Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T99912
(Former ID: TTDR00950)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Kynureninase (KYNU)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
L-kynurenine hydrolase; KYNU
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
KYNU
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Preclinical target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||||
| 2 | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60-2C6Y] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the cleavage of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) and L-3- hydroxykynurenine (L-3OHKyn) into anthranilic acid (AA) and 3- hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-OHAA), respectively. Has a preference for the L-3-hydroxy form. Also has cysteine-conjugate-beta-lyase activity.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Carbon-carbon bonds hydrolase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.7.1.3
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MEPSSLELPADTVQRIAAELKCHPTDERVALHLDEEDKLRHFRECFYIPKIQDLPPVDLS
LVNKDENAIYFLGNSLGLQPKMVKTYLEEELDKWAKIAAYGHEVGKRPWITGDESIVGLM KDIVGANEKEIALMNALTVNLHLLMLSFFKPTPKRYKILLEAKAFPSDHYAIESQLQLHG LNIEESMRMIKPREGEETLRIEDILEVIEKEGDSIAVILFSGVHFYTGQHFNIPAITKAG QAKGCYVGFDLAHAVGNVELYLHDWGVDFACWCSYKYLNAGAGGIAGAFIHEKHAHTIKP ALVGWFGHELSTRFKMDNKLQLIPGVCGFRISNPPILLVCSLHASLEIFKQATMKALRKK SVLLTGYLEYLIKHNYGKDKAATKKPVVNIITPSHVEERGCQLTITFSVPNKDVFQELEK RGVVCDKRNPNGIRVAPVPLYNSFHDVYKFTNLLTSILDSAETKN Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Pyridoxal phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of Homo sapiens kynureninase-3-hydroxyhippuric acid inhibitor complex | PDB:3E9K | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.70 Å | Mutation | No | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
LELPADTVQR
15 IAAELKCHPT25 DERVALHLDE35 EDKLRHFREF46 YIPKIQDLPP56 VDLSLVNKDE 66 NAIYFLGNSL76 GLQPKMVKTY86 LEEELDKWAK96 IAAYGHEVGK106 RPWITGDESI 116 VGLMKDIVGA126 NEKEIALMNA136 LTVNLHLLML146 SFFKPTPKRY156 KILLEAKAFP 166 SDHYAIESQL176 QLHGLNIEES186 MRMIKPREGE196 ETLRIEDILE206 VIEKEGDSIA 216 VILFSGVHFY226 TGQHFNIPAI236 TKAGQAKGCY246 VGFDLAHAVG256 NVELYLHDWG 266 VDFACWCSYK276 YLNAGAGGIA286 GAFIHEKHAH296 TIKPALVGWF306 GHELSTRFKM 316 DNKLQLIPGV326 CGFRISNPPI336 LLVCSLHASL346 EIFKQATMKA356 LRKKSVLLTG 366 YLEYLIKHNY376 GVVNIITPSH395 VEERGCQLTI405 TFSVPNKDVF415 QELEKRGVVC 425 DKRNPNGIRV435 APVPLYNSFH445 DVYKFTNLLT455 SILDS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: 3-Hydroxyhippuric acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of Homo sapiens kynureninase-3-hydroxyhippuric acid inhibitor complex | PDB:3E9K | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.70 Å | Mutation | No | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
LELPADTVQR
