Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T68334
(Former ID: TTDS00438)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Follicle-stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
LGR1; Follitropin receptor; FSH-R
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
FSHR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Female infertility [ICD-11: GA31] | |||||
| Function |
G protein-coupled receptor for follitropin, the follicle-stimulating hormone. Through cAMP production activates the downstream PI3K-AKT and ERK1/ERK2 signaling pathways.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
GPCR rhodopsin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MALLLVSLLAFLSLGSGCHHRICHCSNRVFLCQESKVTEIPSDLPRNAIELRFVLTKLRV
IQKGAFSGFGDLEKIEISQNDVLEVIEADVFSNLPKLHEIRIEKANNLLYINPEAFQNLP NLQYLLISNTGIKHLPDVHKIHSLQKVLLDIQDNINIHTIERNSFVGLSFESVILWLNKN GIQEIHNCAFNGTQLDELNLSDNNNLEELPNDVFHGASGPVILDISRTRIHSLPSYGLEN LKKLRARSTYNLKKLPTLEKLVALMEASLTYPSHCCAFANWRRQISELHPICNKSILRQE VDYMTQARGQRSSLAEDNESSYSRGFDMTYTEFDYDLCNEVVDVTCSPKPDAFNPCEDIM GYNILRVLIWFISILAITGNIIVLVILTTSQYKLTVPRFLMCNLAFADLCIGIYLLLIAS VDIHTKSQYHNYAIDWQTGAGCDAAGFFTVFASELSVYTLTAITLERWHTITHAMQLDCK VQLRHAASVMVMGWIFAFAAALFPIFGISSYMKVSICLPMDIDSPLSQLYVMSLLVLNVL AFVVICGCYIHIYLTVRNPNIVSSSSDTRIAKRMAMLIFTDFLCMAPISFFAISASLKVP