Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T74312
(Former ID: TTDS00090)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT-3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Stem cell tyrosine kinase 1; STK1; STK-1; Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3; Fetal liver kinase-2; FLT-3; FLK2; FLK-2; FL cytokine receptor; CD135
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
FLT3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 8 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||||
| 2 | Bone/articular cartilage neoplasm [ICD-11: 2F7B] | |||||
| 3 | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||||
| 4 | Human immunodeficiency virus disease [ICD-11: 1C60-1C62] | |||||
| 5 | Idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis [ICD-11: CB03] | |||||
| 6 | Mastocytosis [ICD-11: 2A21] | |||||
| 7 | Mature B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85] | |||||
| 8 | Myeloproliferative neoplasm [ICD-11: 2A20] | |||||
| Function |
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for the cytokine FLT3LG and regulates differentiation, proliferation and survival of hematopoietic progenitor cells and of dendritic cells. Promotes phosphorylation of SHC1 and AKT1, and activation of the downstream effector MTOR. Promotes activation of RAS signaling and phosphorylation of downstream kinases, including MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1. Promotes phosphorylation of FES, FER, PTPN6/SHP, PTPN11/SHP-2, PLCG1, and STAT5A and/or STAT5B. Activation of wild-type FLT3 causes only marginal activation of STAT5A or STAT5B. Mutations that cause constitutive kinase activity promote cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis via the activation of multiple signaling pathways.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.10.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MPALARDGGQLPLLVVFSAMIFGTITNQDLPVIKCVLINHKNNDSSVGKSSSYPMVSESP
EDLGCALRPQSSGTVYEAAAVEVDVSASITLQVLVDAPGNISCLWVFKHSSLNCQPHFDL QNRGVVSMVILKMTETQAGEYLLFIQSEATNYTILFTVSIRNTLLYTLRRPYFRKMENQD ALVCISESVPEPIVEWVLCDSQGESCKEESPAVVKKEEKVLHELFGTDIRCCARNELGRE CTRLFTIDLNQTPQTTLPQLFLKVGEPLWIRCKAVHVNHGFGLTWELENKALEEGNYFEM STYSTNRTMIRILFAFVSSVARNDTGYYTCSSSKHPSQSALVTIVEKGFINATNSSEDYE IDQYEEFCFSVRFKAYPQIRCTWTFSRKSFPCEQKGLDNGYSISKFCNHKHQPGEYIFHA ENDDAQFTKMFTLNIRRKPQVLAEASASQASCFSDGYPLPSWTWKKCSDKSPNCTEEITE GVWNRKANRKVFGQWVSSSTLNMSEAIKGFLVKCCAYNSLGTSCETILLNSPGPFPFIQD NISFYATIGVCLLFIVVLTLLICHKYKKQFRYESQLQMVQVTGSSDNEYFYVDFREYEYD LKWEFPRENLEFGKVLGSGAFGKVMNATAYGISKTGVSIQVAVKMLKEKADSSEREALMS ELKMMTQLGSHENIVNLLGACTLSGPIYLIFEYCCYGDLLNYLRSKREKFHRTWTEIFKE HNFSFYPTFQSHPNSSMPGSREVQIHPDSDQISGLHGNSFHSEDEIEYENQKRLEEEEDL NVLTFEDLLCFAYQVAKGMEFLEFKSCVHRDLAARNVLVTHGKVVKICDFGLARDIMSDS