Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T96079
(Former ID: TTDC00121)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Stromal cell-derived factor 1 receptor; SDF-1 receptor; NPYRL; Lipopolysaccharide-associated protein 3; Leukocyte-derived seven transmembrane domain receptor; LPS-associated protein 3; LESTR; LCR1; LAP-3; HM89; Fusin; FB22; Chemokine receptor CXCR4; CXCR-4; CXC-R4; CD184 antigen; CD184
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CXCR4
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Malignant haematopoietic neoplasm [ICD-11: 2B33] | |||||
| 2 | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83] | |||||
| Function |
Involved in the AKT signaling cascade. Plays a role in regulation of cell migration, e. g. during wound healing. Acts as a receptor for extracellular ubiquitin; leading to enhanced intracellular calcium ions and reduced cellular cAMP levels. Binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) et mediates LPS-induced inflammatory response, including TNF secretion by monocytes. Involved in hematopoiesis and in cardiac ventricular septum formation. Also plays an essential role in vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract, probably by regulating vascular branching and/or remodeling processes in endothelial cells. Involved in cerebellar development. In the CNS, could mediate hippocampal-neuron survival. Receptor for the C-X-C chemokine CXCL12/SDF-1 that transduces a signal by increasing intracellular calcium ion levels and enhancing MAPK1/MAPK3 activation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
GPCR rhodopsin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MEGISIYTSDNYTEEMGSGDYDSMKEPCFREENANFNKIFLPTIYSIIFLTGIVGNGLVI
LVMGYQKKLRSMTDKYRLHLSVADLLFVITLPFWAVDAVANWYFGNFLCKAVHVIYTVNL YSSVLILAFISLDRYLAIVHATNSQRPRKLLAEKVVYVGVWIPALLLTIPDFIFANVSEA DDRYICDRFYPNDLWVVVFQFQHIMVGLILPGIVILSCYCIIISKLSHSKGHQKRKALKT TVILILAFFACWLPYYIGISIDSFILLEIIKQGCEFENTVHKWISITEALAFFHCCLNPI LYAFLGAKFKTSAQHALTSVSRGSSLKILSKGKRGGHSSVSTESESSSFHSS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T64X48 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Motixafortide | Drug Info | Approved | Multiple myeloma | [2] | |
| 2 | Plerixafor | Drug Info | Approved | Non-hodgkin lymphoma | [1], [3], [4] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 11 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AMD-070 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Whim syndrome | [5] | |
| 2 | Balixafortide | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Metastatic breast cancer | [6] | |
| 3 | Ulocuplumab | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Multiple myeloma | [7] | |
| 4 | POL-6326 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Human immunodeficiency virus infection | [8] | |
| 5 | TG-0054 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Macular degeneration | [9] | |
| 6 | CTCE-9908 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Sarcoma | [10] | |
