Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T40097
(Former ID: TTDC00102)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Stress-activated protein kinase JNK1 (JNK1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Stress-activated protein kinase 1c; SAPK1c; PRKM8; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8; MAPK 8; MAP kinase 8; JNK-46; C-Jun N-terminal kinase 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MAPK8
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Extracellular stimuli such as proinflammatory cytokines or physical stress stimulate the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAP/JNK) signaling pathway. In this cascade, two dual specificity kinases MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K7/MKK7 phosphorylate and activate MAPK8/JNK1. In turn, MAPK8/JNK1 phosphorylates a number of transcription factors, primarily components of AP-1 such as JUN, JDP2 and ATF2 and thus regulates AP-1 transcriptional activity. Phosphorylates the replication licensing factor CDT1, inhibiting the interaction between CDT1 and the histone H4 acetylase HBO1 to replication origins. Loss of this interaction abrogates the acetylation required for replication initiation. Promotes stressed cell apoptosis by phosphorylating key regulatory factors including p53/TP53 and Yes-associates protein YAP1. In T-cells, MAPK8 and MAPK9 are required for polarized differentiation of T-helper cells into Th1 cells. Contributes to the survival of erythroid cells by phosphorylating the antagonist of cell death BAD upon EPO stimulation. Mediates starvation-induced BCL2 phosphorylation, BCL2 dissociation from BECN1, and thus activation of autophagy. Phosphorylates STMN2 and hence regulates microtubule dynamics, controlling neurite elongation in cortical neurons. In the developing brain, through its cytoplasmic activity on STMN2, negatively regulates the rate of exit from multipolar stage and of radial migration from the ventricular zone. Phosphorylates several other substrates including heat shock factor protein 4 (HSF4), the deacetylase SIRT1, ELK1, or the E3 ligase ITCH. Phosphorylates the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer and plays a role in the regulation of the circadian clock. Phosphorylates the heat shock transcription factor HSF1, suppressing HSF1-induced transcriptional activity. Phosphorylates POU5F1, which results in the inhibition of POU5F1's transcriptional activity and enhances its proteosomal degradation. Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in various processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, transformation and programmed cell death.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.24
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSRSKRDNNFYSVEIGDSTFTVLKRYQNLKPIGSGAQGIVCAAYDAILERNVAIKKLSRP
FQNQTHAKRAYRELVLMKCVNHKNIIGLLNVFTPQKSLEEFQDVYIVMELMDANLCQVIQ MELDHERMSYLLYQMLCGIKHLHSAGIIHRDLKPSNIVVKSDCTLKILDFGLARTAGTSF MMTPYVVTRYYRAPEVILGMGYKENVDLWSVGCIMGEMVCHKILFPGRDYIDQWNKVIEQ LGTPCPEFMKKLQPTVRTYVENRPKYAGYSFEKLFPDVLFPADSEHNKLKASQARDLLSK MLVIDASKRISVDEALQHPYINVWYDPSEAEAPPPKIPDKQLDEREHTIEEWKELIYKEV MDLEERTKNGVIRGQPSPLGAAVINGSQHPSSSSSVNDVSSMSTDPTLASDTDSSLEAAA GPLGCCR Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A05675 ; BADD_A06356 ; BADD_A08298 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T29MD1 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NKP-1339 