NYVVRGNARLPVKWMAPESLFEGIYTIKSDVWSYGILLWEIFSLGVNPYPGIPVDANFYK LIQNGFKMDQPFYATEEIYIIMQSCWAFDSRKRPSFPNLTSFLGCQLADAEEAMYQNVDG RVSECPHTYQNRRPFSREMDLGLLSPQAQVEDS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T91AIW | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 8 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Gilteritinib | Drug Info | Approved | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Intedanib | Drug Info | Approved | Colorectal cancer | [4] | |
| 3 | Midostaurin | Drug Info | Approved | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [5] | |
| 4 | Pacritinib | Drug Info | Approved | Myelofibrosis | [6] | |
| 5 | Pexidartinib | Drug Info | Approved | Tenosynovial giant cell tumour | [7] | |
| 6 | Ponatinib | Drug Info | Approved | Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia | [8], [9] | |
| 7 | Quizartinib | Drug Info | Approved | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [10] | |
| 8 | Zidovudine | Drug Info | Approved | Human immunodeficiency virus infection | [11], [12] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 8 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BMS-690514 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic pain | [17] | |
| 2 | CDX-301 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation | [18] | |
| 3 | TAK-659 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | [3] | |
| 4 | MK-2461 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Alzheimer disease | [22] | |
| 5 | 4SC-203 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [27] | |
| 6 | IMC-EB10 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [28] | |
| 7 | Ki23819 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [29] | |
| 8 | KW-2449 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [30], [31] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Tandutinib | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Anaplastic mixed oligoastrocytoma | [32], [33] | |
| 2 | SU5614 | Drug Info | Terminated | Airway inflammation | [35] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MC-2001 | Drug Info | Preclinical | leukaemia | [34] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 34 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Gilteritinib | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 2 | Intedanib | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | Midostaurin | Drug Info | [1], [36] | |||
