Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T53585
(Former ID: TTDS00195)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
HMGCR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 7 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Cardiovascular disease [ICD-11: BA00-BE2Z] | |||||
| 2 | Dyslipidemia [ICD-11: 5C80-5C81] | |||||
| 3 | Hyper-lipoproteinaemia [ICD-11: 5C80] | |||||
| 4 | Multiple sclerosis [ICD-11: 8A40] | |||||
| 5 | Myocardial infarction [ICD-11: BA41-BA43] | |||||
| 6 | Pain [ICD-11: MG30-MG3Z] | |||||
| 7 | Coronary atherosclerosis [ICD-11: BA80] | |||||
| Function |
Transmembrane glycoprotein that is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis as well as in the biosynthesis of nonsterol isoprenoids that are essential for normal cell function including ubiquinone and geranylgeranyl proteins.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
CH-OH donor oxidoreductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.1.1.34
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MLSRLFRMHGLFVASHPWEVIVGTVTLTICMMSMNMFTGNNKICGWNYECPKFEEDVLSS
DIIILTITRCIAILYIYFQFQNLRQLGSKYILGIAGLFTIFSSFVFSTVVIHFLDKELTG LNEALPFFLLLIDLSRASTLAKFALSSNSQDEVRENIARGMAILGPTFTLDALVECLVIG VGTMSGVRQLEIMCCFGCMSVLANYFVFMTFFPACVSLVLELSRESREGRPIWQLSHFAR VLEEEENKPNPVTQRVKMIMSLGLVLVHAHSRWIADPSPQNSTADTSKVSLGLDENVSKR IEPSVSLWQFYLSKMISMDIEQVITLSLALLLAVKYIFFEQTETESTLSLKNPITSPVVT QKKVPDNCCRREPMLVRNNQKCDSVEEETGINRERKVEVIKPLVAETDTPNRATFVVGNS SLLDTSSVLVTQEPEIELPREPRPNEECLQILGNAEKGAKFLSDAEIIQLVNAKHIPAYK LETLMETHERGVSIRRQLLSKKLSEPSSLQYLPYRDYNYSLVMGACCENVIGYMPIPVGV AGPLCLDEKEFQVPMATTEGCLVASTNRGCRAIGLGGGASSRVLADGMTRGPVVRLPRAC DSAEVKAWLETSEGFAVIKEAFDSTSRFARLQKLHTSIAGRNLYIRFQSRSGDAMGMNMI SKGTEKALSKLHEYFPEMQILAVSGNYCTDKKPAAINWIEGRGKSVVCEAVIPAKVVREV LKTTTEAMIEVNINKNLVGSAMAGSIGGYNAHAANIVTAIYIACGQDAAQNVGSSNCITL MEASGPTNEDLYISCTMPSIEIGTVGGGTNLLPQQACLQMLGVQGACKDNPGENARQLAR IVCGTVMAGELSLMAALAAGHLVKSHMIHNRSKINLQDLQGACTKKTA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A00809 ; BADD_A02409 ; BADD_A05311 ; BADD_A05828 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T21Q0D | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 12 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Aspirin | Drug Info | Approved | Pain | [1], [2] | |
| 2 | Atorvastatin | Drug Info | Approved | Cardiovascular disease | [3] | |
| 3 | Cerivastatin | Drug Info | Approved | Hyperlipidaemia | [4], [5] | |
| 4 | Crestor/TriLipix | Drug Info | Approved | Dyslipidemia | [3] | |
| 5 | Fluvastatin | Drug Info | Approved | Hypercholesterolaemia | [6], [7] | |
| 6 | Lovastatin | Drug Info | Approved | Hypercholesterolaemia | [7], [8] | |
| 7 | PITAVASTATIN CALCIUM | Drug Info | Approved | Dyslipidemia | [3], [9] | |
| 8 | Pravastatin | Drug Info | Approved | Hypercholesterolaemia | [10], [11] | |
| 9 | Rosuvastatin | Drug Info | Approved | Hypercholesterolaemia | [12], [13] | |
| 10 | Simvastatin | Drug Info | Approved | Hypercholesterolaemia | [7], [14] | |
| 11 | Teriflunomide | Drug Info | Approved | Hyperlipidaemia | [1] | |
| 12 | TOCOTRIENOL | Drug Info | Approved | Hyperlipidaemia | [15] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 4 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Premarin/Pravachol | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Hyperlipidaemia | [17] | |
| 2 | CRILVASTATIN | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hyperlipidaemia | [18] | |
| 3 | XZK-monascus | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hyperlipidaemia | [19] | |
| 4 | NCX-6560 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Cardiovascular disease | [17] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 7 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Bervastatin | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Thrombosis | [22] | |
