Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T50224
(Former ID: TTDI03521)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-5 (RSK5)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
S6K-alpha-5; RSKL; RSK-like protein kinase; Nuclear mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1; MSK1; 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 5
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
RPS6KA5
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Phosphorylates CREB1 and ATF1 in response to mitogenic or stress stimuli such as UV-C irradiation, epidermal growth factor (EGF) and anisomycin. Plays an essential role in the control of RELA transcriptional activity in response to TNF and upon glucocorticoid, associates in the cytoplasm with the glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1 and contributes to RELA inhibition and repression of inflammatory gene expression. In skeletal myoblasts is required for phosphorylation of RELA at 'Ser-276' during oxidative stress. In erythropoietin-stimulated cells, is necessary for the 'Ser-727' phosphorylation of STAT3 and regulation of its transcriptional potential. Phosphorylates ETV1/ER81 at 'Ser-191' and 'Ser-216', and thereby regulates its ability to stimulate transcription, which may be important during development and breast tumor formation. Directly represses transcription via phosphorylation of 'Ser-1' of histone H2A. Phosphorylates 'Ser-10' of histone H3 in response to mitogenics, stress stimuli and EGF, which results in the transcriptional activation of several immediate early genes, including proto-oncogenes c-fos/FOS and c-jun/JUN. May also phosphorylate 'Ser-28' of histone H3. Mediates the mitogen- and stress-induced phosphorylation of high mobility group protein 1 (HMGN1/HMG14). In lipopolysaccharide-stimulated primary macrophages, acts downstream of the Toll-like receptor TLR4 to limit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Functions probably by inducing transcription of the MAP kinase phosphatase DUSP1 and the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin 10 (IL10), via CREB1 and ATF1 transcription factors. Plays a role in neuronal cell death by mediating the downstream effects of excitotoxic injury. Phosphorylates TRIM7 at 'Ser-107' in response to growth factor signaling via the MEK/ERK pathway, thereby stimulating its ubiquitin ligase activity. Serine/threonine-protein kinase that is required for the mitogen or stress-induced phosphorylation of the transcription factors CREB1 and ATF1 and for the regulation of the transcription factors RELA, STAT3 and ETV1/ER81, and that contributes to gene activation by histone phosphorylation and functions in the regulation of inflammatory genes.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MEEEGGSSGGAAGTSADGGDGGEQLLTVKHELRTANLTGHAEKVGIENFELLKVLGTGAY