| 4 | Pexidartinib | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 5 | Quizartinib | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 6 | BMS-690514 | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 7 | CDX-301 | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 8 | TAK-659 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 9 | MK-2461 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 10 | Ki23819 | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 11 | Carboxamide derivative 4 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 12 | Pyridine derivative 18 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 13 | Tandutinib | Drug Info | [1], [46] | |||
| 14 | MC-2001 | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 15 | AG1295 | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 16 | SU5614 | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 17 | (1H-indol-2-yl)(5-methoxy-1H-indol-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 18 | (1H-indol-2-yl)(5-phenoxy-1H-indol-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 19 | (1H-indol-2-yl)(6-methoxy-1H-indol-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 20 | (5-fluoro-1H-indol-2-yl)-(1H-indol-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 21 | (benzo[b]furan-2-yl)-(1H-indol-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 22 | AKN-028 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 23 | AST-487 | Drug Info | [51] | |||
| 24 | Bis(5-acetoxybenzo[b]furan-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 25 | Bis(5-aminobenzo[b]furan-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 26 | Bis(5-hydroxybenzo[b]furan-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 27 | Bis(6-hydroxybenzo[b]furan-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 28 | Bis-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-2-yl)-methanone | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 29 | Di(1H-indol-2-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 30 | G749 | Drug Info | [52] | |||
| 31 | PMID21982499C14k | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 32 | PMID22765894C8h | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 33 | PMID24900538C2c | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 34 | URMC-099 | Drug Info | [56] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 3 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pacritinib | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 2 | Ponatinib | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 3 | 4SC-203 | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| Binder | [+] 1 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Zidovudine | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Gilteritinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of FLT3 in complex with gilteritinib | PDB:6JQR | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.20 Å | Mutation | No | [57] |
| PDB Sequence |
RYESQLQMVQ