15 IAAELKCHPT25 DERVALHLDE35 EDKLRHFREF46 YIPKIQDLPP56 VDLSLVNKDE 66 NAIYFLGNSL76 GLQPKMVKTY86 LEEELDKWAK96 IAAYGHEVGK106 RPWITGDESI 116 VGLMKDIVGA126 NEKEIALMNA136 LTVNLHLLML146 SFFKPTPKRY156 KILLEAKAFP 166 SDHYAIESQL176 QLHGLNIEES186 MRMIKPREGE196 ETLRIEDILE206 VIEKEGDSIA 216 VILFSGVHFY226 TGQHFNIPAI236 TKAGQAKGCY246 VGFDLAHAVG256 NVELYLHDWG 266 VDFACWCSYK276 YLNAGAGGIA286 GAFIHEKHAH296 TIKPALVGWF306 GHELSTRFKM 316 DNKLQLIPGV326 CGFRISNPPI336 LLVCSLHASL346 EIFKQATMKA356 LRKKSVLLTG 366 YLEYLIKHNY376 GVVNIITPSH395 VEERGCQLTI405 TFSVPNKDVF415 QELEKRGVVC 425 DKRNPNGIRV435 APVPLYNSFH445 DVYKFTNLLT455 SILDS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tryptophan metabolism | hsa00380 | Affiliated Target |
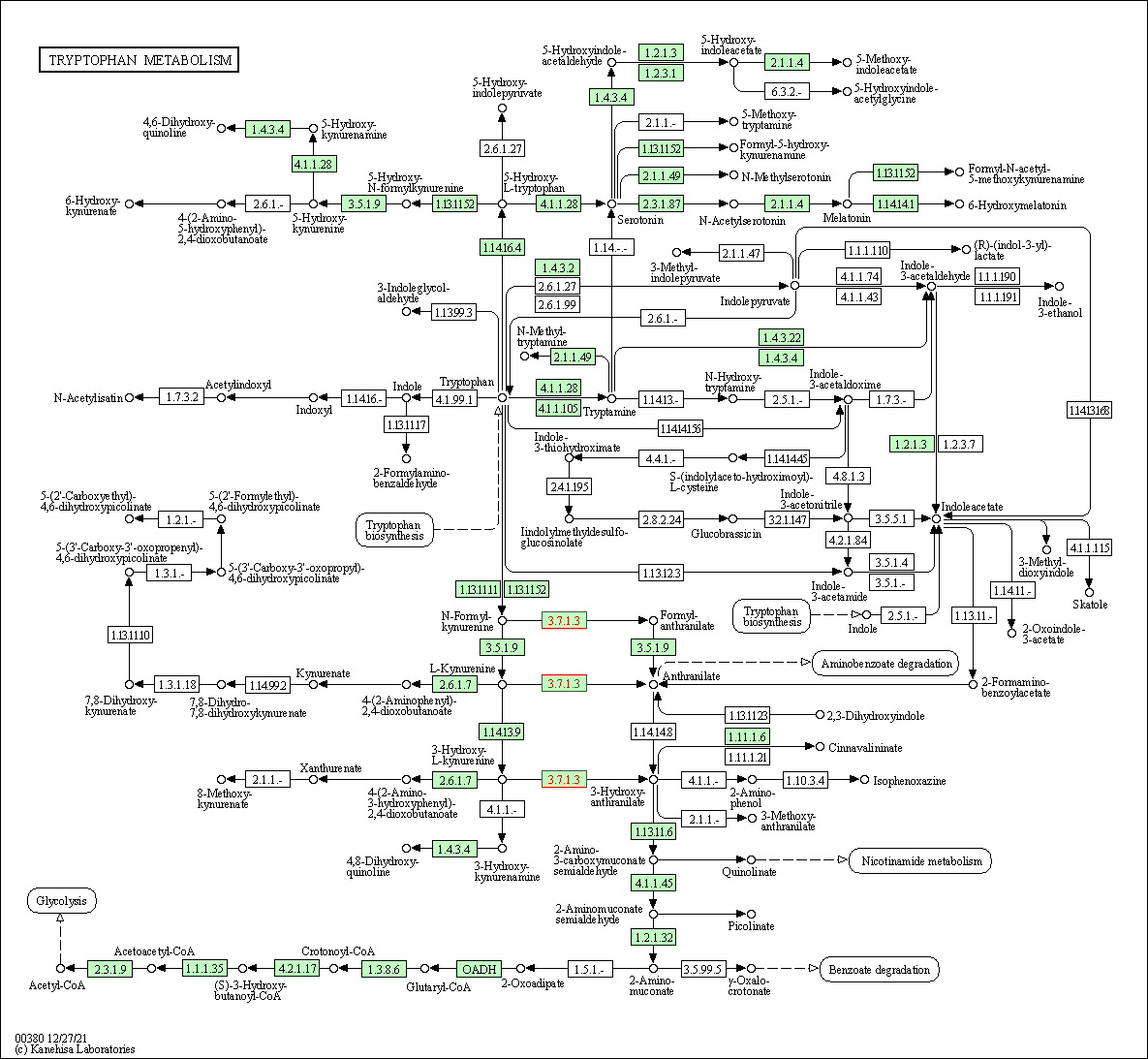
|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 9 | Degree centrality | 9.67E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 3.30E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.36E-01 | Radiality | 1.14E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.61E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.56E+00 | Topological coefficient | 3.50E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 5 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Superpathway of tryptophan utilization | |||||
| 2 | Tryptophan degradation | |||||
| 3 | L-kynurenine degradation | |||||
| 4 | Tryptophan degradation to 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate semialdehyde | |||||
| 5 | NAD de novo biosynthesis | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 2 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Tryptophan metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TSLP Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Tryptophan Metabolism | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Tryptophan catabolism | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 4 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Tryptophan metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Metabolism of amino acids and derivatives | |||||
| 3 | NAD Biosynthesis II (from tryptophan) | |||||
| 4 | Selenium Micronutrient Network | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Comparative inhibition by substrate analogues 3-methoxy- and 3-hydroxydesaminokynurenine and an improved 3 step purification of recombinant human kynureninase. BMC Biochem. 2003 Sep 24;4:13. | |||||
| REF 2 | 2-Amino-4-[3'-hydroxyphenyl]-4-hydroxybutanoic acid; a potent inhibitor of rat and recombinant human kynureninase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2002 Feb 11;12(3):361-3. | |||||
| REF 3 | Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 May;18(5):379-401. | |||||
| REF 4 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 5 | Crystal structure of the Homo sapiens kynureninase-3-hydroxyhippuric acid inhibitor complex: insights into the molecular basis of kynureninase substrate specificity. J Med Chem. 2009 Jan 22;52(2):389-96. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

