Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T37961
(Former ID: TTDI03430)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
PAK-1 protein kinase (PAK1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
p65-PAK; p21-activated kinase 1; Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1; PAK-1; Alpha-PAK
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PAK1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Can directly phosphorylate BAD and protects cells against apoptosis. Activated by interaction with CDC42 and RAC1. Functions as GTPase effector that links the Rho-related GTPases CDC42 and RAC1 to the JNK MAP kinase pathway. Phosphorylates and activates MAP2K1, and thereby mediates activation of downstream MAP kinases. Involved in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, actin stress fibers and of focal adhesion complexes. Phosphorylates the tubulin chaperone TBCB and thereby plays a role in the regulation of microtubule biogenesis and organization of the tubulin cytoskeleton. Plays a role in the regulation of insulin secretion in response to elevated glucose levels. Part of a ternary complex that contains PAK1, DVL1 and MUSK that is important for MUSK-dependent regulation of AChR clustering during the formation of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Activity is inhibited in cells undergoing apoptosis, potentially due to binding of CDC2L1 and CDC2L2. Phosphorylates MYL9/MLC2. Phosphorylates RAF1 at 'Ser-338' and 'Ser-339' resulting in: activation of RAF1, stimulation of RAF1 translocation to mitochondria, phosphorylation of BAD by RAF1, and RAF1 binding to BCL2. Phosphorylates SNAI1 at 'Ser-246' promoting its transcriptional repressor activity by increasing its accumulation in the nucleus. In podocytes, promotes NR3C2 nuclear localization. Required for atypical chemokine receptor ACKR2-induced phosphorylation of LIMK1 and cofilin (CFL1) and for the up-regulation of ACKR2 from endosomal compartment to cell membrane, increasing its efficiency in chemokine uptake and degradation. In synapses, seems to mediate the regulation of F-actin cluster formation performed by SHANK3, maybe through CFL1 phosphorylation and inactivation. Plays a role in RUFY3-mediated facilitating gastric cancer cells migration and invasion. In response to DNA damage, phosphorylates MORC2 which activates its ATPase activity and facilitates chromatin remodeling. Protein kinase involved in intracellular signaling pathways downstream of integrins and receptor-type kinases that plays an important role in cytoskeleton dynamics, in cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, apoptosis, mitosis, and in vesicle-mediated transport processes.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSNNGLDIQDKPPAPPMRNTSTMIGAGSKDAGTLNHGSKPLPPNPEEKKKKDRFYRSILP