| 7 | USL311 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Recurring respiratory infection | [11] | |
| 8 | ALX-0651 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Haematological malignancy | [14] | |
| 9 | CTCE-0214 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Constitutional neutropenia | [15] | |
| 10 | MSX-122 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [16] | |
| 11 | PF-06747143 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [17] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 3 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Garnocestim | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Bone marrow transplantation | [18] | |
| 2 | SURADISTA | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [19] | |
| 3 | KRH-2731 | Drug Info | Terminated | Human immunodeficiency virus infection | [21] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 5 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Antagonist | [+] 18 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Motixafortide | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 2 | Plerixafor | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | AMD-070 | Drug Info | [22], [23] | |||
| 4 | Balixafortide | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 5 | Ulocuplumab | Drug Info | [17], [25] | |||
| 6 | POL-6326 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 7 | USL311 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 8 | MSX-122 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 9 | PF-06747143 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 10 | AT-009 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 11 | GSK-812397 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 12 | isothiourea-1a | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 13 | isothiourea-1t | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 14 | LP-0067 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 15 | T134 | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 16 | T140 | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 17 | T22 | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 18 | viral macrophage inflammatory protein-II | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 25 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TG-0054 | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 2 | ALX-0651 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 3 | Cyclo(-D-Ala-D-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 4 | Cyclo(-D-MeTyr-D-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 5 | Cyclo(-D-MeTyr-L-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 6 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-Arg-Arg-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 7 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-Ala-L-Arg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 8 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-Arg-L-Arg-L-MeNal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 9 