule antagonists of prostaglandin-E2 receptor EP2.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 Jul;25(7):837-44. | |||||
| REF 22 | PGF(2alpha) FP receptor contributes to brain damage following transient focal brain ischemia. Neurotox Res. 2009 Jan;15(1):62-70. | |||||
| REF 23 | Role of nitric oxide in PGF2 alpha-induced ocular hyperemia. Exp Eye Res. 1994 Oct;59(4):401-7. | |||||
| REF 24 | THG113: a novel selective FP antagonist that delays preterm labor. Semin Perinatol. 2002 Dec;26(6):389-97. | |||||
| REF 25 | Replacement of the carboxylic acid group of prostaglandin f(2alpha) with a hydroxyl or methoxy substituent provides biologically unique compounds. Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug;130(8):1933-43. | |||||
| REF 26 | Identification by site-directed mutagenesis of amino acids contributing to ligand-binding specificity or signal transduction properties of the human FP prostanoid receptor. Biochem J. 2003 Apr 15;371(Pt 2):443-9. | |||||
| REF 27 | Design and synthesis of 13,14-dihydro prostaglandin F(1alpha) analogues as potent and selective ligands for the human FP receptor. J Med Chem. 2000 Mar 9;43(5):945-52. | |||||
| REF 28 | AL-8810: a novel prostaglandin F2 alpha analog with selective antagonist effects at the prostaglandin F2 alpha (FP) receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1278-84. | |||||
| REF 29 | Preclinical pharmacology of AL-12182, a new ocular hypotensive 11-oxa prostaglandin analog. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Oct;22(5):291-309. | |||||
| REF 30 | Arrest of preterm labor in rat and mouse by an oral and selective nonprostanoid antagonist of the prostaglandin F2alpha receptor (FP). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007 Jul;197(1):54.e1-9. | |||||
| REF 31 | The utilization of recombinant prostanoid receptors to determine the affinities and selectivities of prostaglandins and related analogs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Jan 17;1483(2):285-93. | |||||
| REF 32 | Ligand binding specificities of the eight types and subtypes of the mouse prostanoid receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;122(2):217-24. | |||||
| REF 33 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 344). | |||||
| REF 34 | Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the human prostanoid FP receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2632-6. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

