Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T20891
(Former ID: TTDR00273)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase-1 (PDPK1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
PDK1; HPDK1; 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; 3'-phosphoinositide dependent kinase 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PDPK1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A80-2A86] | |||||
| Function |
Its targets include: protein kinase B (PKB/AKT1, PKB/AKT2, PKB/AKT3), p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RPS6KB1), p90 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RPS6KA1, RPS6KA2 and RPS6KA3), cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PRKACA), protein kinase C (PRKCD and PRKCZ), serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK1, SGK2 and SGK3), p21-activated kinase-1 (PAK1), protein kinase PKN (PKN1 and PKN2). Plays a central role in the transduction of signals from insulin by providing the activating phosphorylation to PKB/AKT1, thus propagating the signal to downstream targets controlling cell proliferation and survival, as well as glucose and amino acid uptake and storage. Negatively regulates the TGF-beta-induced signaling by: modulating the association of SMAD3 and SMAD7 with TGF-beta receptor, phosphorylating SMAD2, SMAD3, SMAD4 and SMAD7, preventing the nuclear translocation of SMAD3 and SMAD4 and the translocation of SMAD7 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in response to TGF-beta. Activates PPARG transcriptional activity and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Activates the NF-kappa-B pathway via phosphorylation of IKKB. The tyrosine phosphorylated form is crucial for the regulation of focal adhesions by angiotensin II. Controls proliferation, survival, and growth of developing pancreatic cells. Participates in the regulation of Ca(2+) entry and Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels of mast cells. Essential for the motility of vascular endothelial cells (ECs) and is involved in the regulation of their chemotaxis. Plays a critical role in cardiac homeostasis by serving as a dual effector for cell survival and beta-adrenergic response. Plays an important role during thymocyte development by regulating the expression of key nutrient receptors on the surface of pre-T cells and mediating Notch-induced cell growth and proliferative responses. Provides negative feedback inhibition to toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappa-B activation in macrophages. Isoform 3 is catalytically inactive. Serine/threonine kinase which acts as a master kinase, phosphorylating and activating a subgroup of the AGC family of protein kinases.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MARTTSQLYDAVPIQSSVVLCSCPSPSMVRTQTESSTPPGIPGGSRQGPAMDGTAAEPRP
GAGSLQHAQPPPQPRKKRPEDFKFGKILGEGSFSTVVLARELATSREYAIKILEKRHIIK ENKVPYVTRERDVMSRLDHPFFVKLYFTFQDDEKLYFGLSYAKNGELLKYIRKIGSFDET CTRFYTAEIVSALEYLHGKGIIHRDLKPENILLNEDMHIQITDFGTAKVLSPESKQARAN SFVGTAQYVSPELLTEKSACKSSDLWALGCIIYQLVAGLPPFRAGNEYLIFQKIIKLEYD FPEKFFPKARDLVEKLLVLDATKRLGCEEMEGYGPLKAHPFFESVTWENLHQQTPPKLTA YLPAMSEDDEDCYGNYDNLLSQFGCMQVSSSSSSHSLSASDTGLPQRSGSNIEQYIHDLD SNSFELDLQFSEDEKRLLLEKQAGGNPWHQFVENNLILKMGPVDKRKGLFARRRQLLLTE