580 VTGSSDNEYF590 YVDFREYEYD600 LKWEFPRENL610 EFGKVLGSGA620 FGKVMNATAY 630 GISVSIQVAV643 KMLKEDSSER655 EALMSELKMM665 TQLGSHENIV675 NLLGACTLSG 685 PIYLIFEYCC695 YGDLLNYLRS705 KREKFSNVLT784 FEDLLCFAYQ794 VAKGMEFLEF 804 KSCVHRDLAA814 RNVLVTHGKV824 VKICDFMSDS840 NYVVRGNARL850 PVKWMAPESL 860 FEGIYTIKSD870 VWSYGILLWE880 IFSLGVNPYP890 GIPVDANFYK900 LIQNGFKMDQ 910 PFYATEEIYI920 IMQSCWAFDS930 RKRPSFPNLT940 SFLGCQLADA950 E |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: AC220 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of FLT3 with a small molecule inhibitor | PDB:4RT7 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.10 Å | Mutation | No | [58] |
| PDB Sequence |
YDLKWEFPRE
608 NLEFGKVLGS618 GAFGKVMNAT628 AYGISGVSIQ640 VAVKMLKDSS653 EREALMSELK 663 MMTQLGSHEN673 IVNLLGACTL683 SGPIYLIFEY693 CCYGDLLNYL703 RSKRNVLTFE 786 DLLCFAYQVA796 KGMEFLEFKS806 CVHRDLAARN816 VLVTHGKVVK826 ICDFGLARDI 836 MSDSNYVVRG846 NARLPVKWMA856 PESLFEGIYT866 IKSDVWSYGI876 LLWEIFSLGV 886 NPYPGIPVDA896 NFYKLIQNGF906 KMDQPFYATE916 EIYIIMQSCW926 AFDSRKRPSF 936 PNLTSFLGCQ946 LADA
|
|||||
|
|
LYS614
3.931
LEU616
3.618
VAL624
4.059
ALA642
3.482
LYS644
3.460
GLU661
2.840
MET664
4.588
MET665
3.715
LEU668
3.595
ILE674
4.579
VAL675
3.915
PHE691
3.593
GLU692
4.562
TYR693
3.410
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
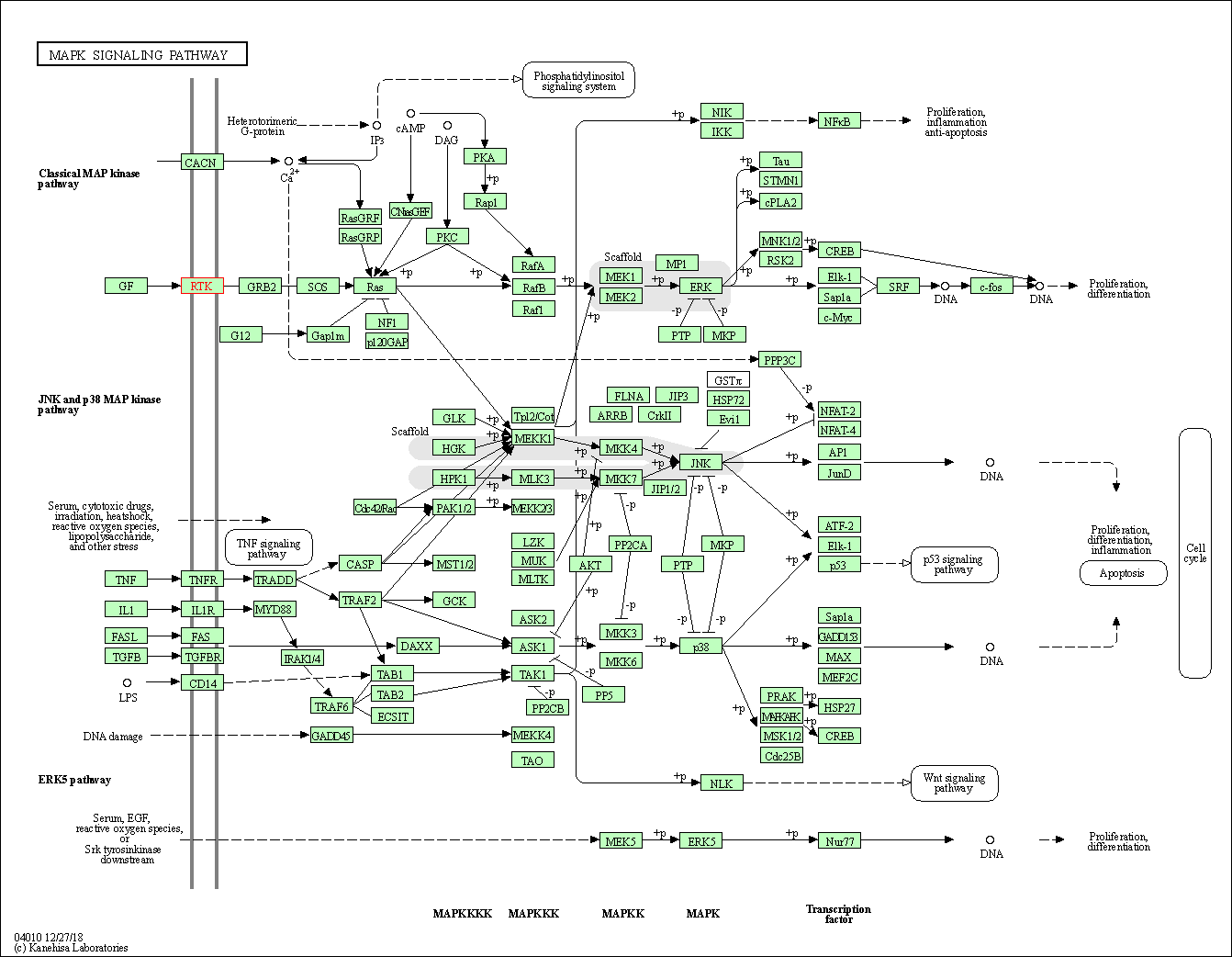
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |
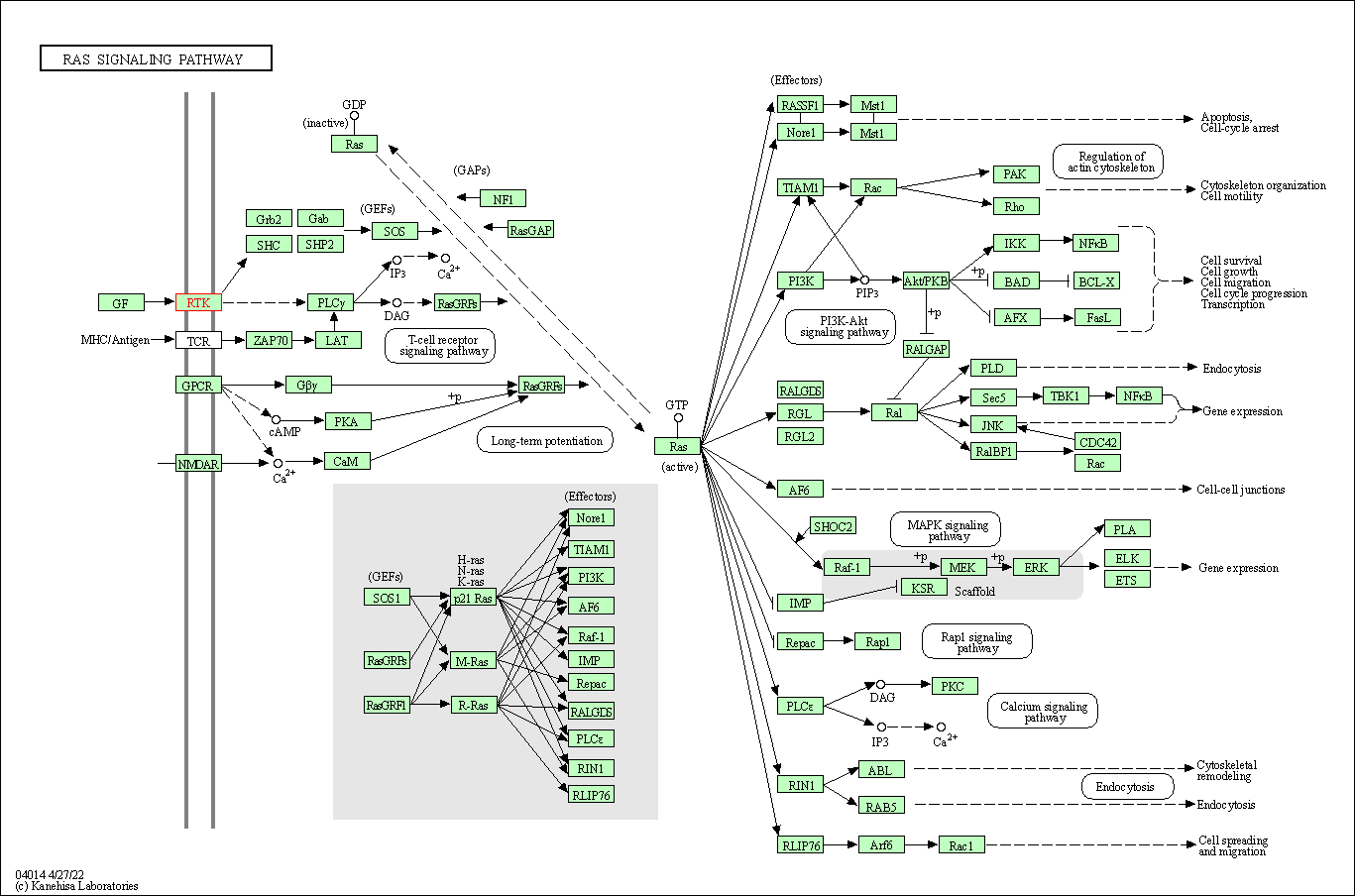
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | hsa04640 | Affiliated Target |
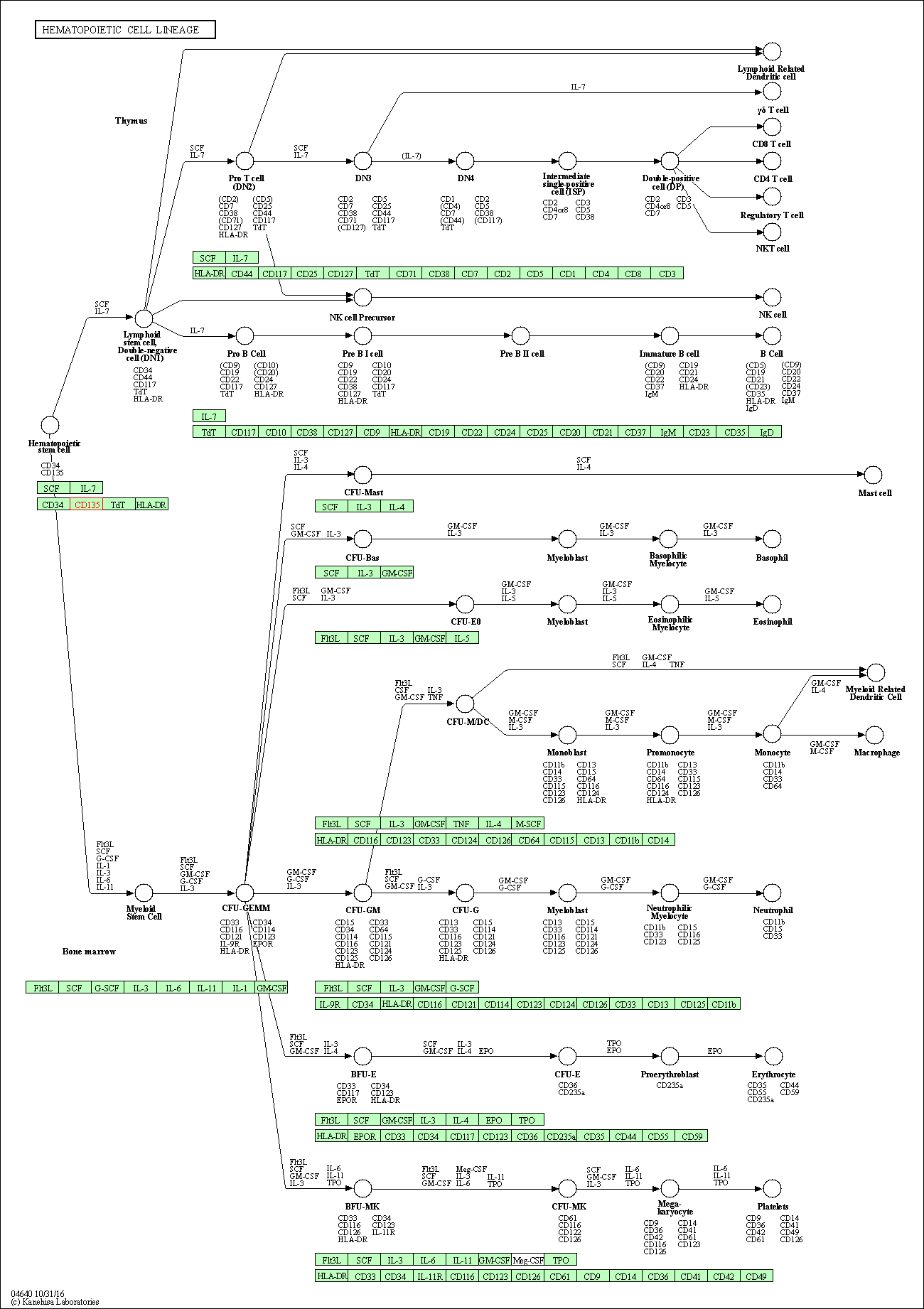
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 10 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.75E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.40E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.78E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 6.96E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.81E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 6 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | |||||
| 2 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | |||||
| 3 | Pathways in cancer | |||||
| 4 | Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | |||||
| 5 | Acute myeloid leukemia | |||||
| 6 | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | A comparison of physicochemical property profiles of marketed oral drugs and orally bioavailable anti-cancer protein kinase inhibitors in clinical development. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(14):1408-22. | |||||
| REF 2 | 2018 FDA drug approvals.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 Feb;18(2):85-89. | |||||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 4 | 2014 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Feb;14(2):77-81. | |||||