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-beta-Ala-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 10 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-D-Ala-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 11 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-L-Ala-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 12 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-L-Pic-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 13 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-Sar-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 14 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-Arg-L-MeArg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 15 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-D-MeArg-L-Arg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 16 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-Ala-L-Arg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 17 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-Arg-L-Arg-L-Ala-Sar-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 18 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-Arg-L-Arg-L-MeNal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 19 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-beta-Ala-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 20 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-D-Ala-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 21 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 22 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-Arg-L-Arg-L-Nal-L-Ala-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 23 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-Arg-L-MeArg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 24 | Cyclo(-D-Tyr-L-MeArg-L-Arg-L-Nal-Gly-) | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 25 | ND-401 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 7 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CTCE-9908 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 2 | Garnocestim | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 3 | SURADISTA | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 4 | CTCE-0324 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 5 | CXCR4 gene disrupted T cells | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 6 | KUR-CXCR4 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 7 | NB-325 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 3 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CTCE-0214 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 2 | ATI-2341 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 3 | CXCL8 | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| Binder | [+] 1 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | KRH-2731 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Isothiourea-1t | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | The 2.5 A structure of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor in complex with small molecule antagonist IT1t | PDB:3ODU | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.50 Å | Mutation | Yes | [41] |
| PDB Sequence |
PCFREENANF
36 NKIFLPTIYS46 IIFLTGIVGN56 GLVILVMGYQ66 KKLRSMTDKY76 RLHLSVADLL 86 FVITLPFWAV96 DAVANWYFGN106 FLCKAVHVIY116 TVNLYSSVWI126 LAFISLDRYL 136 AIVHATNSQR146 PRKLLAEKVV156 YVGVWIPALL166 LTIPDFIFAN176 VSEADDRYIC 186 DRFYPNDLWV196 VVFQFQHIMV206 GLILPGIVIL216 SCYCIIISKL226 SHSGSNIFEM 1006 LRIDEGLRLK1016 IYKDTEGYYT1026 IGIGHLLTKS1036 PSLNAAKSEL1046 DKAIGRNTNG 1056 VITKDEAEKL1066 FNQDVDAAVR1076 GILRNAKLKP1086 VYDSLDAVRR1096 AALINMVFQM 1106 GETGVAGFTN1116 SLRMLQQKRW1126 DEAAVNLAKS1136 RWYNQTPNRA1146 KRVITTFRTG 1156 TWDAYGSKGH232 QKRKALKTTV242 ILILAFFACW252 LPYYIGISID262 SFILLEIIKQ 272 GCEFENTVHK282 WISITEALAF292 FHCCLNPILY302 AFLGAKFKTS312 AQHALTSGRP 322 LEVLFQ
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Oleic acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | The 2.5 A structure of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor in complex with small molecule antagonist IT1t | PDB:3ODU | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.50 Å | Mutation | Yes | [41] |
| PDB Sequence |
PCFREENANF
36 NKIFLPTIYS46 IIFLTGIVGN56 GLVILVMGYQ66 KKLRSMTDKY76 RLHLSVADLL 86 FVITLPFWAV96 DAVANWYFGN106 FLCKAVHVIY116 TVNLYSSVWI126 LAFISLDRYL 136 AIVHATNSQR146 PRKLLAEKVV156 YVGVWIPALL166 LTIPDFIFAN176 VSEADDRYIC 186 DRFYPNDLWV196 VVFQFQHIMV206 GLILPGIVIL216 SCYCIIISKL226 SHSGSNIFEM 1006 LRIDEGLRLK1016 IYKDTEGYYT1026 IGIGHLLTKS1036 PSLNAAKSEL1046 DKAIGRNTNG 1056 VITKDEAEKL1066 FNQDVDAAVR1076 GILRNAKLKP1086 VYDSLDAVRR1096 AALINMVFQM 1106 GETGVAGFTN1116 SLRMLQQKRW1126 DEAAVNLAKS1136 RWYNQTPNRA1146 KRVITTFRTG 1156 TWDAYGSKGH232 QKRKALKTTV242 ILILAFFACW252 LPYYIGISID262 SFILLEIIKQ 272 GCEFENTVHK282 WISITEALAF292 FHCCLNPILY302 AFLGAKFKTS312 AQHALTSGRP 322 LEVLFQ
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viral life cycle - HIV-1 | hsa03250 | Affiliated Target |
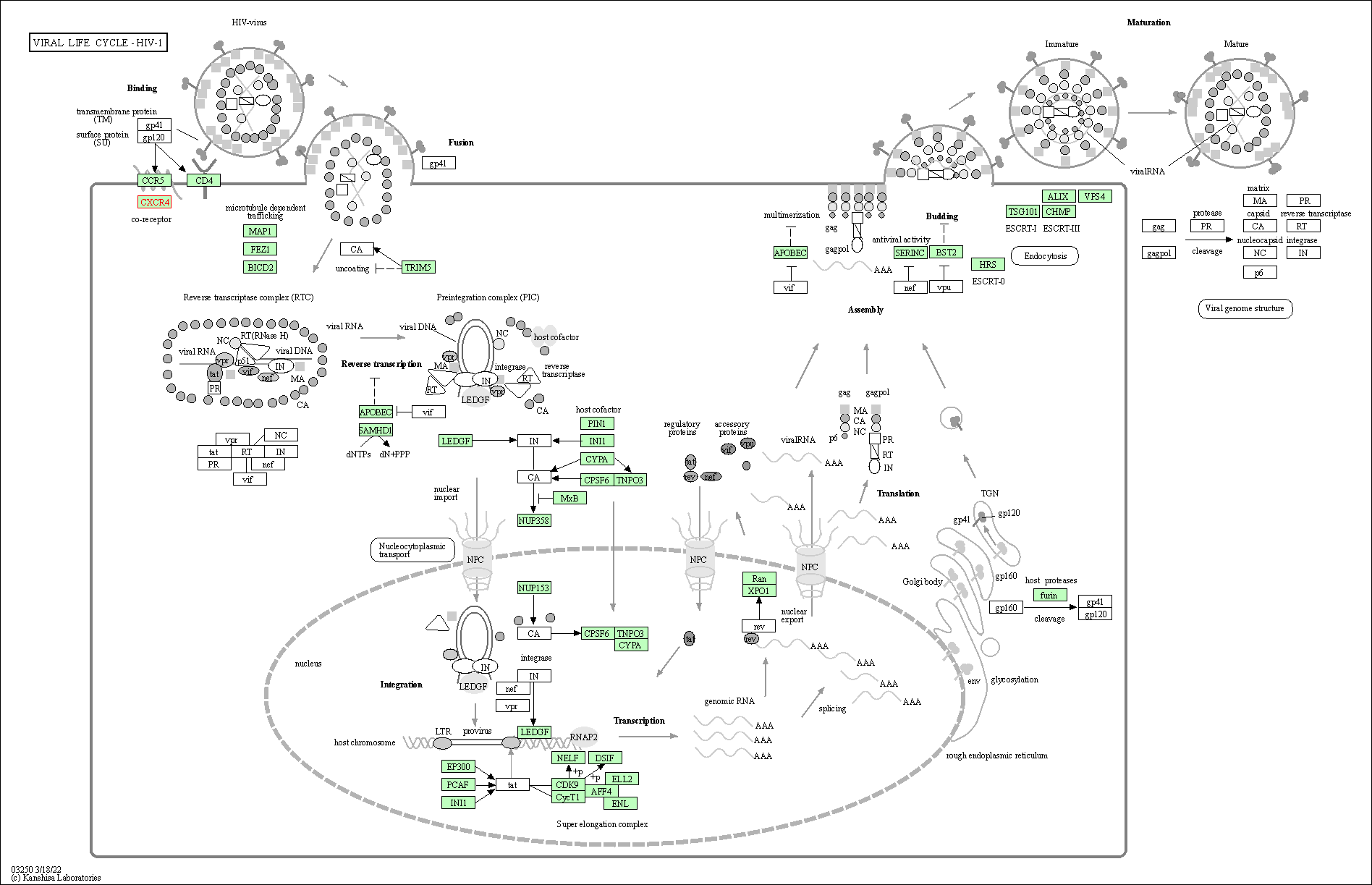
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Information processing in viruses | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Virion - Human immunodeficiency virus | hsa03260 | Affiliated Target |
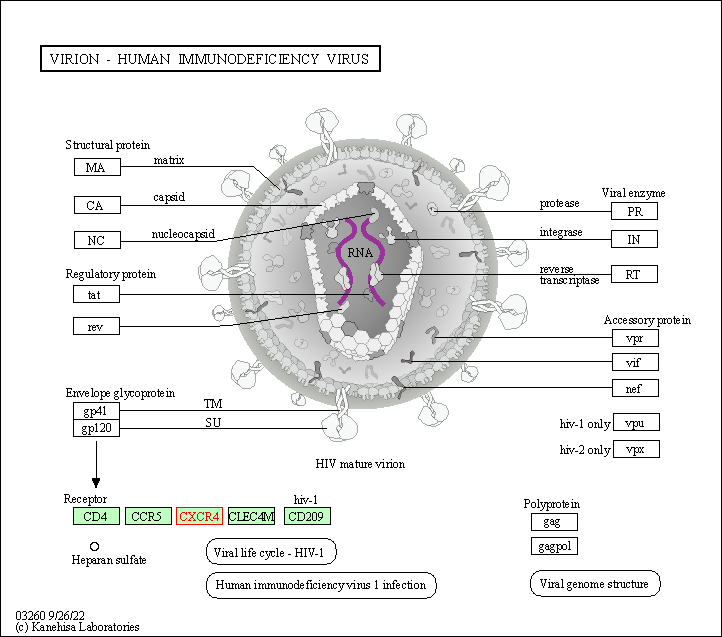
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Information processing in viruses | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |
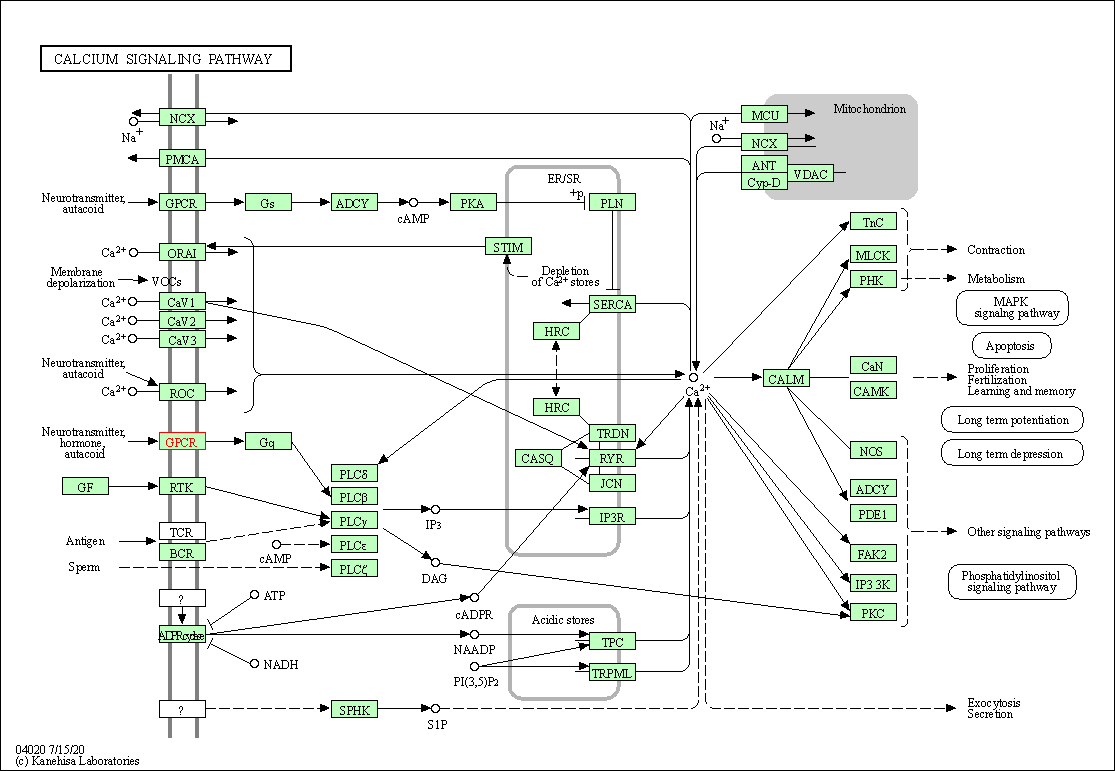
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |
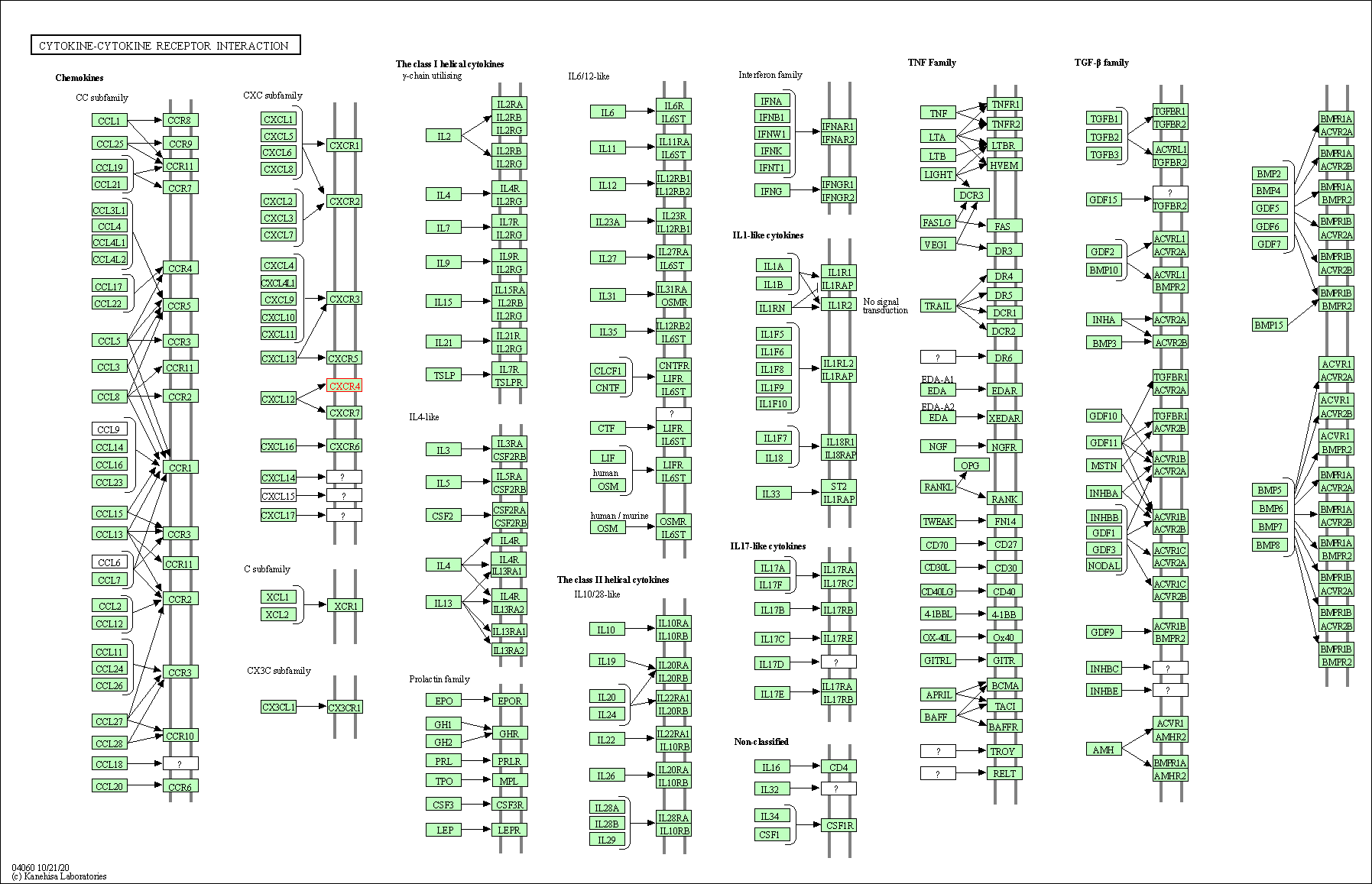
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor | hsa04061 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Endocytosis | hsa04144 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Axon guidance | hsa04360 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | hsa04670 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Intestinal immune network for IgA production | hsa04672 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 33 | Degree centrality | 