| 2 | BMY-21950 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Hyperlipidaemia | [23], [24] | |
| 3 | RBx10558 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Hyperlipidaemia | [25] | |
| 4 | PF-3052334 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Arteriosclerosis | [26] | |
| 5 | BMY-22089 | Drug Info | Terminated | Hyperlipidaemia | [29], [30] | |
| 6 | CP-83101 | Drug Info | Terminated | Arteriosclerosis | [31] | |
| 7 | SR12813 | Drug Info | Terminated | Arteriosclerosis | [32], [33] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 113 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Aspirin | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Atorvastatin | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 3 | Cerivastatin | Drug Info | [7], [35], [36] | |||
| 4 | Crestor/TriLipix | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 5 | Fluvastatin | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 6 | Lovastatin | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 7 | PITAVASTATIN CALCIUM | Drug Info | [39], [40] | |||
| 8 | Pravastatin | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 9 | Rosuvastatin | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 10 | Simvastatin | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 11 | Teriflunomide | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 12 | TOCOTRIENOL | Drug Info | [43], [3] | |||
| 13 | CRILVASTATIN | Drug Info | [44], [3] | |||
| 14 | NCX-6560 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 15 | 2-cyclopropyl-4-substituted-phenoxy-quinoline derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 16 | Atorvastatin lactole derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 17 | Hexahydro naphthalene derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 18 | Hexahydro naphthalene derivative 2 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 19 | Hexahydro naphthalene derivative 3 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 20 | Lactol derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 21 | Lactol derivative 2 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 22 | Pitavastatin derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 23 | PMID27537201-Compound-Figure13b | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 24 | PMID27537201-Compound-Figure13c | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 25 | PMID27537201-Compound-Figure15a | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 26 | PMID27537201-Compound-Figure15b | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 27 | PMID27537201-Compound-Figure17 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 28 | Poly-substituted azoles statin lactone derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 29 | Poly-substituted azoles statin lactone derivative 2 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 30 | Poly-substituted miazine derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 31 | Pravastatin derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 32 | Quinoline derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 33 | Quinoline derivative 16 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 34 | Quinoline derivative 17 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 35 | Sterol derivative 1 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 36 | Sterol derivative 3 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 37 | Bervastatin | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 38 | BMY-21950 | Drug Info | [48], [3] | |||
| 39 | RBx10558 | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 40 | PF-3052334 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 41 | BMY-22089 | Drug Info | [48], [3] | |||