| REF 5 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2018 | |||||
| REF 6 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2022. Application Number: 208712. | |||||
| REF 7 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health Human Services. 2019 | |||||
| REF 8 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5890). | |||||
| REF 9 | Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Feb;12(2):87-90. | |||||
| REF 10 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2023. Application Number: 216993 | |||||
| REF 11 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4825). | |||||
| REF 12 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 13 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5672). | |||||
| REF 14 | Emerging drugs for psoriasis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):145-63. | |||||
| REF 15 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7886). | |||||
| REF 16 | Metabolism and bioactivation of famitinib, a novel inhibitor of receptor tyrosine kinase, in cancer patients. Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;168(7):1687-706. | |||||
| REF 17 | A novel epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor promotes apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells resistant to erlotinib. Cancer Res. 2007 Jul 1;67(13):6253-62. | |||||
| REF 18 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02129075) CDX-1401 and Poly-ICLC Vaccine Therapy With or Without CDX-301in Treating Patients With Stage IIB-IV Melanoma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 19 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03194685) Study of FF-10101-01 in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 20 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03850574) Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of HM43239 in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 21 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03008187) SEL24/MEN1703 in Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 22 | MK-2461, a novel multitargeted kinase inhibitor, preferentially inhibits the activated c-Met receptor. Cancer Res. 2010 Feb 15;70(4):1524-33. | |||||
| REF 23 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03564288) Study to Find a Safe and Effective Dose of SKI-G-801 in the Treatment of Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 24 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03541369) Safety, Tolerability, PK, PD, and Efficacy of AMG 427 in Subjects With Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia (20170528). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 25 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03690154) A Phase 1 Study to Evaluate FN-1501 Monotherapy in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors and R/R AML. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 26 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03510104) Pharmacokinetic and Safety Study of MRX-2843 in Adults With Relapsed/Refractory Advanced and/or Metastatic Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 27 | 2011 Pipeline of 4SC AG. | |||||
| REF 28 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00887926) Study of EB10 in Patients With Leukemia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 29 | KRN633: A selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase that suppresses tumor angiogenesis and growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 Dec;3(12):1639-49. | |||||
| REF 30 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5691). | |||||
| REF 31 | KW-2449, a novel multikinase inhibitor, suppresses the growth of leukemia cells with FLT3 mutations or T315I-mutated BCR/ABL translocation. Blood. 2009 Aug 20;114(8):1607-17. | |||||
| REF 32 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5695). | |||||
| REF 33 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800017148) | |||||
| REF 34 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021088) | |||||
| REF 35 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800014776) | |||||
| REF 36 | CBL exon 8/9 mutants activate the FLT3 pathway and cluster in core binding factor/11q deletion acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome subt... Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Apr 1;15(7):2238-47. | |||||
| REF 37 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 38 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1807). | |||||
| REF 39 | Preclinical pharmacokinetics and in vitro metabolism of BMS-690514, a potent inhibitor of EGFR and VEGFR2. J Pharm Sci. 2010 Aug;99(8):3579-93. | |||||
| REF 40 | Efficacy and safety of CDX-301, recombinant human Flt3L, at expanding dendritic cells and hematopoietic stem cells in healthy human volunteers. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015 Jul;50(7):924-30. | |||||
| REF 41 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | |||||
| REF 42 | IMC-EB10, an anti-FLT3 monoclonal antibody, prolongs survival and reduces nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient engraftment of some acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines and primary leukemic samples. Cancer Res. 2006 May 1;66(9):4843-51. | |||||