GDKTNKKKEKERPEISLPSDFEHTIHVGFDAVTGEFTGMPEQWARLLQTSNITKSEQKKN PQAVLDVLEFYNSKKTSNSQKYMSFTDKSAEDYNSSNALNVKAVSETPAVPPVSEDEDDD DDDATPPPVIAPRPEHTKSVYTRSVIEPLPVTPTRDVATSPISPTENNTTPPDALTRNTE KQKKKPKMSDEEILEKLRSIVSVGDPKKKYTRFEKIGQGASGTVYTAMDVATGQEVAIKQ MNLQQQPKKELIINEILVMRENKNPNIVNYLDSYLVGDELWVVMEYLAGGSLTDVVTETC MDEGQIAAVCRECLQALEFLHSNQVIHRDIKSDNILLGMDGSVKLTDFGFCAQITPEQSK RSTMVGTPYWMAPEVVTRKAYGPKVDIWSLGIMAIEMIEGEPPYLNENPLRALYLIATNG TPELQNPEKLSAIFRDFLNRCLEMDVEKRGSAKELLQHQFLKIAKPLSSLTPLIAAAKEA TKNNH Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T71V6E | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of phosphorylated PAK1 kinase domain in complex with ATP | PDB:3Q53 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.09 Å | Mutation | Yes | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
DEEILEKLRS
259 IVSVGDPKKK269 YTRFEKIGQG279 ASGTVYTAMD289 VATGQEVAIR299 QMNLQQQPKK 309 ELIINEILVM319 RENKNPNIVN329 YLDSYLVGDE339 LWVVMEYLAG349 GSLTDVVTET 359 CMDEGQIAAV369 CRECLQALEF379 LHSNQVIHRD389 IKSDNILLGM399 DGSVKLTDFG 409 FCAQITPEQS419 KRSMVGTPYW430 MAPEVVTRKA440 YGPKVDIWSL450 GIMAIEMIEG 460 EPPYLNENPL470 RALYLIATNG480 TPELQNPEKL490 SAIFRDFLNR500 CLEMDVEKRG 510 SAKELIQHQF520 LKIAKPLSSL530 TPLIAAAKEA540 T