| 42 | CP-83101 | Drug Info | [51] | |||
| 43 | (E)-5-octadecen-7,9-diynoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 44 | (E)-octadecan-9-ynoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 45 | (R)-Mevalonate | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 46 | (Z)-5-octadecen-7,9-diynoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 47 | (Z)-7-octedecan-9-ynoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 48 | 1,4-Dithiothreitol | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 49 | 2'-Monophosphoadenosine 5'-Diphosphoribose | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 50 | 3-(1,3 dodecadiynyl)-6-oxiranebutanoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 51 | 3-Hydroxy-3-Methyl-Glutaric Acid | Drug Info | [55], [56] | |||
| 52 | 5-ketodihydromevinolin | Drug Info | [57] | |||
| 53 | 6-hydroxy-7,9-octadecadiynoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 54 | 7,9-octadecadiynoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 55 | 7,9-tetradecadiynoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 56 | 9-octadecynoic acid | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 57 | BPL-001 | Drug Info | [58] | |||
| 58 | Brutieridin | Drug Info | [58] | |||
| 59 | DFGYVAE | Drug Info | [59] | |||
| 60 | FPYVAE peptide | Drug Info | [59] | |||
| 61 | GFPDGG | Drug Info | [60] | |||
| 62 | GFPEGG | Drug Info | [60] | |||
| 63 | GFPTGG | Drug Info | [60] | |||
| 64 | GLPTGG | Drug Info | [60] | |||
| 65 | Nicotinamide-Adenine-Dinucleotide | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 66 | o-hydroxyatorvastatin | Drug Info | [61] | |||
| 67 | PMID15686906C17 | Drug Info | [62] | |||
| 68 | PMID15686906C29 | Drug Info | [62] | |||
| 69 | PMID1656041C11dd | Drug Info | [63] | |||
| 70 | PMID1656041C11ff | Drug Info | [63] | |||
| 71 | PMID1656041C11jj | Drug Info | [63] | |||
| 72 | PMID1656041C11nn | Drug Info | [63] | |||
| 73 | PMID1656041C4ff | Drug Info | [63] | |||
| 74 | PMID1656041C74 | Drug Info | [63] | |||
| 75 | PMID17560788C29f | Drug Info | [64] | |||
| 76 | PMID17574411C41 | Drug Info | [65] | |||
| 77 | PMID17574411C42 | Drug Info | [65] | |||
| 78 | PMID17574412C33 | Drug Info | [66] | |||
| 79 | PMID18072721C50 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 80 | PMID18155906C16f | Drug Info | [67] | |||
| 81 | PMID18412317C13b | Drug Info | [68] | |||
| 82 | PMID1875346C18 | Drug Info | [69] | |||
| 83 | PMID1895299C1 | Drug Info | [70] | |||
| 84 | PMID1895299C4p | Drug Info | [70] | |||
| 85 | PMID1895299C6v | Drug Info | [70] | |||
| 86 | PMID19502059C25d | Drug Info | [71] | |||
| 87 | PMID1992138C8b | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 88 | PMID1992149C13 | Drug Info | [73] | |||
| 89 | PMID1992149C9 | Drug Info | [74] | |||
| 90 | PMID2153213C13b | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 91 | PMID2153213C13g | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 92 | PMID2153213C1a | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 93 | PMID2153213C1e | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 94 | PMID2153213C1f | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 95 | PMID2153213C2c | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 96 | PMID2153213C2d | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 97 | PMID2153213C2f | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 98 | PMID2231594C3j | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 99 | PMID2231594C3k | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 100 | PMID2231594C3u | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 101 | PMID2296027C25 | Drug Info | [77] | |||
| 102 | PMID2296036C2g | Drug Info | [78] | |||