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 56 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NKP-1339 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 2 | 7-azaindole derivative 1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 3 | 7-azaindole derivative 3 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 4 | 7-azaindole derivative 5 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 5 | PMID25991433-Compound-A1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 6 | PMID25991433-Compound-A10 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 7 | PMID25991433-Compound-A11 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 8 | PMID25991433-Compound-A2 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 9 | PMID25991433-Compound-A6 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 10 | PMID25991433-Compound-A7 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 11 | PMID25991433-Compound-A8 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 12 | PMID25991433-Compound-A9 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 13 | PMID25991433-Compound-D1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 14 | PMID25991433-Compound-D2 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 15 | PMID25991433-Compound-E1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 16 | PMID25991433-Compound-E2 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 17 | PMID25991433-Compound-E5 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 18 | PMID25991433-Compound-Eb | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 19 | PMID25991433-Compound-F2 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 20 | PMID25991433-Compound-G1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 21 | PMID25991433-Compound-G2 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 22 | PMID25991433-Compound-G4 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 23 | PMID25991433-Compound-H2 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 24 | PMID25991433-Compound-H3 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 25 | PMID25991433-Compound-J2 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 26 | PMID25991433-Compound-J3 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 27 | PMID25991433-Compound-K2 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 28 | PMID25991433-Compound-L1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 29 | PMID25991433-Compound-N1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 30 | PMID25991433-Compound-N3 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 31 | PMID25991433-Compound-O3 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 32 | PMID25991433-Compound-P1 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 33 | PMID25991433-Compound-P6 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 34 | 2,6-Dihydroanthra/1,9-Cd/Pyrazol-6-One | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 35 | 2-(2-(butylamino)pyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzoic acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 36 | 2-(2-(pentyloxy)pyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzoic acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 37 | 2-(2-(phenylamino)pyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzamide | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 38 | 2-(2-butoxypyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzoic acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 39 | 2-(2-phenoxypyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzoic acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 40 | 2-(2-propoxypyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzoic acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 41 | 2-(2-sec-butoxypyrimidin-4-ylamino)benzoic acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 42 | 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 43 | Aminopyridine deriv. 