Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T63846
(Former ID: TTDI03277)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1; IRAK-1; IRAK
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
IRAK1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Involved in Toll-like receptor (TLR) and IL-1R signaling pathways. Is rapidly recruited by MYD88 to the receptor-signaling complex upon TLR activation. Association with MYD88 leads to IRAK1 phosphorylation by IRAK4 and subsequent autophosphorylation and kinase activation. Phosphorylates E3 ubiquitin ligases Pellino proteins (PELI1, PELI2 and PELI3) to promote pellino-mediated polyubiquitination of IRAK1. Then, the ubiquitin-binding domain of IKBKG/NEMO binds to polyubiquitinated IRAK1 bringing together the IRAK1-MAP3K7/TAK1-TRAF6 complex and the NEMO-IKKA-IKKB complex. In turn, MAP3K7/TAK1 activates IKKs (CHUK/IKKA and IKBKB/IKKB) leading to NF-kappa-B nuclear translocation and activation. Alternatively, phosphorylates TIRAP to promote its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Phosphorylates the interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) to induce its activation and translocation to the nucleus, resulting in transcriptional activation of type I IFN genes, which drive the cell in an antiviral state. When sumoylated, translocates to the nucleus and phosphorylates STAT3. Serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays a critical role in initiating innate immune response against foreign pathogens.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAGGPGPGEPAAPGAQHFLYEVPPWVMCRFYKVMDALEPADWCQFAALIVRDQTELRLCE