LITVSKAKILLVLFHPINSCANPFLYAIFTKNFRRDFFILLSKCGCYEMQAQIYRTETSS TVHNTHPRNGHCSSAPRVTNGSTYILVPLSHLAQN Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T42HHN | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 3 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Follitropin beta | Drug Info | Approved | Female infertility | [2] | |
| 2 | Menotropins | Drug Info | Approved | Female infertility | [3] | |
| 3 | Urofollitropin | Drug Info | Approved | Female infertility | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Binder | [+] 3 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Follitropin beta | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 2 | Menotropins | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | Urofollitropin | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 3 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Long-acting FSH conjugate | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 2 | PRX-111 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 3 | Recombinant follicle stimulating hormone | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |
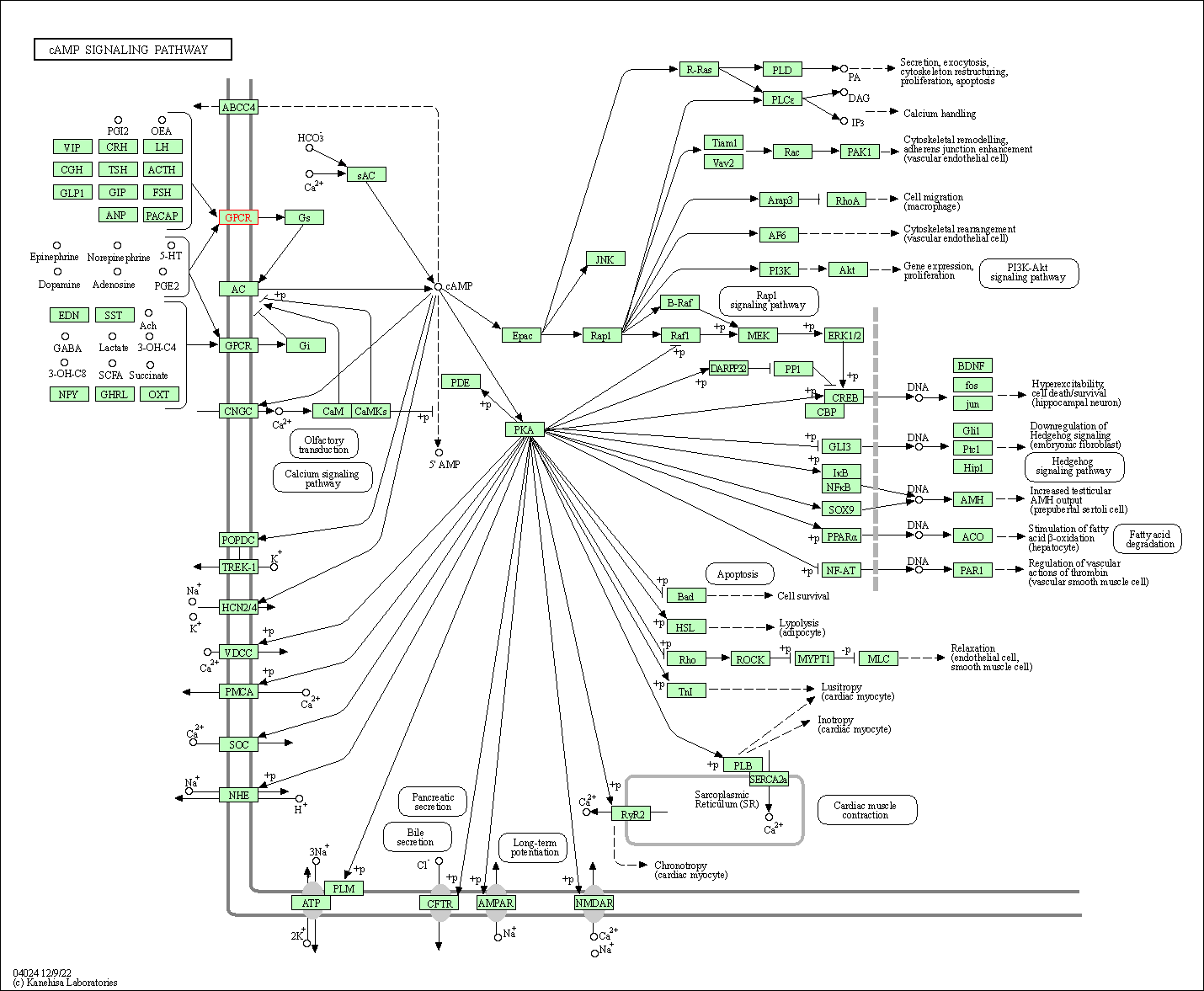
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |
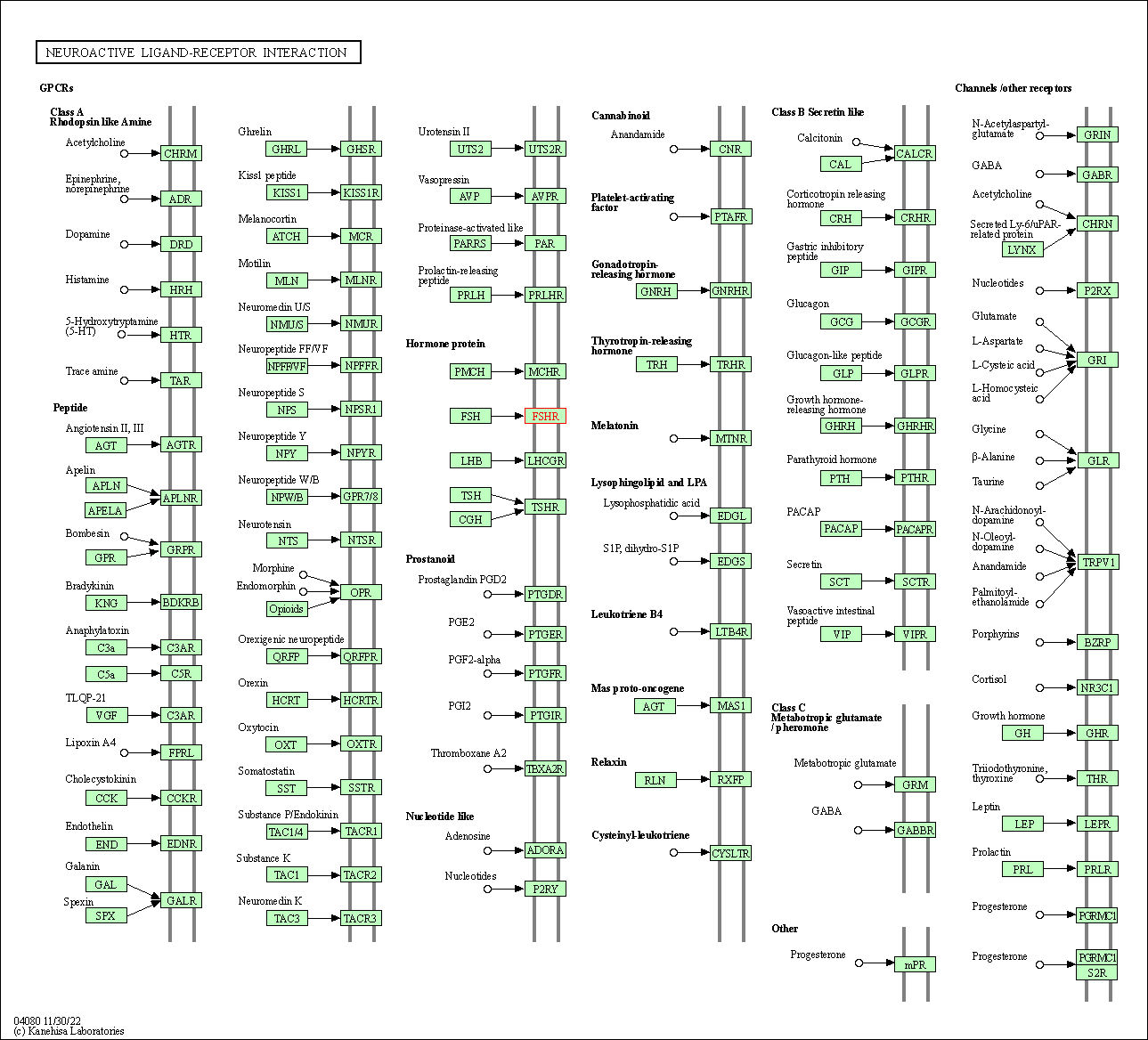