GPHLYYVDPVNKVLKGEIPWSQELRPEAKNFKTFFVHTPNRTYYLMDPSGNAHKWCRKIQ EVWRQRYQSHPDAAVQ Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AR-12 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Lymphoma | [2], [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AR-12 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 7 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BX-795 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 2 | BX-912 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | GSK-2334470 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 4 | L-serine-O-phosphate | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 5 | PF-5177624 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 6 | PHT-427 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 7 | PMID20005102C1 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human PDK1 Kinase Domain in Complex with Allosteric Compound PSE10 Bound to the PIF-Pocket | PDB:5LVO | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.09 Å | Mutation | Yes | [10] |
| PDB Sequence |
QPRKKRPEDF
82 KFGKILGEGS92 FSTVVLAREL102 ATSREYAIKI112 LEKRHIIKEN122 KVPYVTRERD 132 VMSRLDHPFF142 VKLYFTFQDD152 EKLYFGLSYA162 KNGELLKYIR172 KIGSFDETCT 182 RFYTAEIVSA192 LEYLHGKGII202 HRDLKPENIL212 LNEDMHIQIT222 DFGTAKVLSP 232 ESKQARANFV243 GTAQYVSPEL253 LTEKSACKSS263 DLWALGCIIY273 QLVAGLPPFR 283 AGNEGLIFAK293 IIKLEYDFPE303 KFFPKARDLV313 EKLLVLDATK323 RLGCEEMEGY 333 GPLKAHPFFE343 SVTWENLHQQ353 TPPKLT
|
|||||
|
|
LEU88
3.009
GLY89
2.407
GLU90
2.837
GLY91
2.767
SER92
1.945
PHE93
4.090
SER94
1.823
THR95
4.911
VAL96
2.726
ALA109
2.982
LYS111
2.180
GLU130
4.976
VAL143
2.632