| 103 | PMID2296036C2t | Drug Info | [78] | |||
| 104 | PMID2296036C4d | Drug Info | [78] | |||
| 105 | PMID2296036C4i | Drug Info | [78] | |||
| 106 | PMID2909732C7 | Drug Info | [79] | |||
| 107 | PMID7932551C9 | Drug Info | [80] | |||
| 108 | PMID8246233C28 | Drug Info | [81] | |||
| 109 | PMID8246233C35 | Drug Info | [81] | |||
| 110 | PMID8246233C5ab | Drug Info | [81] | |||
| 111 | PMID8246234C3h | Drug Info | [82] | |||
| 112 | PMID8246237C18t | Drug Info | [83] | |||
| 113 | PMID8426367C18 | Drug Info | [84] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 5 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Premarin/Pravachol | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 2 | XZK-monascus | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 3 | SR12813 | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 4 | MT-001 | Drug Info | [58] | |||
| 5 | NCX-1067 | Drug Info | [58] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 1 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Mevastatin | Drug Info | [52] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Atorvastatin | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | COMPLEX OF THE CATALYTIC PORTION OF HUMAN HMG-COA REDUCTASE WITH ATORVASTATIN | PDB:1HWK | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.22 Å | Mutation | Yes | [85] |
| PDB Sequence |
PRPNEECLLS
463 DAEIIQLVNA473 KHIPAYKLET483 LIETHERGVS493 IRRQLLSKKL503 SEPSSLQYLP 513 YRDYNYSLVM523 GACCENVIGY533 MPIPVGVAGP543 LCLDEKEFQV553 PMATTEGCLV 563 ASTNRGCRAI573 GLGGGASSRV583 LADGMTRGPV593 VRLPRACDSA603 EVKAWLETSE 613 GFAVIKEAFD623 STSRFARLQK633 LHTSIAGRNL643 YIRFQSRSGD653 AMGMNMISKG 663 TEKALSKLHE673 YFPEMQILAV683 SGNYCTDKKP693 AAINWIEGRG703 KSVVCEAVIP 713 AKVVREVLKT723 TTEAMIEVNI733 NKNLVGSAMA743 GSIGGYNAHA753 ANIVTAIYIA 763 CGQDAAQNVG773 SSNCITLMEA783 SGPTNEDLYI793 SCTMPSIEIG803 TVGGGTNLLP 813 QQACLQMLGV823 QGACKDNPGE833 NARQLARIVC843 GTVMAGELSL853 MAALAAGH |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Fluvastatin | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | COMPLEX OF THE CATALYTIC PORTION OF HUMAN HMG-COA REDUCTASE WITH FLUVASTATIN | PDB:1HWI | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | Yes | [85] |
| PDB Sequence |
LSDAEIIQLV
471 NLETLIETHE489 RGVSIRRQLL499 SKKLSEPSSL509 QYLPYRDYNY519 SLVMGACCEN 529 VIGYMPIPVG539 VAGPLCLDEK549 EFQVPMATTE559 GCLVASTNRG569 CRAIGLGGGA 579 SSRVLADGMT589 RGPVVRLPRA599 CDSAEVKAWL609 ETSEGFAVIK619 EAFDSTSRFA 629 RLQKLHTSIA639 GRNLYIRFQS649 RSGDAMGMNM659 ISKGTEKALS669 KLHEYFPEMQ 679 ILAVSGNYCT689 DKKPAAINWI699 EGRGKSVVCE709 AVIPAKVVRE719 VLKTTTEAMI 729 EVNINKNLVG739 SAMAGSIGGY749 NAHAANIVTA759 IYIACGQDAA769 QNVGSSNCIT 779 LMEASGPTNE789 DLYISCTMPS799 IEIGTVGGGT809 NLLPQQACLQ819 MLGVQGACKD 829 NPGENARQLA839 RIVCGTVMAG849 ELSLMAALAA859 GHL
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patched domain-containing protein 4 (PTCHD4) | 20.732 (34/164) | 1.00E-03 |
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | hsa00900 | Affiliated Target |
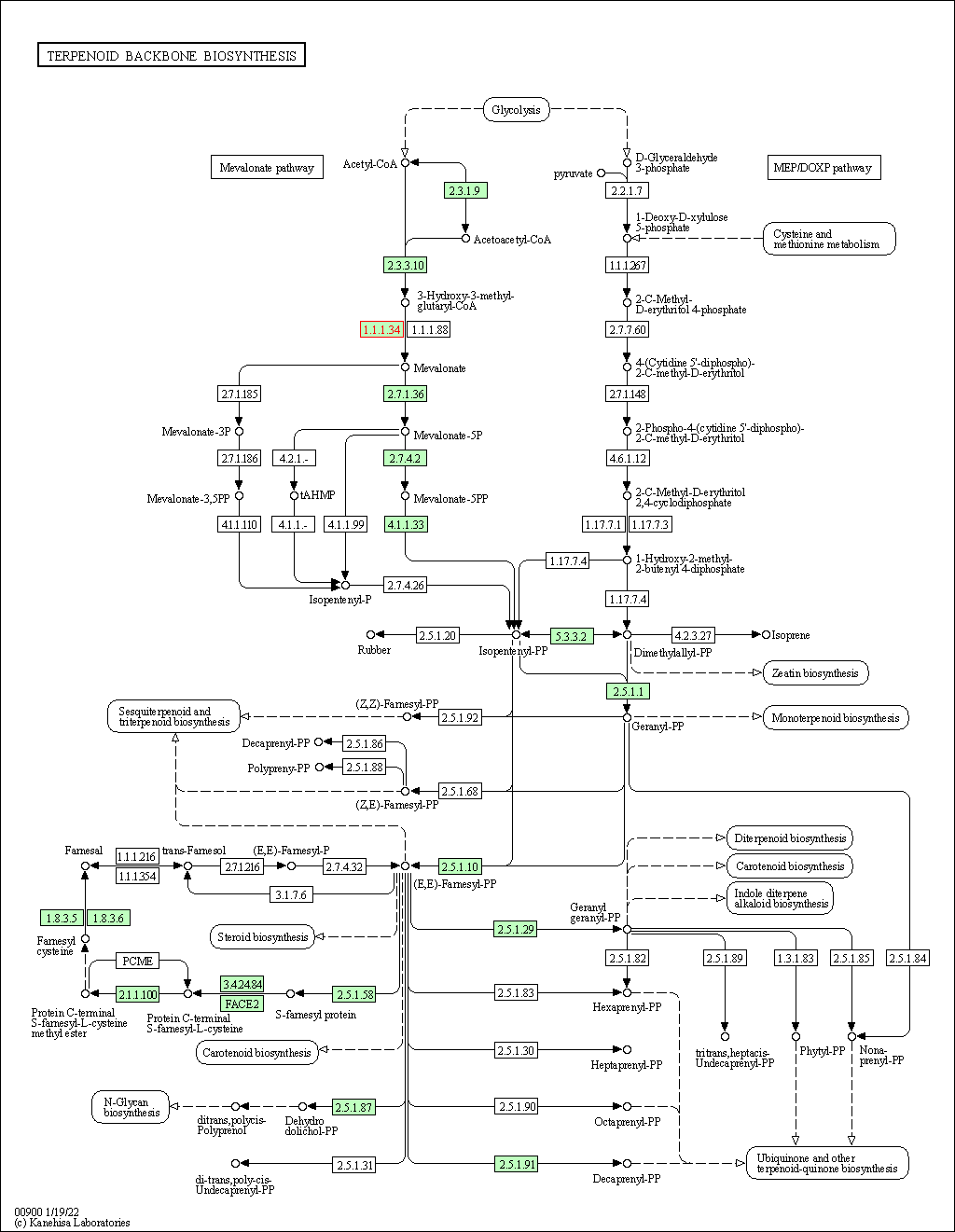
|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | Affiliated Target |
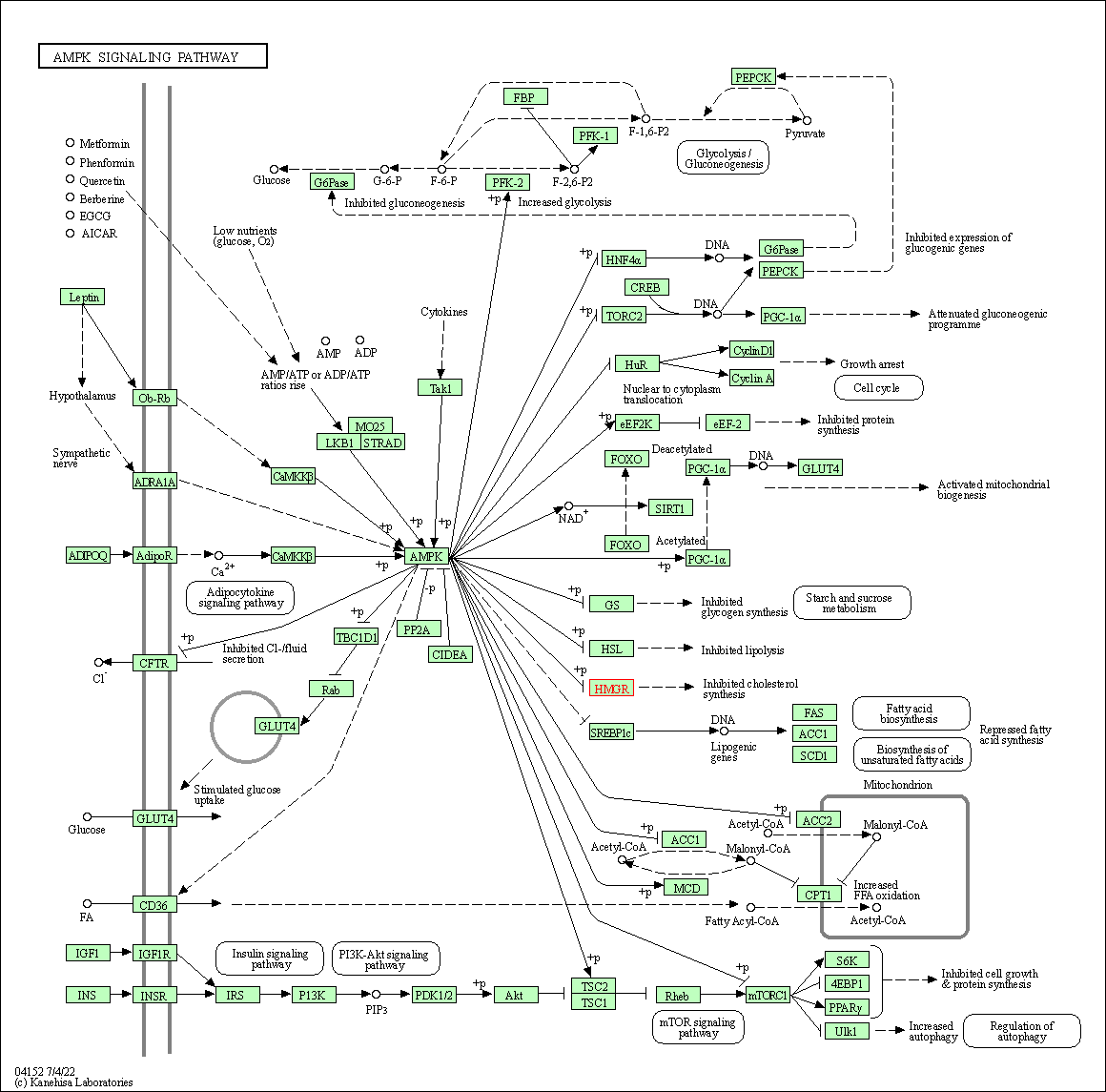
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Bile secretion | hsa04976 | Affiliated Target |
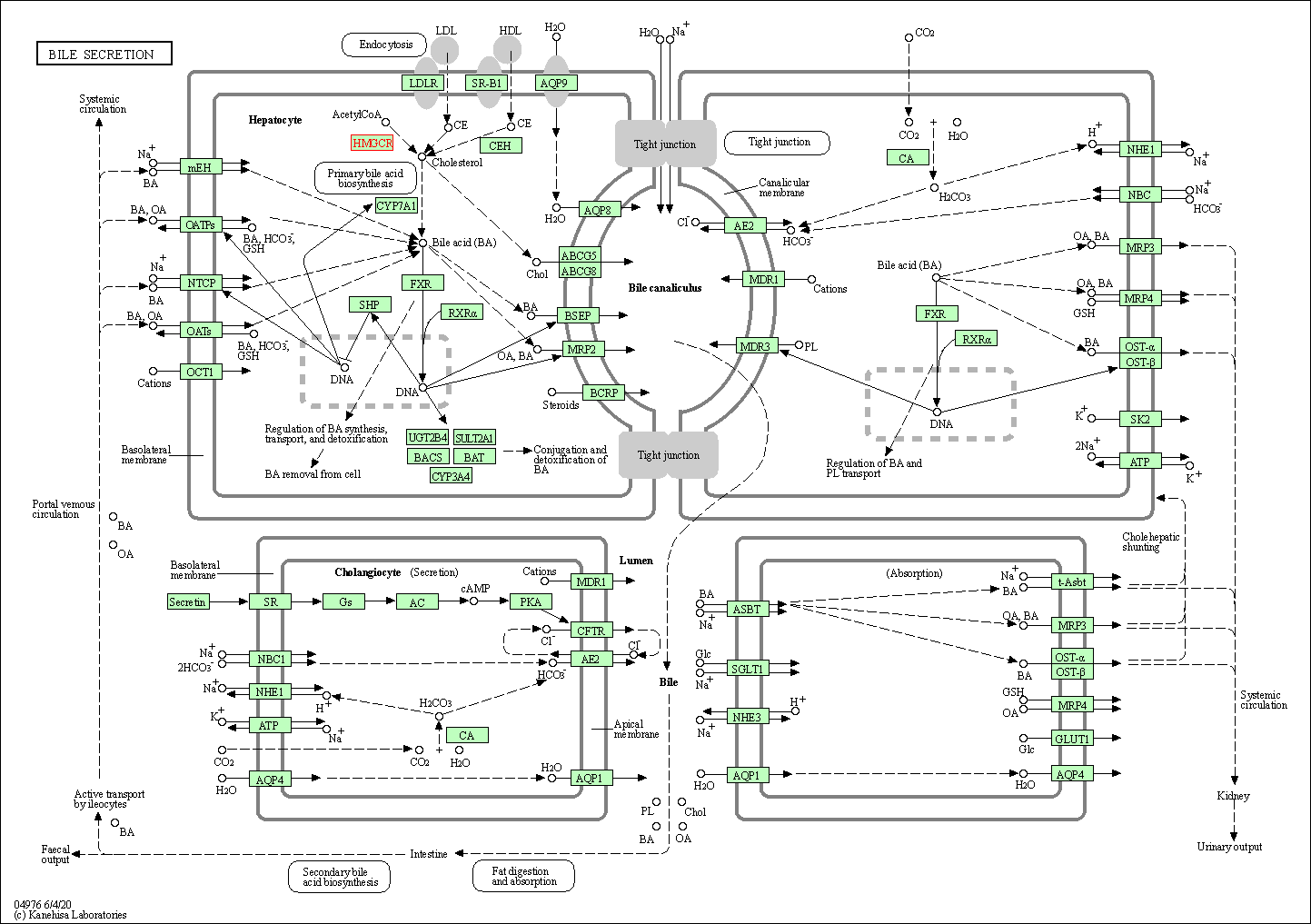
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 11 | Degree centrality | 1.18E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.62E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.09E-01 | Radiality | 1.36E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.64E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.76E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.68E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 3 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Superpathway of geranylgeranyldiphosphate biosynthesis I (via mevalonate) | |||||