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ovarian steroidogenesis | hsa04913 | Affiliated Target |
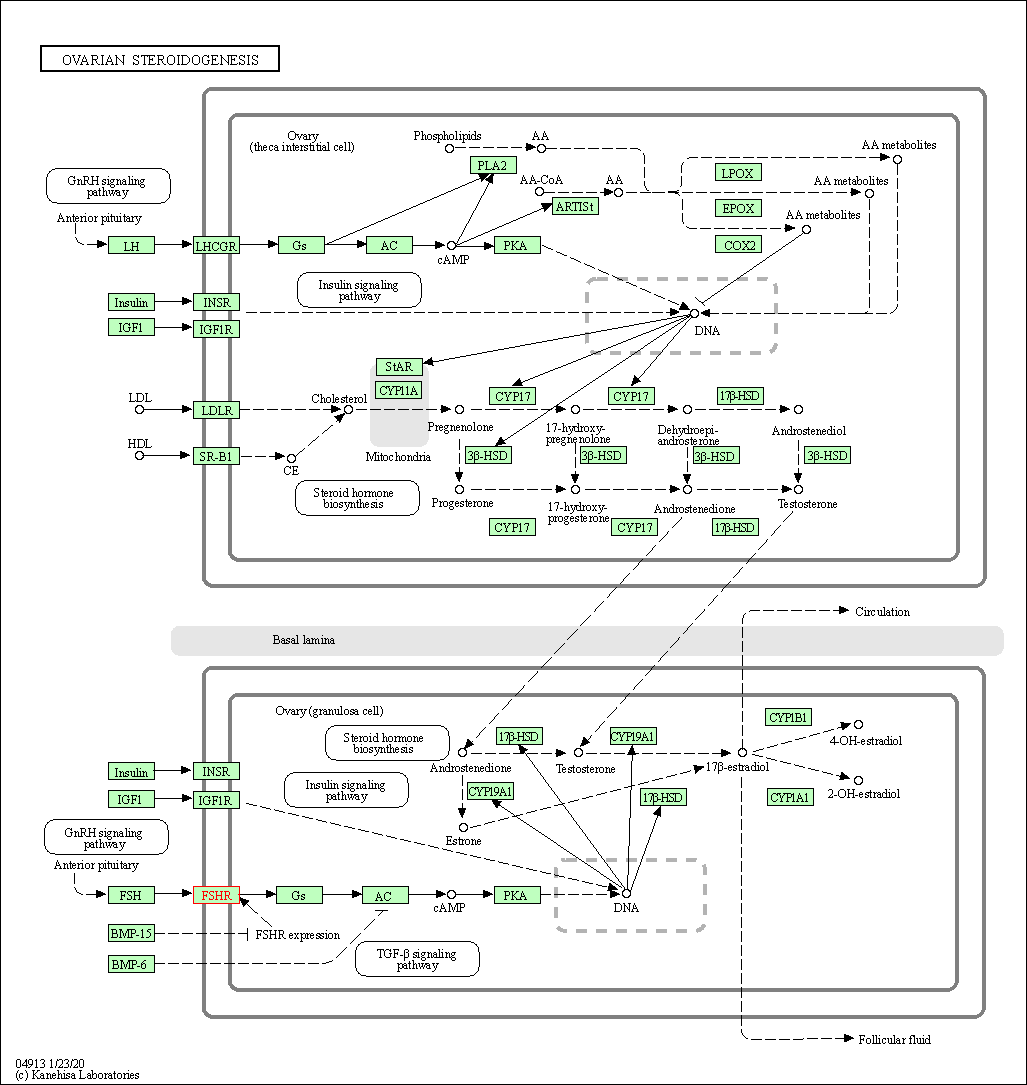
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 3 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 2.11E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.90E-01 | Radiality | 1.32E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.43E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.33E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 3 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | cAMP signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| 3 | Ovarian steroidogenesis | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 2 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Vasopressin Regulation of Water Homeostasis | |||||
| 2 | Intracellular Signalling Through FSH Receptor and Follicle Stimulating Hormone | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Hormone ligand-binding receptors | |||||
| 2 | G alpha (s) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 7 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||||
| 2 | Ovarian Infertility Genes | |||||
| 3 | Peptide GPCRs | |||||
| 4 | FSH signaling pathway | |||||
| 5 | GPCR ligand binding | |||||
| 6 | GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| 7 | GPCRs, Other | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| Target QSAR Model | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | The role of gonadotropins in ovulation induction. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Feb;172(2 Pt 2):759-65. | |||||
| REF 2 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 020328. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 1728). | |||||
| REF 5 | Opportunities and challenges in antiparasitic drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005 Sep;4(9):727-40. | |||||
| REF 6 | Follitropin-alpha (Gonal-F) versus follitropin-beta (Puregon) in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation for in vitro fertilization: is there any diffe... Fertil Steril. 2009 Apr;91(4 Suppl):1522-5. | |||||
| REF 7 | Follicle-stimulating hormone in clinical practice: an update. Treat Endocrinol. 2004;3(3):161-71. | |||||
| REF 8 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 253). | |||||
| REF 9 | A naturally occurring basically charged human follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) variant inhibits FSH-induced androgen aromatization and tissue-type plasminogen activator enzyme activity in vitro. Neuroendocrinology. 1998 Mar;67(3):153-63. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