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: PF-3758309 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Back pocket flexibility provides group-II PAK selectivity for type 1 kinase inhibitors | PDB:4O0R | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.40 Å | Mutation | No | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
SDEEILEKLR
258 SIVSVGDPKK268 KYTRFEKIGQ278 GASGTVYTAM288 DVATGQEVAI298 KQMNLQQQPK 308 KELIINEILV318 MRENKNPNIV328 NYLDSYLVGD338 ELWVVMEYLA348 GGSLTDVVTE 358 TCMDEGQIAA368 VCRECLQALE378 FLHSNQVIHR388 NIKSDNILLG398 MDGSVKLTDF 408 GFCAQITPEQ418 SKRSEMVGTP428 YWMAPEVVTR438 KAYGPKVDIW448 SLGIMAIEMI 458 EGEPPYLNEN468 PLRALYLIAT478 NGTPELQNPE488 KLSAIFRDFL498 NRCLEMDVEK 508 RGSAKELLQH518 QFLKIAKPLS528 SLTPLIAAAK538 EAT
|
|||||
|
|
ILE276
3.167
GLY277
3.961
GLN278
4.567
GLY279
3.634
SER281
3.723
GLY282
3.261
THR283
4.243
VAL284
3.749
ALA297
3.190
LYS299
3.548
VAL328
3.976
MET344
3.815
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Axon guidance | hsa04360 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hippo signaling pathway - multiple species | hsa04392 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
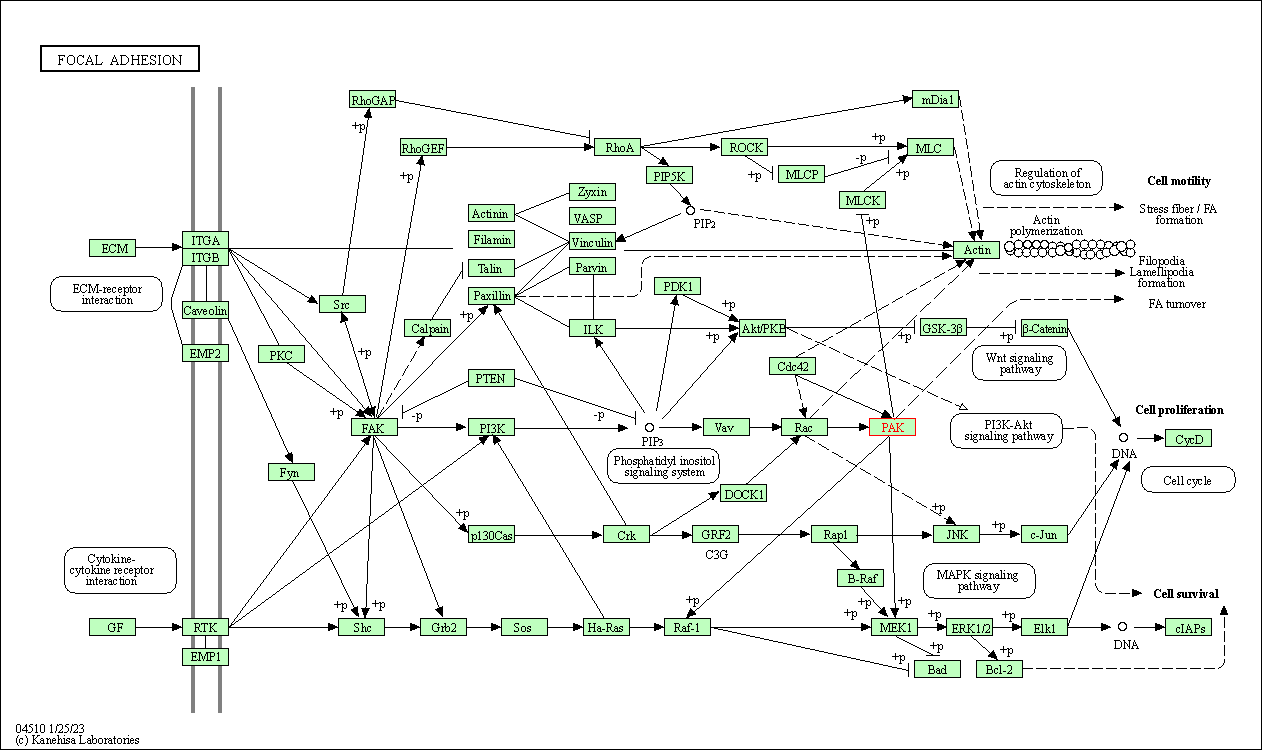
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |
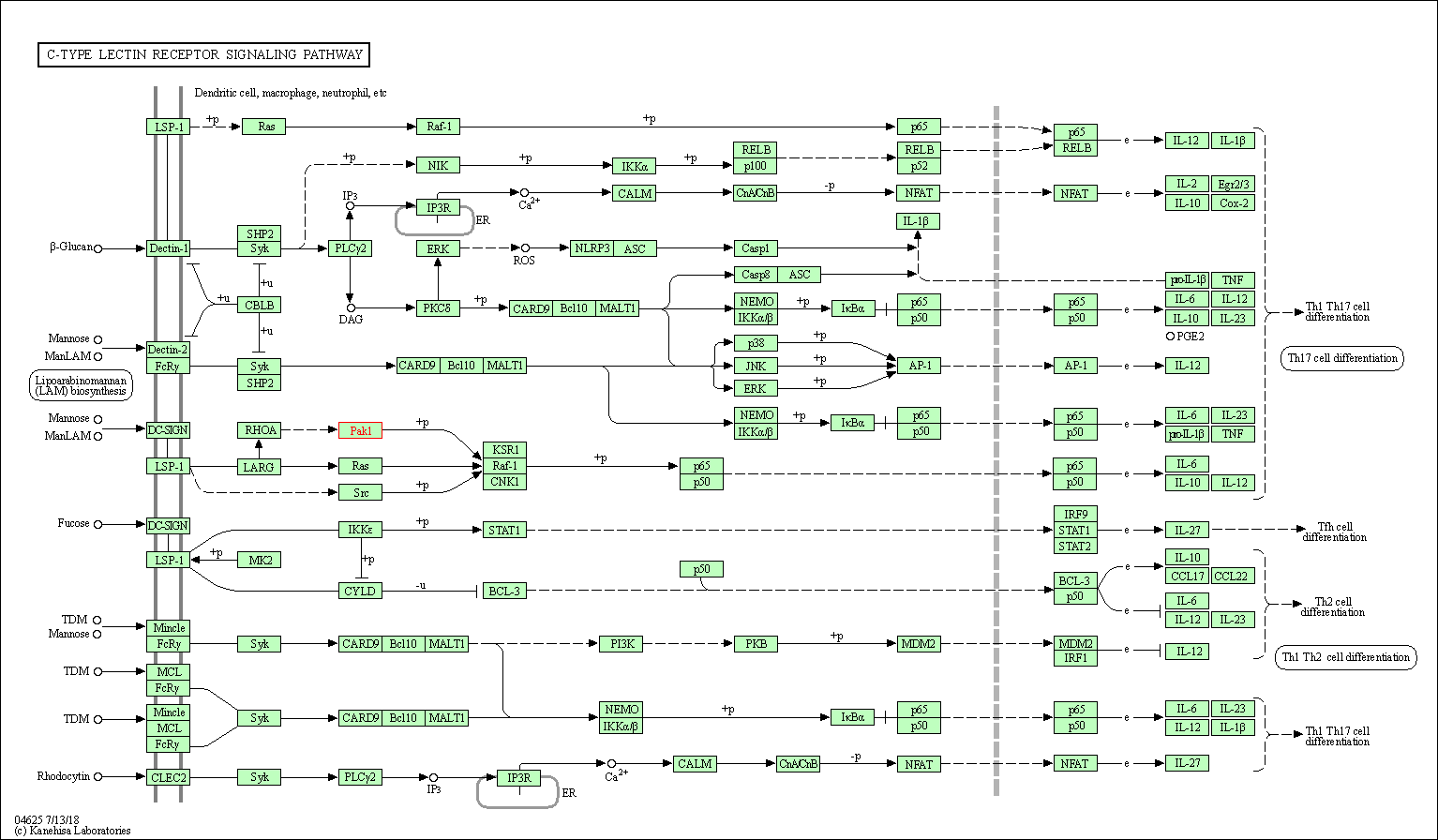
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |
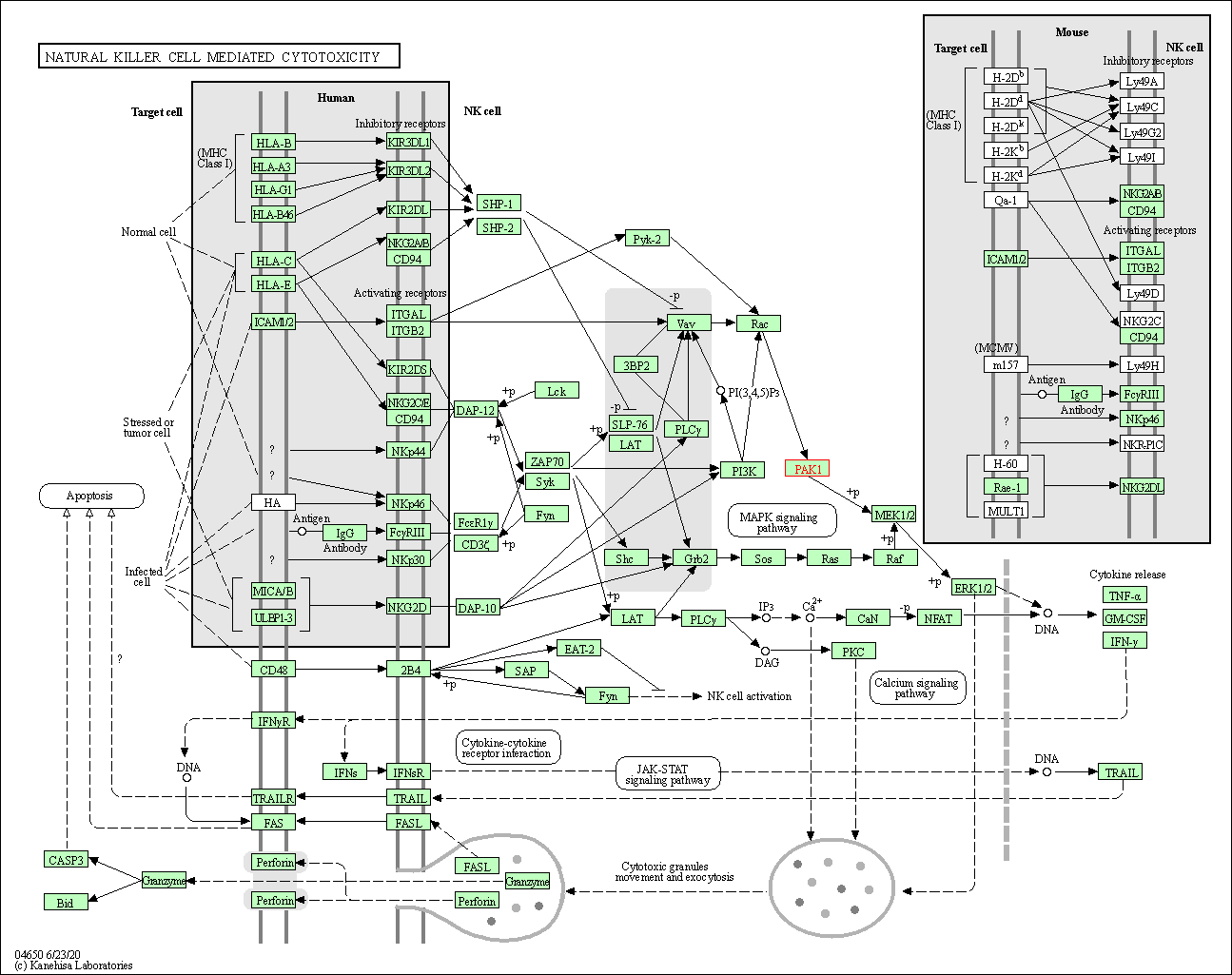
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |
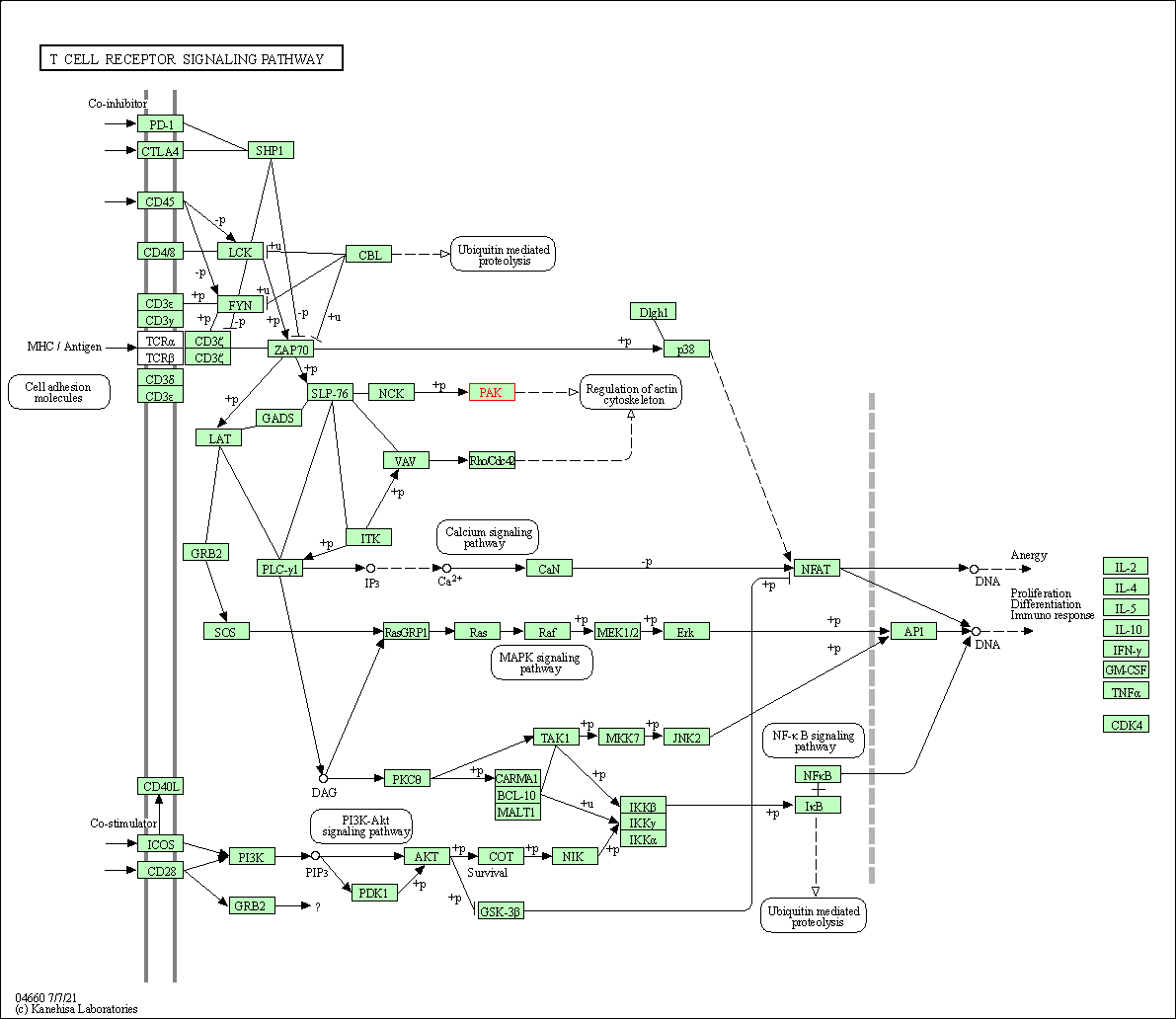
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 22 | Degree centrality | 2.36E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.56E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.46E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.64E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.17E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.85E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | PAK1: A Therapeutic Target for Cancer Treatment. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2013 Mar 19;4(5):431-2. | |||||
| REF 2 | 2,3,5-Trisubstituted pyridines as selective AKT inhibitors. Part II: Improved drug-like properties and kinase selectivity from azaindazoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jan 15;20(2):679-83. | |||||
| REF 3 | Pyridylthiazole-based ureas as inhibitors of Rho associated protein kinases (ROCK1 and 2). Medchemcomm. 2012 Jun 1;3(6):699-709. | |||||
| REF 4 | Structural insights into the autoactivation mechanism of p21-activated protein kinase. Structure. 2011 Dec 7;19(12):1752-61. | |||||
| REF 5 | Back pocket flexibility provides group II p21-activated kinase (PAK) selectivity for type I 1/2 kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2014 Feb 13;57(3):1033-45. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