| 2 | Superpathway of cholesterol biosynthesis | |||||
| 3 | Mevalonate pathway | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 5 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | |||||
| 2 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 3 | Biosynthesis of antibiotics | |||||
| 4 | AMPK signaling pathway | |||||
| 5 | Bile secretion | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 3 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL5 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | TGF_beta_Receptor Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 3 | TSH Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cholesterol biosynthesis | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Steroid Biosynthesis | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 7 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Statin Pathway | |||||
| 2 | Regulation of Lipid Metabolism by Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) | |||||
| 3 | Activation of Gene Expression by SREBP (SREBF) | |||||
| 4 | SREBF and miR33 in cholesterol and lipid homeostasis | |||||
| 5 | Integrated Breast Cancer Pathway | |||||
| 6 | SREBP signalling | |||||
| 7 | Cholesterol Biosynthesis | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| Target QSAR Model | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Emerging drugs in peripheral arterial disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 Mar;11(1):75-90. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4139). | |||||
| REF 3 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2950). | |||||
| REF 5 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800001906) | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2951). | |||||
| REF 7 | Emerging therapies for multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):99-127. | |||||
| REF 8 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2739). | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800004764) | |||||
| REF 10 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2953). | |||||
| REF 11 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 12 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2954). | |||||
| REF 13 | Emerging drugs for acute and chronic heart failure: current and future developments. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2007 Mar;12(1):75-95. | |||||
| REF 14 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2955). | |||||
| REF 15 | Vitamin E: tocopherols and tocotrienols as potential radiation countermeasures. J Radiat Res. 2013 Nov 1;54(6):973-88. | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01126073) A Double Blind, Randomized Study to Compare Influence of Niacin/Laropiprant on Functional and Morphological Characteristics of Arterial Wall and Parameters of Inflammation in Subjects With Coronary Heart Disease Already Treated With a Statin in Miran Sebestjen, University Medical Centre Ljubljana. | |||||
| REF 17 | Lovastatin and beyond: the history of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003 Jul;2(7):517-26. | |||||
| REF 18 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002276) | |||||
| REF 19 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800036391) | |||||
| REF 20 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800001903) | |||||
| REF 21 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800001230) | |||||
| REF 22 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002290) | |||||
| REF 23 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2981). | |||||
| REF 24 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002314) | |||||