RSGQRTASVLWPWINRNARVADLVHILTHLQLLRARDIITAWHPPAPLPSPGTTAPRPSS IPAPAEAEAWSPRKLPSSASTFLSPAFPGSQTHSGPELGLVPSPASLWPPPPSPAPSSTK PGPESSVSLLQGARPFPFCWPLCEISRGTHNFSEELKIGEGGFGCVYRAVMRNTVYAVKR LKENADLEWTAVKQSFLTEVEQLSRFRHPNIVDFAGYCAQNGFYCLVYGFLPNGSLEDRL HCQTQACPPLSWPQRLDILLGTARAIQFLHQDSPSLIHGDIKSSNVLLDERLTPKLGDFG LARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVARTQTVRGTLAYLPEEYIKTGRLAVDTDTFSFGVVVLETLAG QRAVKTHGARTKYLKDLVEEEAEEAGVALRSTQSTLQAGLAADAWAAPIAMQIYKKHLDP RPGPCPPELGLGLGQLACCCLHRRAKRRPPMTQVYERLEKLQAVVAGVPGHSEAASCIPP SPQENSYVSSTGRAHSGAAPWQPLAAPSGASAQAAEQLQRGPNQPVESDESLGGLSAALR SWHLTPSCPLDPAPLREAGCPQGDTAGESSWGSGPGSRPTAVEGLALGSSASSSSEPPQI IINPARQKMVQKLALYEDGALDSLQLLSSSSLPGLGLEQDRQGPEESDEFQS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T27F5B | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: IRAK4 inhibitor 4b | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human IRAK1 | PDB:6BFN | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.26 Å | Mutation | No | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
SRPFPFCWPL