3.55E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.91E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.42E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 7.77E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.80E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.02E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Emerging therapies for multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):99-127. | |||||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2023. Application Number: 217159 | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 844). | |||||
| REF 4 | 2008 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 Feb;8(2):93-6. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03995108) Efficacy and Safety Study of Mavorixafor in Participants With Warts, Hypogammaglobulinemia, Infections, and Myelokathexis (WHIM) Syndrome. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03786094) Pivotal Study in HER2 Negative, Locally Recurrent or Metastatic Breast Cancer (FORTRESS). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | Opportunities for therapeutic antibodies directed at G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017 Sep 1;16(9):661. | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01105403) Exploratory Study on POL6326 in Stem Cell Mobilization. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01018979) Safety and PK/PD of TG-0054 in Multiple Myeloma, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Hodgkin Disease Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | A CXCR4 antagonist CTCE-9908 inhibits primary tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer. J Surg Res. 2009 Aug;155(2):231-6. | |||||
| REF 11 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02305563) Phase 1 Study of BMS-936564. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01139788) A Study of LY2624587 in Patients With Advanced Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 14 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01374503) First in Man Study of ALX-0651, a Nanobody Inhibiting CXCR4. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 15 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021975) | |||||
| REF 16 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800027582) | |||||
| REF 17 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 18 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800010770) | |||||
| REF 19 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800004409) | |||||
| REF 20 | AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 2019 Nov 4;18(1):153. | |||||
| REF 21 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800020279) | |||||
| REF 22 | Pharmacokinetic effect of AMD070, an Oral CXCR4 antagonist, on CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 substrates midazolam and dextromethorphan in healthy volunteers. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2008 Apr 15;47(5):559-65. | |||||
| REF 23 | Effect of low-dose ritonavir on the pharmacokinetics of the CXCR4 antagonist AMD070 in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 May;52(5):1630-4. | |||||