| REF 25 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025331) | |||||
| REF 26 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025539) | |||||
| REF 27 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800011586) | |||||
| REF 28 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002307) | |||||
| REF 29 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2973). | |||||
| REF 30 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800004222) | |||||
| REF 31 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800000245) | |||||
| REF 32 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2763). | |||||
| REF 33 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002306) | |||||
| REF 34 | Equally potent inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis in human hepatocytes have distinguishable effects on different cytochrome P450 enzymes. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2000 Dec;21(9):353-64. | |||||
| REF 35 | Emerging antidyslipidemic drugs. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Jun;13(2):363-81. | |||||
| REF 36 | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor has protective effects against stroke events in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke. 2003 Jan;34(1):157-63. | |||||
| REF 37 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of AstraZeneca (2009). | |||||
| REF 38 | Microarray and biochemical analysis of lovastatin-induced apoptosis of squamous cell carcinomas. Neoplasia. 2002 Jul-Aug;4(4):337-46. | |||||
| REF 39 | Cholesterol-lowering effect of NK-104, a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, in guinea pig model of hyperlipidemia. Arzneimittelforschung. 2001;51(3):197-203. | |||||
| REF 40 | Synthesis and HMG CoA reductase inhibition of 4-thiophenyl quinolines as potential hypocholesterolemic agents. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Dec 15;15(24):7809-29. | |||||
| REF 41 | A randomized, double-blind trial comparing the efficacy and safety of pitavastatin versus pravastatin in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2002 Jun;162(2):373-9. | |||||
| REF 42 | New dimension of statin action on ApoB atherogenicity. Clin Cardiol. 2003 Jan;26(1 Suppl 1):I7-10. | |||||
| REF 43 | Inhibitory effect of delta-tocotrienol, a HMG CoA reductase inhibitor, on monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2002 Oct;48(5):332-7. | |||||
| REF 44 | Differences in hypolipidaemic effects of two statins on Hep G2 cells or human hepatocytes in primary culture. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;118(7):1862-8. | |||||
| REF 45 | NMR evaluation of total statin content and HMG-CoA reductase inhibition in red yeast rice (Monascus spp.) food supplements. Chin Med. 2012 Mar 22;7:8. | |||||
| REF 46 | HMG-CoA Reductase inhibitors: an updated review of patents of novel compounds and formulations (2011-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016 Nov;26(11):1257-1272. | |||||
| REF 47 | Effects of simvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Clin Cardiol. 2003 Jan;26(1):18-24. | |||||
| REF 48 | Selective inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in liver versus extrahepatic tissues by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. J Lipid Res. 1990 Jul;31(7):1271-82. | |||||
| REF 49 | New Frontiers in the Treatment of Diabetic Dyslipidemia. Rev Diabet Stud. 2013 Summer-Fall; 10(2-3): 204-212. | |||||
| REF 50 | Substituted pyrazoles as hepatoselective HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: discovery of (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-4-isopropyl-5-(4-methyl-benzylca... J Med Chem. 2008 Jan 10;51(1):31-45. | |||||
