Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D07NOI
|
||||
| Former ID |
DCL000356
|
||||
| Drug Name |
BAY-57-9352
|
||||
| Synonyms |
Telatinib; Bay 57-9352
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Solid tumours [ICD9: 140-199, 210-229; ICD10:C00-D48] | Phase 2 | [548058] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
||||
| Company |
Bayer AG
|
||||
| Structure |
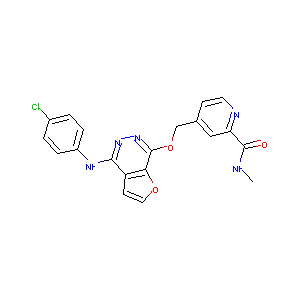
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C20H16ClN5O3
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CNC(=O)C1=NC=CC(=C1)COC2=NN=C(C3=C2OC=C3)NC4=CC=C(C=C4)<br />Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C20H16ClN5O3/c1-22-19(27)16-10-12(6-8-23-16)11-29-20-17-15(7-9-28-17)18(25-26-20)24-14-4-2-13(21)3-5-14/h2-10H,11H2,1H3,(H,22,27)(H,24,25)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QFCXANHHBCGMAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 332012-40-5
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
14831018, 24115824, 44844835, 75059184, 123051133, 124360774, 124757885, 124955475, 125164687, 126661316, 126731532, 131477698, 135260928, 135367560, 136348776, 136349488, 136367619, 136367765, 137156647, 143010267, 152048944, 160680893, 162011760, 162038009, 162202687, 163348562, 163908069, 164042063, 164765235, 170502613, 172919643, 174528808, 198939231, 223396209, 223705027, 227479450, 242060040, 245318899, 251971207, 252110147, 252216386
|
||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor | Target Info | Inhibitor | [536474] | |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Target Info | Inhibitor | [536474] | ||
| NetPath Pathway | IL2 Signaling Pathway | ||||
| PANTHER Pathway | Angiogenesis | ||||
| VEGF signaling pathway | |||||
| Pathway Interaction Database | HIF-2-alpha transcription factor network | ||||
| Beta3 integrin cell surface interactions | |||||
| Signaling events mediated by TCPTP | |||||
| SHP2 signaling | |||||
| S1P1 pathway | |||||
| VEGF and VEGFR signaling network | |||||
| Integrins in angiogenesis | |||||
| Signaling events mediated by VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 | |||||
| Notch-mediated HES/HEY network | |||||
| References | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