| REF 24 | Anti-ageing pipeline starts to mature.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018 Sep;17(9):609-612. | |||||
| REF 25 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 26 | CXCR4 inhibitors: tumor vasculature and therapeutic challenges. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2012 Sep;7(3):251-64. | |||||
| REF 27 | CXCR4 Antagonist TG-0054 Mobilizes Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Attenuates Inflammation, and Preserves Cardiac Systolic Function in a Porcine Model of Myocardial Infarction. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(7):1313-28. | |||||
| REF 28 | Therapeutic antibodies directed at G protein-coupled receptors. MAbs. 2010 Nov-Dec; 2(6): 594-606. | |||||
| REF 29 | Beneficial effect of a CXCR4 agonist in murine models of systemic inflammation. Inflammation. 2012 Feb;35(1):130-7. | |||||
| REF 30 | Comparative evaluation of CC chemokine-induced migration of murine CD8alpha+ and CD8alpha- dendritic cells and their in vivo trafficking. J Leukoc Biol. 2004 Feb;75(2):275-85. | |||||
| REF 31 | CN patent application no. 101094684, With the combination of chemokine activation progenitor cells/stem cells. | |||||
| REF 32 | Suradista NSC 651016 inhibits the angiogenic activity of CXCL12-stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha. Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Dec;8(12):3955-60. | |||||
| REF 33 | Progress in targeting HIV-1 entry. Drug Discov Today. 2005 Aug 15;10(16):1085-94. | |||||
| REF 34 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 71). | |||||
| REF 35 | Noncompetitive allosteric inhibitors of the inflammatory chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2: prevention of reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Aug 10;101(32):11791-6. | |||||
| REF 36 | Structure-activity relationships of cyclic peptide-based chemokine receptor CXCR4 antagonists: disclosing the importance of side-chain and backbone... J Med Chem. 2007 Jan 25;50(2):192-8. | |||||
| REF 37 | Identification of novel non-peptide CXCR4 antagonists by ligand-based design approach. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Jul 15;18(14):4124-9. | |||||
| REF 38 | Orally bioavailable isothioureas block function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in vitro and in vivo. J Med Chem. 2008 Dec 25;51(24):7915-20. | |||||
| REF 39 | A low-molecular-weight inhibitor against the chemokine receptor CXCR4: a strong anti-HIV peptide T140. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Dec 30;253(3):877-82. | |||||
| REF 40 | A broad-spectrum chemokine antagonist encoded by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Science. 1997 Sep 12;277(5332):1656-9. | |||||
| REF 41 | Structures of the CXCR4 chemokine GPCR with small-molecule and cyclic peptide antagonists. Science. 2010 Nov 19;330(6007):1066-71. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