| REF 51 | Efficacy, tissue distribution and biliary excretion of methyl (3R*,5S*)-(E)-3,5-dihydroxy-9,9-diphenyl-6,8-nonadienoate (CP-83101), a hepatoselective inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase activity in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 15;40(6):1281-93. | |||||
| REF 52 | Regulation of CYP2B6 and CYP3A expression by hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A inhibitors in primary cultured human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002 Dec;30(12):1400-5. | |||||
| REF 53 | The novel cholesterol-lowering drug SR-12813 inhibits cholesterol synthesis via an increased degradation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A r... J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 14;271(24):14376-82. | |||||
| REF 54 | Novel Acetylenic Acids from the Root Bark of Paramacrolobium caeruleum: Inhibitors of 3-Hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase J. Nat. Prod. 52(1):153-161 (1989). | |||||
| REF 55 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 56 | Molecular docking of the highly hypolipidemic agent alpha-asarone with the catalytic portion of HMG-CoA reductase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Feb 15;15(4):989-94. | |||||
| REF 57 | Total synthesis and biological evaluation of structural analogues of compactin and dihydromevinolin. J Med Chem. 1987 Oct;30(10):1858-73. | |||||
| REF 58 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 639). | |||||
| REF 59 | Peptide fragmentation as an approach in modeling of an active peptide and designing a competitive inhibitory peptide for HMG-CoA reductase. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Jun 15;18(12):4300-9. | |||||
| REF 60 | Binding effect and design of a competitive inhibitory peptide for HMG-CoA reductase through modeling of an active peptide backbone. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Feb 1;16(3):1309-18. | |||||
| REF 61 | Thermodynamic and structure guided design of statin based inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Med Chem. 2008 Jul 10;51(13):3804-13. | |||||
| REF 62 | Three-dimensional quantitative structure (3-D QSAR) activity relationship studies on imidazolyl and N-pyrrolyl heptenoates as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGR) inhibitors by comparativemolecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Feb 15;15(4):1027-32. | |||||
| REF 63 | Synthesis and biological activity of new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. 3. Lactones of 6-phenoxy-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoic acids. J Med Chem. 1991 Oct;34(10):2962-83. | |||||
| REF 64 | Discovery of pyrrole-based hepatoselective ligands as potent inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Aug 15;15(16):5576-89. | |||||
| REF 65 | Design and synthesis of novel, conformationally restricted HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Aug 15;17(16):4531-7. | |||||
| REF 66 | Design and synthesis of hepatoselective, pyrrole-based HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Aug 15;17(16):4538-44. | |||||
| REF 67 | Hepatoselectivity of statins: design and synthesis of 4-sulfamoyl pyrroles as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Feb 1;18(3):1151-6. | |||||
| REF 68 | (3R,5S,E)-7-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(methyl(1-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)amino)pyrimidin-5-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid (BMS-644950): a rationally designed orally efficacious 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-a reductase inhibitor with reduced myotoxicity potential. J Med Chem. 2008 May 8;51(9):2722-33. | |||||