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Adenine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human PDK1 Kinase Domain in Complex with Adenine Bound to the ATP-Binding Site | PDB:5LVM | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.26 Å | Mutation | Yes | [10] |
| PDB Sequence |
KKRPEDFKFG
85 KILGEGSFST95 VVLARELATS105 REYAIKILEK115 RHIIKENKVP125 YVTRERDVMS 135 RLDHPFFVKL145 YFTFQDDEKL155 YFGLSYAKNG165 ELLKYIRKIG175 SFDETCTRFY 185 TAEIVSALEY195 LHGKGIIHRD205 LKPENILLNE215 DMHIQITDFG225 TAKVLSPESK 235 QARANFVGTA246 QYVSPELLTE256 KSACKSSDLW266 ALGCIIYQLV276 AGLPPFRAGN 286 EGLIFAKIIK296 LEYDFPEKFF306 PKARDLVEKL316 LVLDATKRLG326 CEEMEGYGPL 336 KAHPFFESVT346 WENLHQQTPP356 KLT
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |
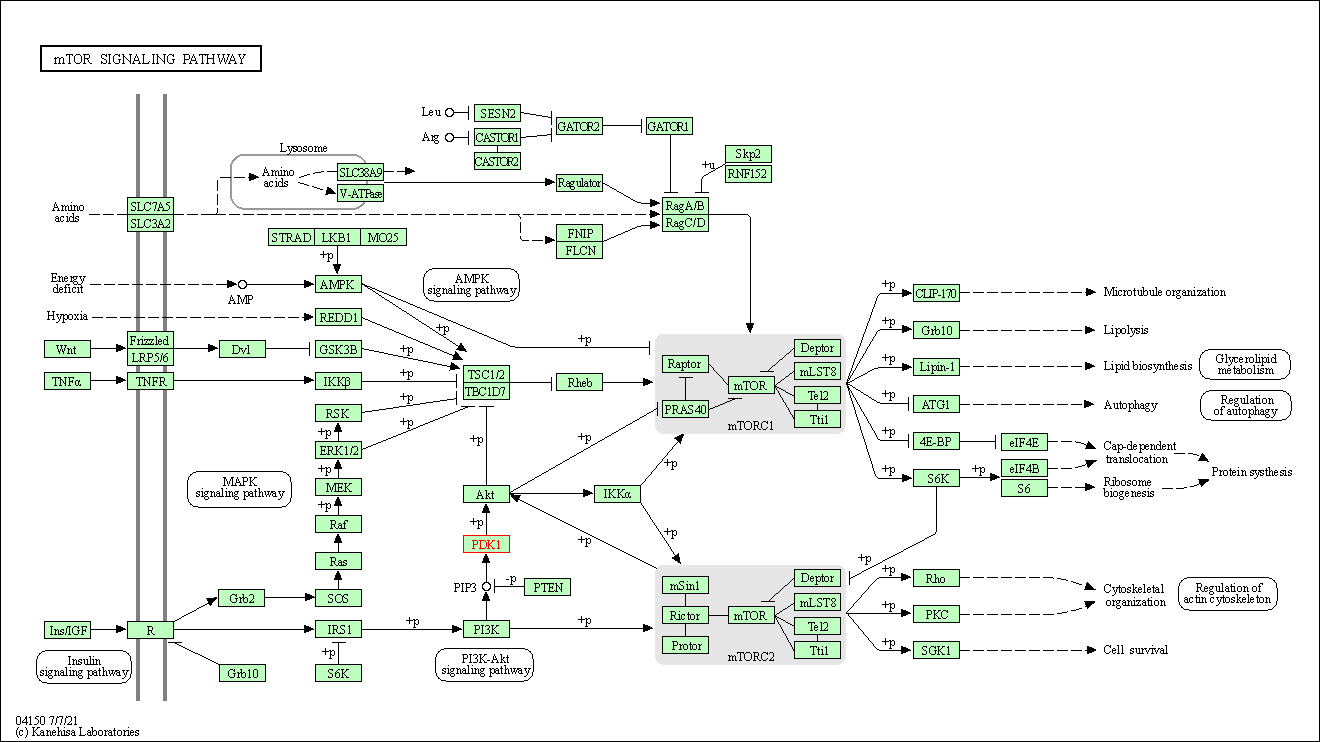
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
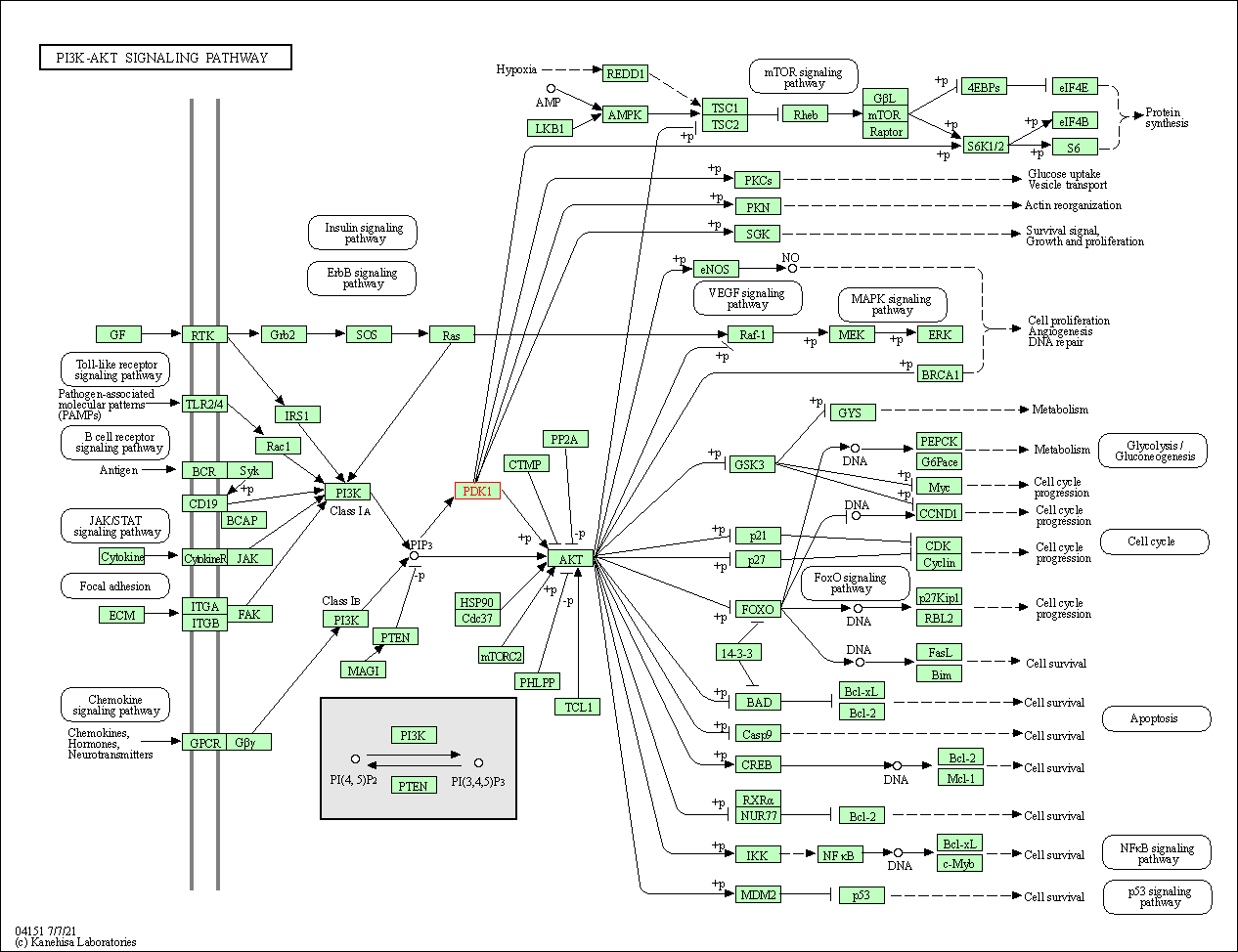
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | Affiliated Target |
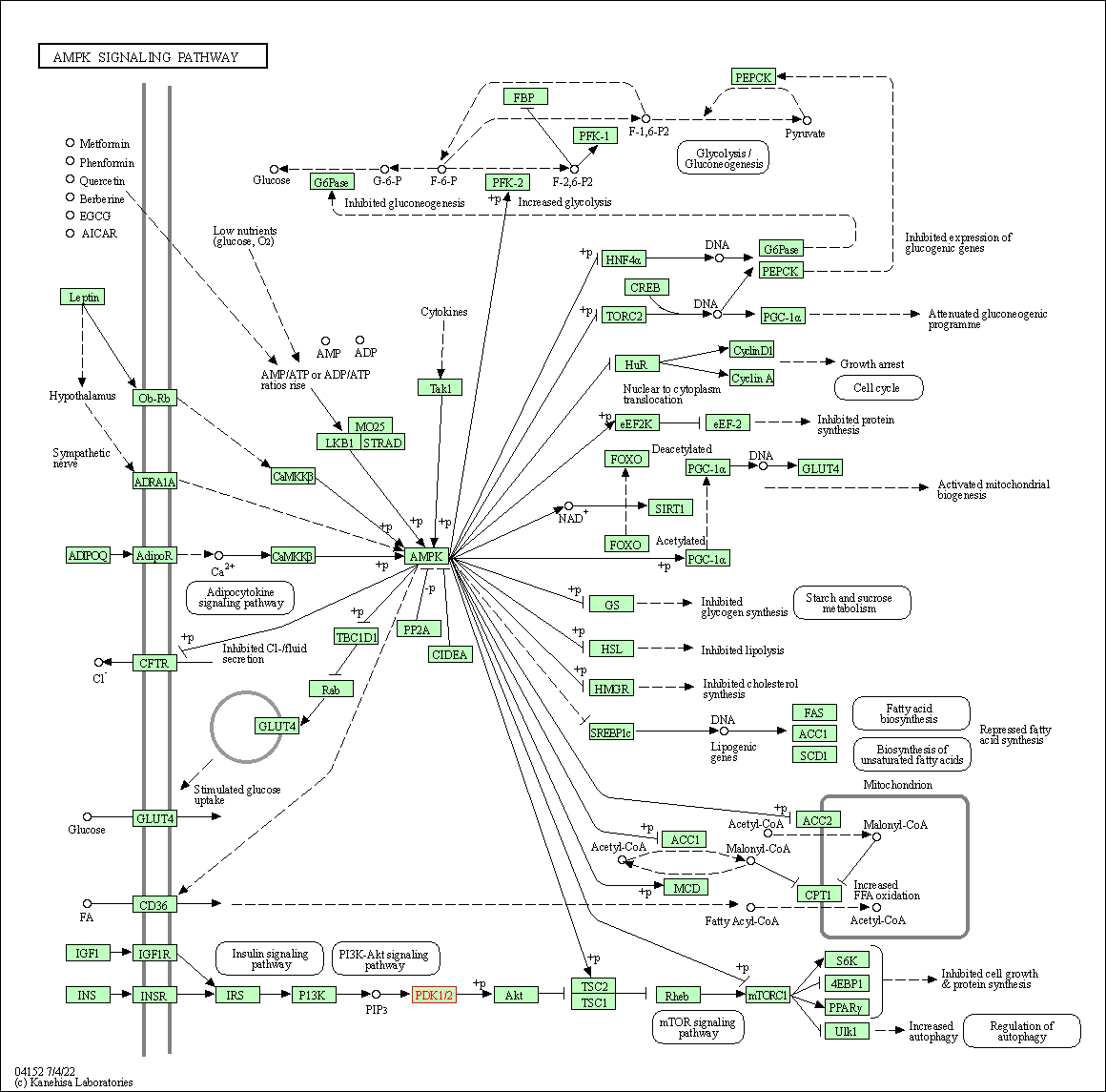
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |
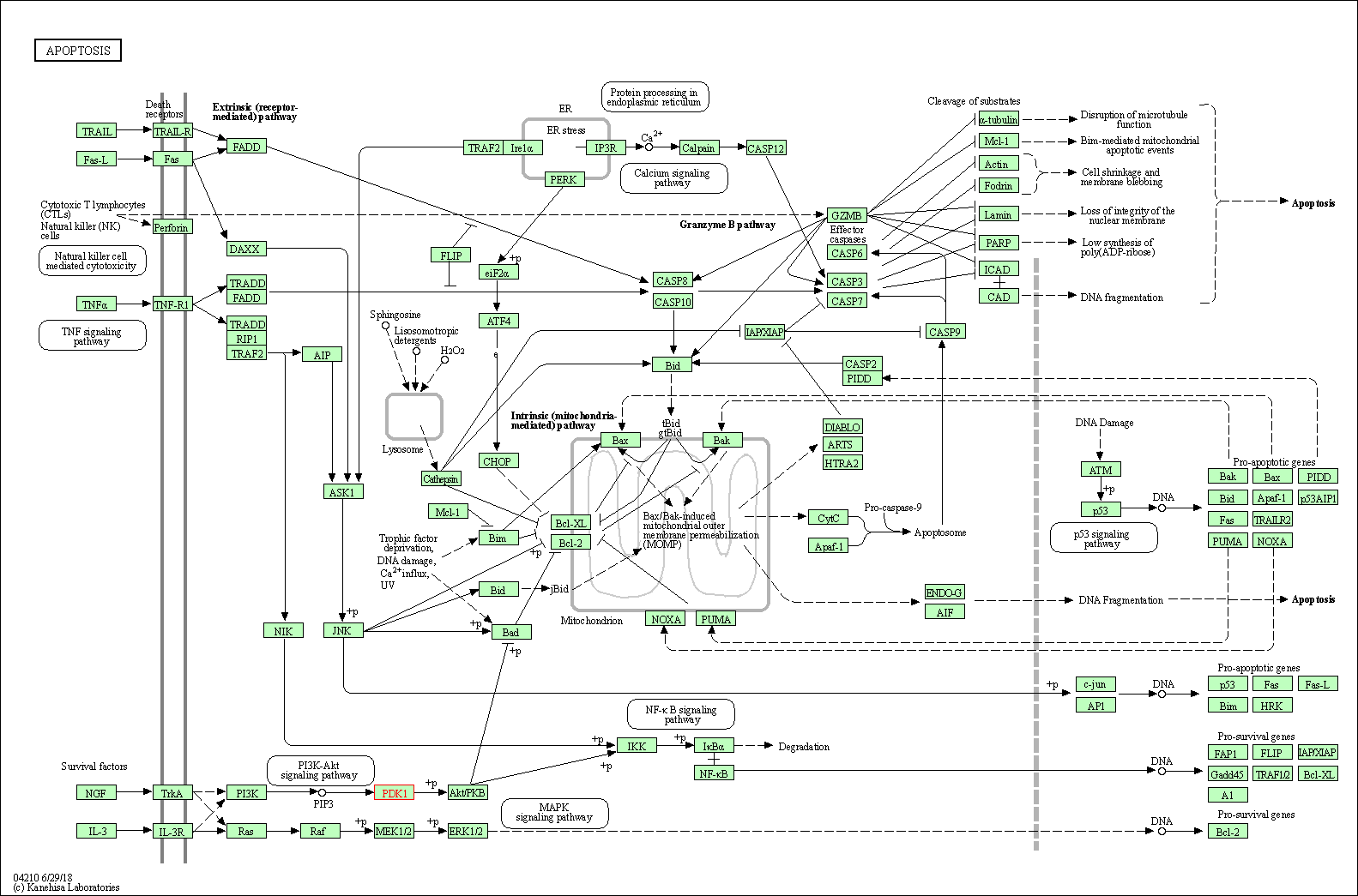
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Axon guidance | hsa04360 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | hsa04960 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 18 | Degree centrality | 1.93E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 4.49E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.48E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.63E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.58E+01 | Topological coefficient | 9.13E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 