GKVFLVRKISGHDTGKLYAMKVLKKATIVQKAKTTEHTRTERQVLEHIRQSPFLVTLHYA FQTETKLHLILDYINGGELFTHLSQRERFTEHEVQIYVGEIVLALEHLHKLGIIYRDIKL ENILLDSNGHVVLTDFGLSKEFVADETERAYSFCGTIEYMAPDIVRGGDSGHDKAVDWWS LGVLMYELLTGASPFTVDGEKNSQAEISRRILKSEPPYPQEMSALAKDLIQRLLMKDPKK RLGCGPRDADEIKEHLFFQKINWDDLAAKKVPAPFKPVIRDELDVSNFAEEFTEMDPTYS PAALPQSSEKLFQGYSFVAPSILFKRNAAVIDPLQFHMGVERPGVTNVARSAMMKDSPFY QHYDLDLKDKPLGEGSFSICRKCVHKKSNQAFAVKIISKRMEANTQKEITALKLCEGHPN IVKLHEVFHDQLHTFLVMELLNGGELFERIKKKKHFSETEASYIMRKLVSAVSHMHDVGV VHRDLKPENLLFTDENDNLEIKIIDFGFARLKPPDNQPLKTPCFTLHYAAPELLNQNGYD ESCDLWSLGVILYTMLSGQVPFQSHDRSLTCTSAVEIMKKIKKGDFSFEGEAWKNVSQEA KDLIQGLLTVDPNKRLKMSGLRYNEWLQDGSQLSSNPLMTPDILGSSGAAVHTCVKATFH AFNKYKREGFCLQNVDKAPLAKRRKMKKTSTSTETRSSSSESSHSSSSHSHGKTTPTKTL QPSNPADSNNPETLFQFSDSVA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: AMP-PNP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the C-terminal kinase domain of msk1 in complex with AMP-PNP | PDB:3KN5 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.40 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
KDSPFYQHYD