202 CEISRGTHNF212 SEELKIGEGG222 FGCVYRAVMR232 NTVYAVKRLK242 EWTAVKQSFL 257 TEVEQLSRFR267 HPNIVDFAGY277 CAQNGFYCLV287 YGFLPNGSLE297 DRLHCQTQAC 307 PPLSWPQRLD317 ILLGTARAIQ327 FLHQDSPSLI337 HGDIKSSNVL347 LDERLTPKLG 357 DFGLARFSRT383 VRGTLAYLPE393 EYIKTGRLAV403 DTDTFSFGVV413 VLETLAGQRA 423 VKTHGARTKY433 LKDLVEEEAE443 EAGVAAADAW465 AAPIAMQIYK475 KHLDPRPGPC 485 PPELGLGLGQ495 LACCCLHRRA505 KRRPPMTQVY515 ERLEKLQAVV525 A |
|||||
|
|
ILE218
3.473
GLY219
4.101
PHE223
3.735
VAL226
3.841
ALA237
3.476
LYS239
3.876
VAL272
4.000
TYR288
3.565
GLY289
3.799
PHE290
3.634
LEU291
3.040
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |
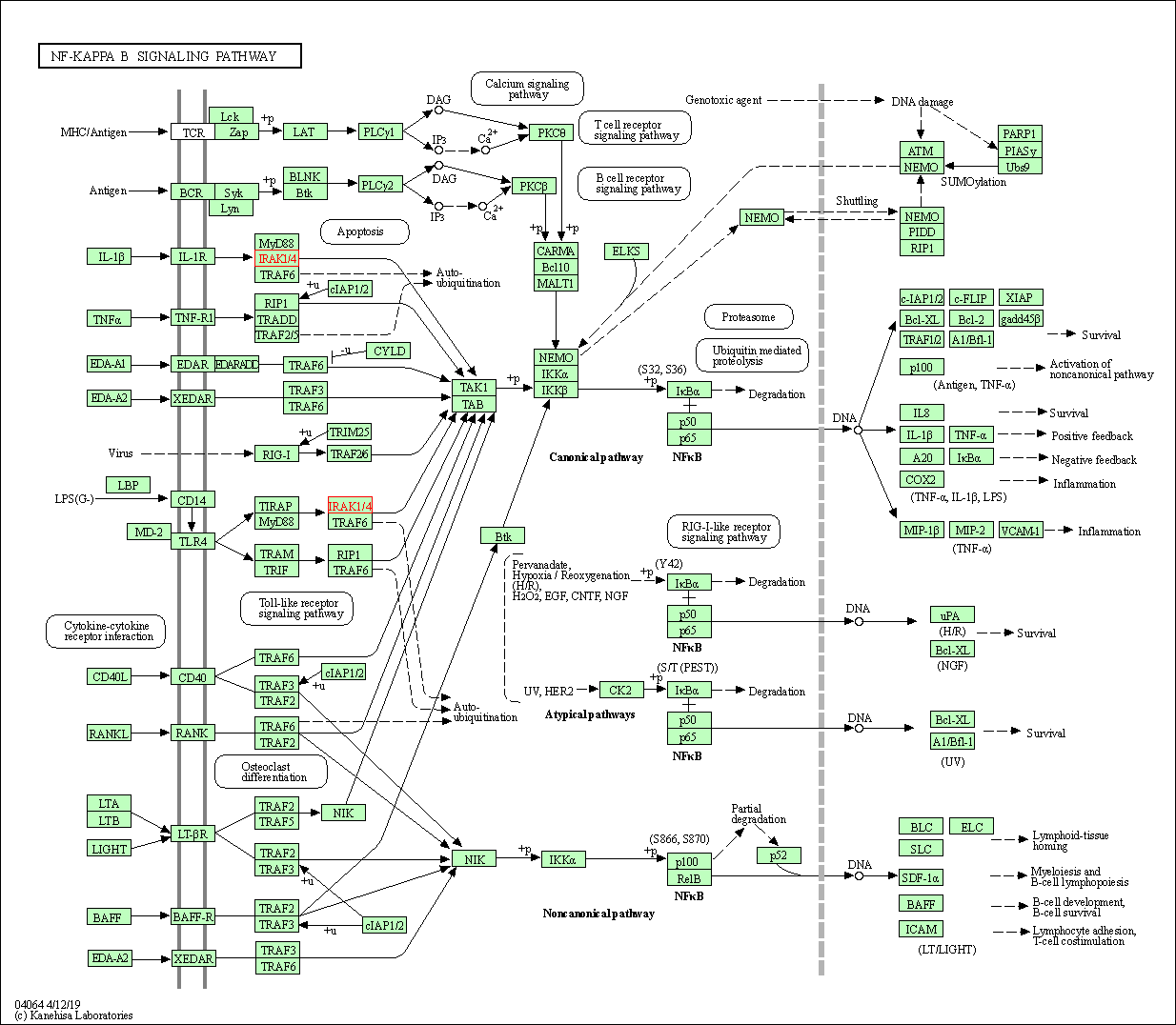
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |
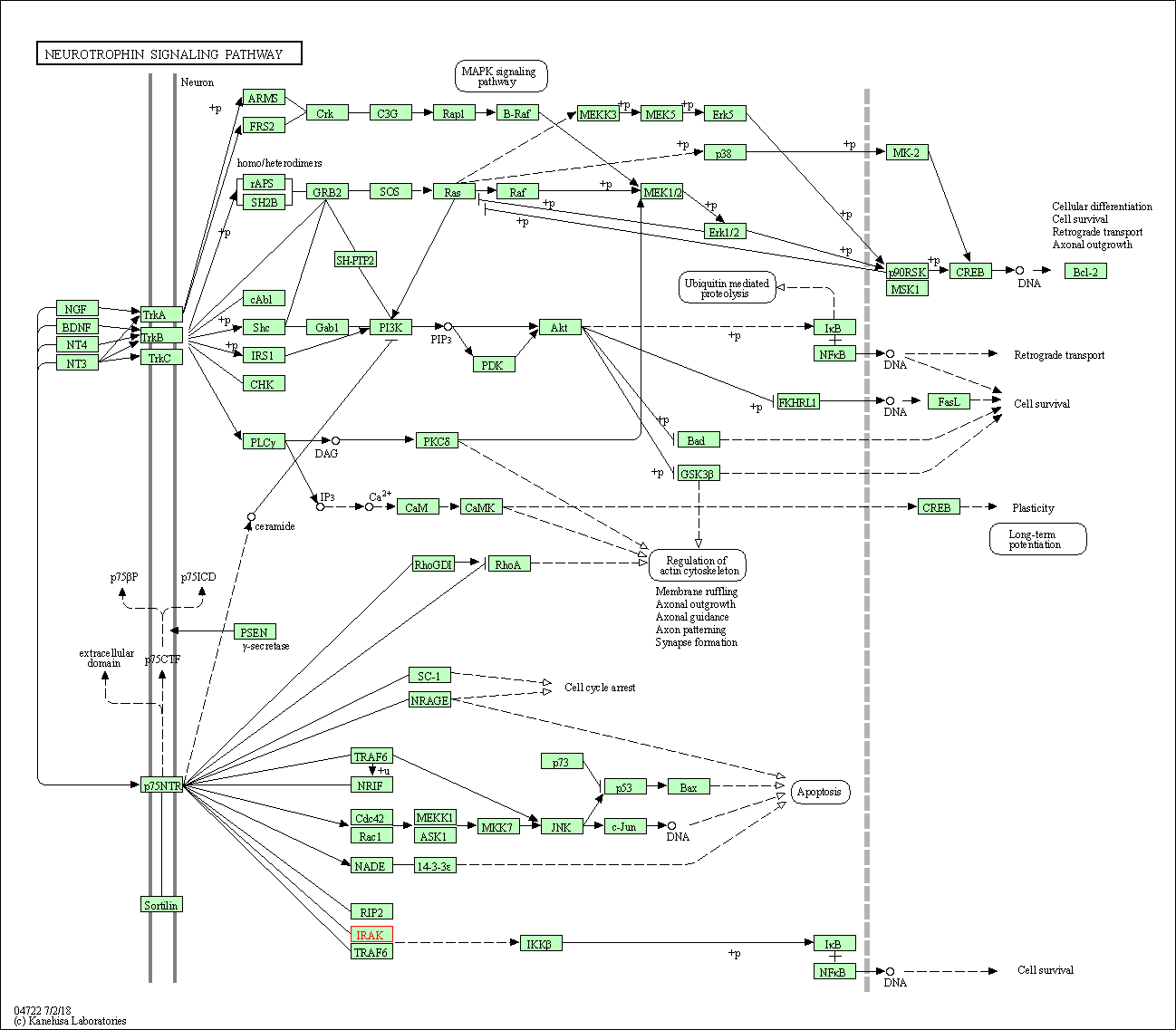
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 34 | Degree centrality | 3.65E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 4.76E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.36E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.71E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.85E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.72E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4): a patent review (2012-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016 Aug;26(8):917-32. | |||||
| REF 2 | Discovery and initial SAR of inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Jun 1;16(11):2842-5. | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2042). | |||||
| REF 4 | Crystal structure of human IRAK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Dec 19;114(51):13507-13512. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