| REF 69 | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase inhibitors. 7. Modification of the hexahydronaphthalene moiety of simvastatin: 5-oxygenated and 5-oxa derivatives. J Med Chem. 1991 Aug;34(8):2489-95. | |||||
| REF 70 | Phosphorus-containing inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. 2. Synthesis and biological activities of a series of substituted pyridines containing a hydroxyphosphinyl moiety. J Med Chem. 1991 Sep;34(9):2804-15. | |||||
| REF 71 | Application of a 3,3-diphenylpentane skeleton as a multi-template for creation of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Aug 1;19(15):4228-31. | |||||
| REF 72 | Inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. 4. trans-6-[2-(substituted-quinolinyl)ethenyl/ethyl]tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2 H-pyran-2-ones, a novel series of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1991 Jan;34(1):367-73. | |||||
| REF 73 | Relationship between tissue selectivity and lipophilicity for inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. J Med Chem. 1991 Jan;34(1):463-6. | |||||
| REF 74 | Inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. 6. trans-6-[2-(2-N-heteroaryl-3,5-disubstituted- pyrazol-4-yl)ethyl/ethenyl]tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-ones. J Med Chem. 1992 May 29;35(11):2095-103. | |||||
| REF 75 | Synthesis and biological activity of new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. 2. Derivatives of 7-(1H-pyrrol-3-yl)-substituted-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6(E)-enoic (-heptanoic) acids. J Med Chem. 1990 Jan;33(1):61-70. | |||||
| REF 76 | Phosphorus-containing inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. 1. 4-[(2-arylethyl)hydroxyphosphinyl]-3-hydroxy-butanoic acids: a new class of cell-selective inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. J Med Chem. 1990 Nov;33(11):2952-6. | |||||
| REF 77 | Inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. 2. 1,3,5-trisubstituted [2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2-oxopyran-6-yl)ethyl]pyrazoles. J Med Chem. 1990 Jan;33(1):31-8. | |||||
| REF 78 | Synthesis and biological activity of new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. 1. Lactones of pyridine- and pyrimidine-substituted 3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic (-heptanoic) acids. J Med Chem. 1990 Jan;33(1):52-60. | |||||
| REF 79 | Synthesis and biological evaluation of a monocyclic, fully functional analogue of compactin. J Med Chem. 1989 Jan;32(1):197-202. | |||||
| REF 80 | Synthesis and biological activity of bile acid-derived HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. The role of 21-methyl in recognition of HMG-CoA reductase and the ileal bile acid transport system. J Med Chem. 1994 Sep 30;37(20):3240-6. | |||||
| REF 81 | Inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. 1. 3,5-Dihydroxy-7-(N-imidazolyl)-6-heptenoates and -heptanoates, a novel series of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1993 Nov 12;36(23):3646-57. | |||||
| REF 82 | Inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. 2. 3,5-Dihydroxy-7-(N-pyrrolyl)-6-heptenoates, a novel series of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1993 Nov 12;36(23):3658-62. | |||||
| REF 83 | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: design, synthesis, and biological activity of tetrahydroindazole-substituted 3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid sodium salts. J Med Chem. 1993 Nov 12;36(23):3674-85. | |||||
| REF 84 | 32-Methyl-32-oxylanosterols: dual-action inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis. J Med Chem. 1993 Feb 5;36(3):410-6. | |||||
| REF 85 | Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001 May 11;292(5519):1160-4. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