424 LDLKDKPLGE434 GSFSICRKCV444 HKKSNQAFAV454 KIISKRMEAN464 TQKEITALKL 474 CEGHPNIVKL484 HEVFHDQLHT494 FLVMELLNGG504 ELFERIKKKK514 HFSETEASYI 524 MRKLVSAVSH534 MHDVGVVHRD544 LKPENLLFTD554 LEIKIIDFGF568 ARLKPPNGYD 600 ESCDLWSLGV610 ILYTMLSGQV620 PFQCTSAVEI637 MKKIKKGDFS647 FEGEAWKNVS 657 QEAKDLIQGL667 LTVDPNKRLK677 MSGLRYNEWL687 QDGSQLSSNP697 LMTPDILGSS 707 GAAVHTCVKA717 TFHAFNKYKR727 EG
|
|||||
|
|
LEU432
2.773
GLY433
3.628
GLU434
2.835
GLY435
4.004
CYS440
4.456
ALA453
3.849
VAL482
4.311
MET498
3.901
GLU499
2.827
LEU500
3.446
LEU501
2.822
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Oxamic acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of C-terminal domain of MSK1 in complex with in covalently bound literature RSK2 inhibitor pyrrolopyrimidine cyanoacrylamide compound 25 (co-crystal) | PDB:7UP6 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.60 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
DSPFYQHYDL
425 DLKDKPLGEG435 SFSICRKCVH445 KKSNQAFAVK455 IISKRMEANT465 QKEITALKLC 475 EGHPNIVKLH485 EVFHDQLHTF495 LVMELLNGGE505 LFERIKKKKH515 FSETEASYIM 525 RKLVSAVSHM535 HDVGVVHRDL545 KPENLLFTDE555 NLEIKIIDFG567 FARLKPGYDE 600 SCDLWSLGVI610 LYTMLSGQVP620 FQSAVEIMKK639 IKKGDFSFEG649 EAWKNVSQEA 659 KDLIQGLLTV669 DPNKRLKMSG679 LRYNEWLQDG689 SQLSSNPLMT699 PDILGSS |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
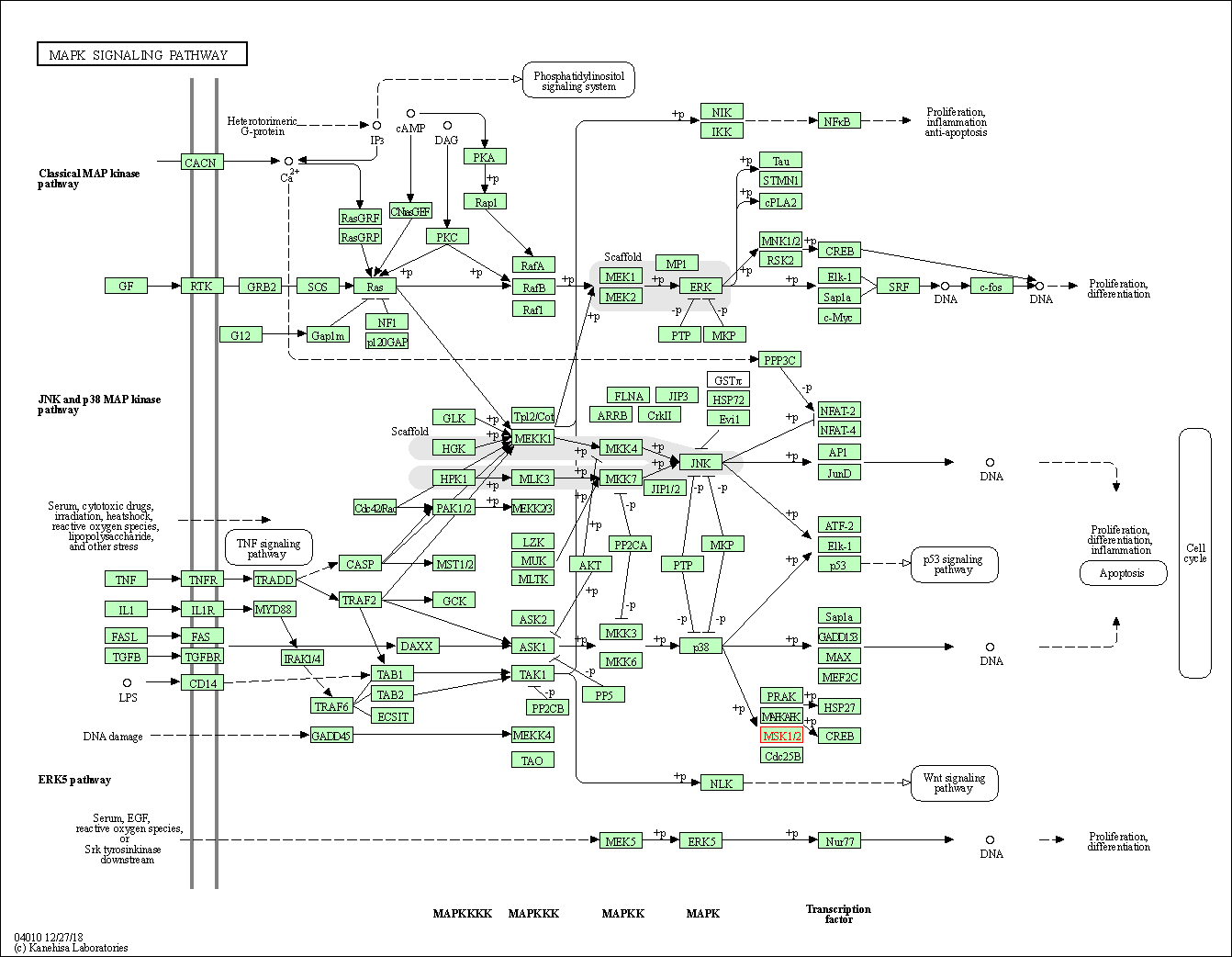
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |
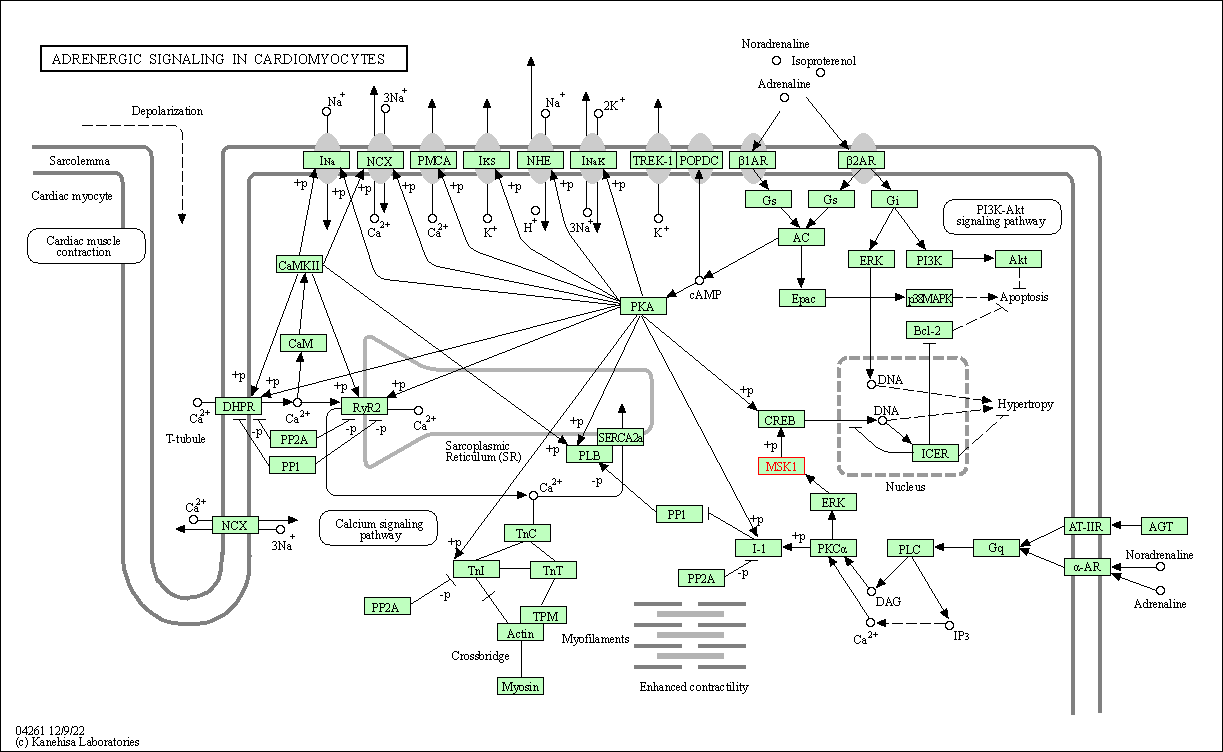
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |
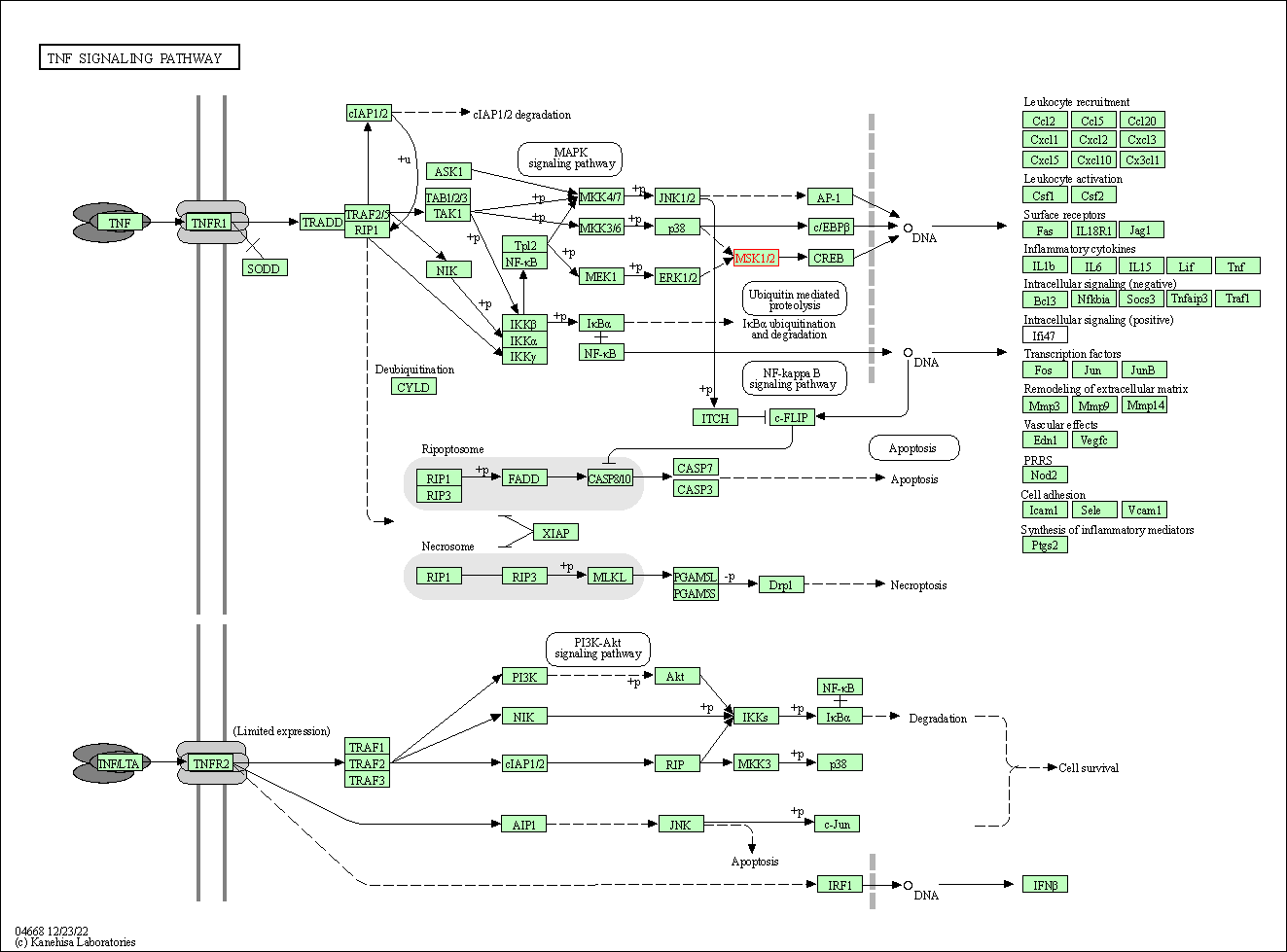
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |
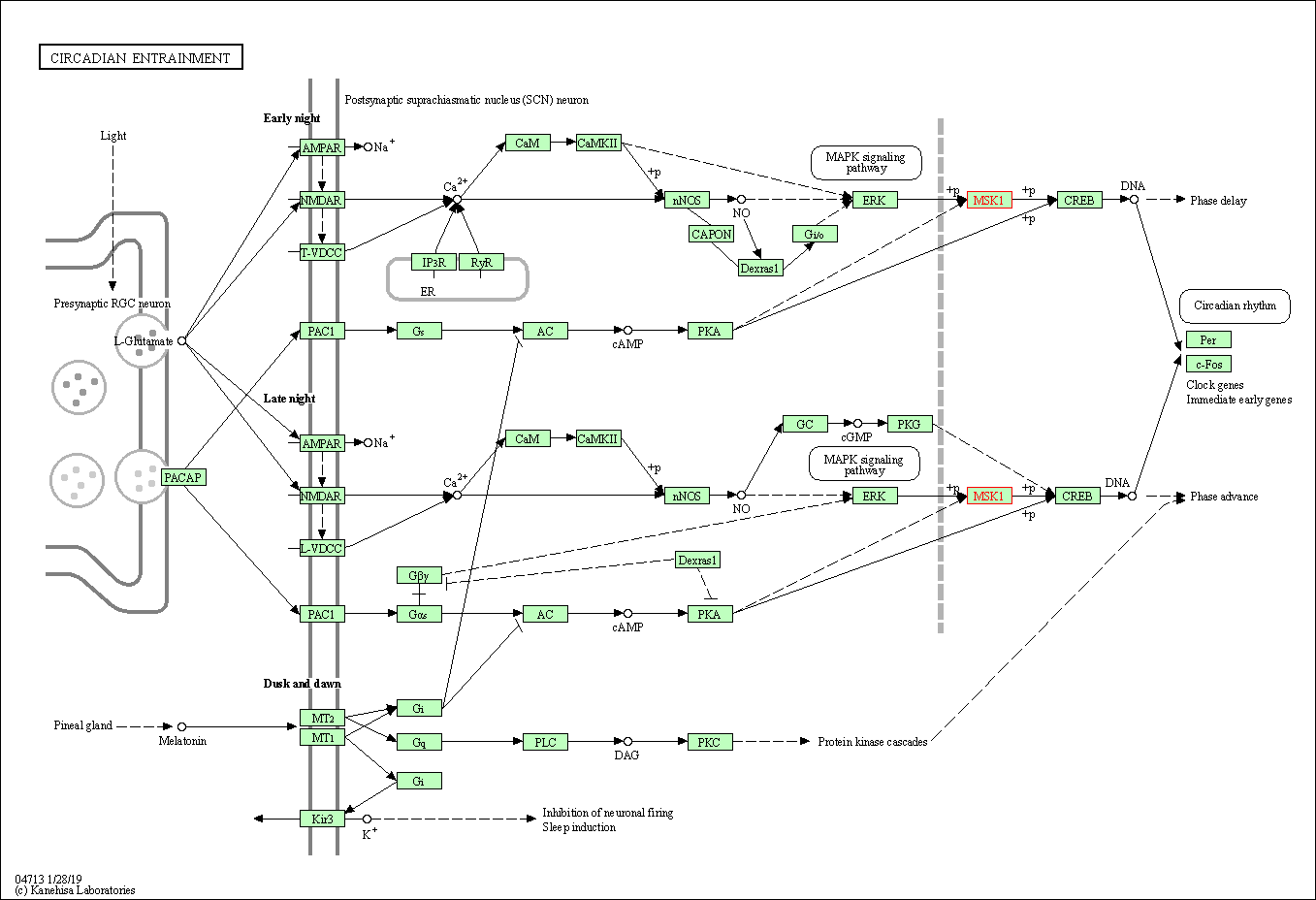
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 6 | Degree centrality | 6.45E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 6.14E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.22E-01 | Radiality | 1.39E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.33E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.30E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.03E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | (1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-ylamine derivatives: further optimisation as highly potent and selective MSK-1-inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jul 15;15(14):3407-11. | |||||
| REF 2 | The crystal structure of the active form of the C-terminal kinase domain of mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1. J Mol Biol. 2010 May 28;399(1):41-52. | |||||
| REF 3 | Discovery and Characterization of a Novel Series of Chloropyrimidines as Covalent Inhibitors of the Kinase MSK1. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022 Jun 25;13(7):1099-1108. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