| REF 43 | Targeting FMS-related tyrosine kinase receptor 3 with the human immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody IMC-EB10. Cancer. 2010 Feb 15;116(4 Suppl):1013-7. | |||||
| REF 44 | Identification of Ki23819, a highly potent inhibitor of kinase activity of mutant FLT3 receptor tyrosine kinase. Leukemia. 2005 Jun;19(6):930-5. | |||||
| REF 45 | RET kinase inhibitors: a review of recent patents (2012-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Jan;27(1):91-99. | |||||
| REF 46 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Takeda (2009). | |||||
| REF 47 | Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2003 Oct;17(10):1961-6. | |||||
| REF 48 | Inhibition of FLT3 and PDGFR tyrosine kinase activity by bis(benzo[b]furan-2-yl)methanones. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Mar 1;15(5):2187-97. | |||||
| REF 49 | FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3-internal tandem duplication tyrosine kinase inhibitors display a nonoverlapping profile of resistance mutations in vitro. Cancer Res. 2009 Apr 1;69(7):3032-41. | |||||
| REF 50 | Novel bis(1H-indol-2-yl)methanones as potent inhibitors of FLT3 and platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. J Med Chem. 2006 Jun 1;49(11):3101-15. | |||||
| REF 51 | Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol. 2011 Oct 30;29(11):1046-51. | |||||
| REF 52 | G-749, a novel FLT3 kinase inhibitor, can overcome drug resistance for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2014 Apr 3;123(14):2209-19. | |||||
| REF 53 | 7-(4H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-yl)benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridines: a novel class of Pim kinase inhibitors with potent cell antiproliferative activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Nov 15;21(22):6687-92. | |||||
| REF 54 | The design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Aug 1;22(15):4979-85. | |||||
| REF 55 | Discovery of Disubstituted Imidazo[4,5-b]pyridines and Purines as Potent TrkA Inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jul 26;3(9):705-9. | |||||
| REF 56 | Discovery, synthesis, and characterization of an orally bioavailable, brain penetrant inhibitor of mixed lineage kinase 3. J Med Chem. 2013 Oct 24;56(20):8032-48. | |||||
| REF 57 | Effect of Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) ligand (FL) on antitumor activity of gilteritinib, a FLT3 inhibitor, in mice xenografted with FL-overexpressing cells. Oncotarget. 2019 Oct 22;10(58):6111-6123. | |||||
| REF 58 | Characterizing and Overriding the Structural Mechanism of the Quizartinib-Resistant FLT3 "Gatekeeper" F691L Mutation with PLX3397. Cancer Discov. 2015 Jun;5(6):668-79. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