8005). | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00978523) Study of AR-12 (2-Amino-N-[4-[5-(2 Phenanthrenyl)-3-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl] Phenyl]-Acetamide) in Adult Patients With Advanced or Recurrent Solid Tumors orLymphoma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | Novel small molecule inhibitors of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1. J Biol Chem. 2005 May 20;280(20):19867-74. | |||||
| REF 5 | Genetic inactivation or pharmacological inhibition of Pdk1 delays development and inhibits metastasis of Braf(V600E)::Pten(-/-) melanoma. Oncogene. 2014 Aug 21;33(34):4330-9. | |||||
| REF 6 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 7 | Targeting 3-phosphoinoside-dependent kinase-1 to inhibit insulin-like growth factor-I induced AKT and p70 S6 kinase activation in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48402. | |||||
| REF 8 | Molecular pharmacology and antitumor activity of PHT-427, a novel Akt/phosphatidylinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 pleckstrin homology domain inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Mar;9(3):706-17. | |||||
| REF 9 | 2,3,5-Trisubstituted pyridines as selective AKT inhibitors. Part II: Improved drug-like properties and kinase selectivity from azaindazoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jan 15;20(2):679-83. | |||||
| REF 10 | Bidirectional Allosteric Communication between the ATP-Binding Site and the Regulatory PIF Pocket in PDK1 Protein Kinase. Cell Chem Biol. 2016 Oct 20;23(10):1193-1205. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