2 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 44 | AS-601245 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 45 | Bisindolylmaleimide-I | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 46 | CI-1040 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 47 | KN-62 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 48 | KT-5720 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 49 | N-(4-amino-5-cyano-6-ethoxypyridin-2-yl)acetamide | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 50 | N-(4-amino-5-cyano-6-phenylpyridin-2-yl)acetamide | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 51 | N-(4-amino-6-butoxy-5-cyanopyridin-2-yl)acetamide | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 52 | N-(6-ethoxypyridin-2-yl)acetamide | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 53 | NM-PP1 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 54 | RO-316233 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 55 | Ro31-8220 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 56 | STAUROSPORINONE | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of DARPin-DARPin rigid fusion, variant DD_232_11_D12 in complex JNK1a1 and JIP1 peptide | PDB:5LW1 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.20 Å | Mutation | No | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
NNFYSVEIGD
17 STFTVLKRYQ27 NLKPIGSGAQ37 GIVCAAYDAI47 LERNVAIKKL57 SRPFQNQTHA 67 KRAYRELVLM77 KCVNHKNIIG87 LLNVFTPQKS97 LEEFQDVYIV107 MELMDANLCQ 117 VIQMELDHER127 MSYLLYQMLC137 GIKHLHSAGI147 IHRDLKPSNI157 VVKSDCTLKI 167 LDFGLARTAG177 TSFMMTPYVV187 TRYYRAPEVI197 LGMGYKENVD207 LWSVGCIMGE 217 MVCHKILFPG227 RDYIDQWNKV237 IEQLGTPCPE247 FMKKLQPTVR257 TYVENRPKYA 267 GYSFEKLFPD277 VLFPADSEHN287 KLKASQARDL297 LSKMLVIDAS307 KRISVDEALQ 317 HPYINVWYDP327 SEAEAPPPKI337 PDKQLDEREH347 TIEEWKELIY357 KEVMD |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: AMP-PNP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Linear binding motifs for JNK and for calcineurin antagonistically control the nuclear shuttling of NFAT4 | PDB:2XRW | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.33 Å | Mutation | No | [13] |
| PDB Sequence |
GSRSKRDNNF
10 YSVEIGDSTF20 TVLKRYQNLK30 PIGSGAQGIV40 CAAYDAILER50 NVAIKKLSRP 60 FQNQTHAKRA70 YRELVLMKCV80 NHKNIIGLLN90 VFTPQKSLEE100 FQDVYIVMEL 110 MDANLCQVIQ120 MELDHERMSY130 LLYQMLCGIK140 HLHSAGIIHR150 DLKPSNIVVK 160 SDCTLKILDF170 GLRYYRAPEV196 ILGMGYKENV206 DIWSVGCIMG216 EMIKGGVLFP 226 GTDHIDQWNK236 VIEQLGTPCP246 EFMKKLQPTV256 RTYVENRPKY266 AGYSFEKLFP 276 DVLFPADSEH286 NKLKASQARD296 LLSKMLVIDA306 SKRISVDEAL316 QHPYINVWYD 326 PSEAEAPPPK336 IPDKQLDERE346 HTIEEWKELI356 YKEVMDLEH
|
|||||
|
|
ILE32
3.588
GLY33
3.637
SER34
3.495
GLY35
3.676
ALA36
4.377
GLY38
3.677
VAL40
3.680
ALA53
3.555
LYS55
2.925
ILE86
3.792
MET108
3.607
GLU109
2.962
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
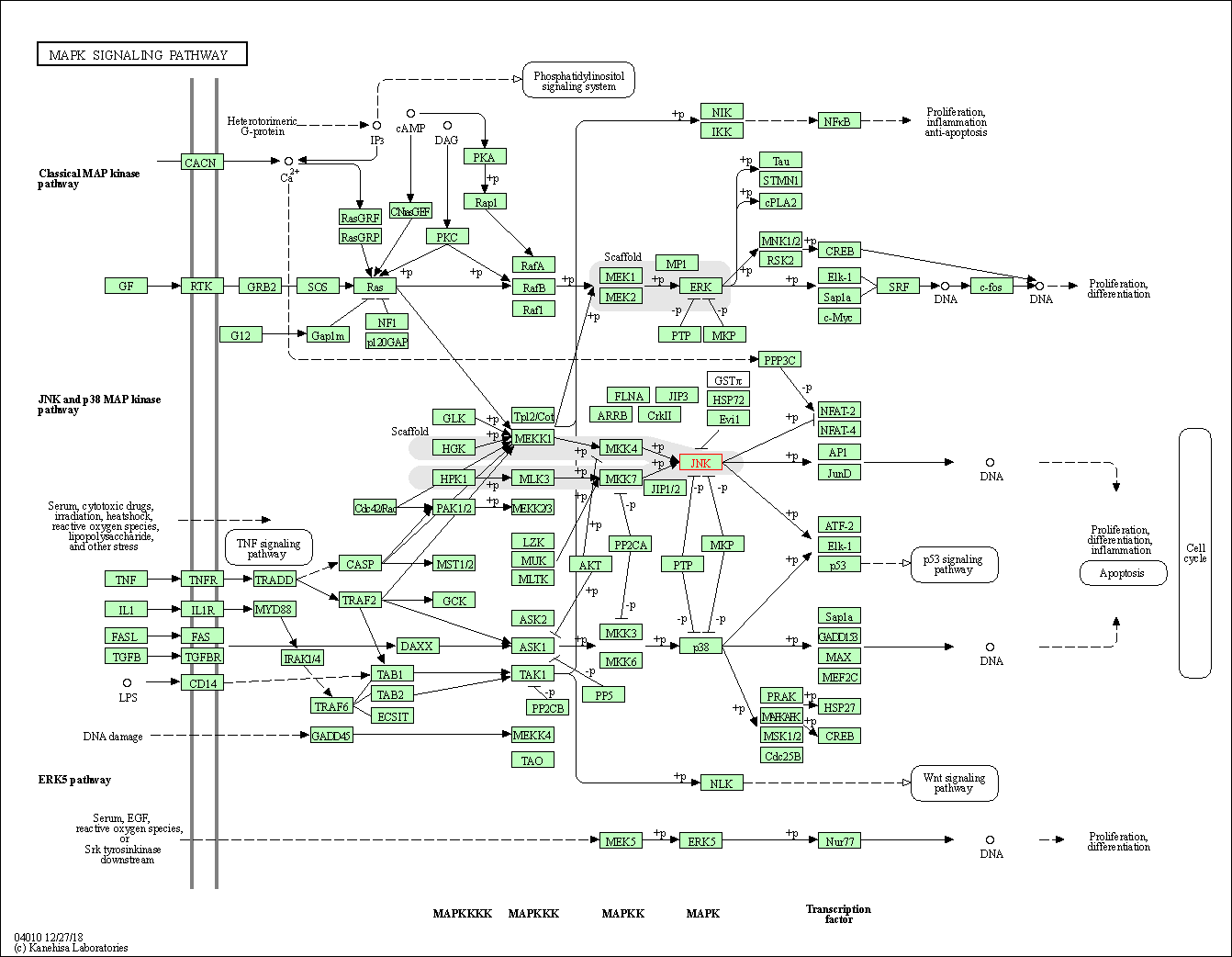
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |
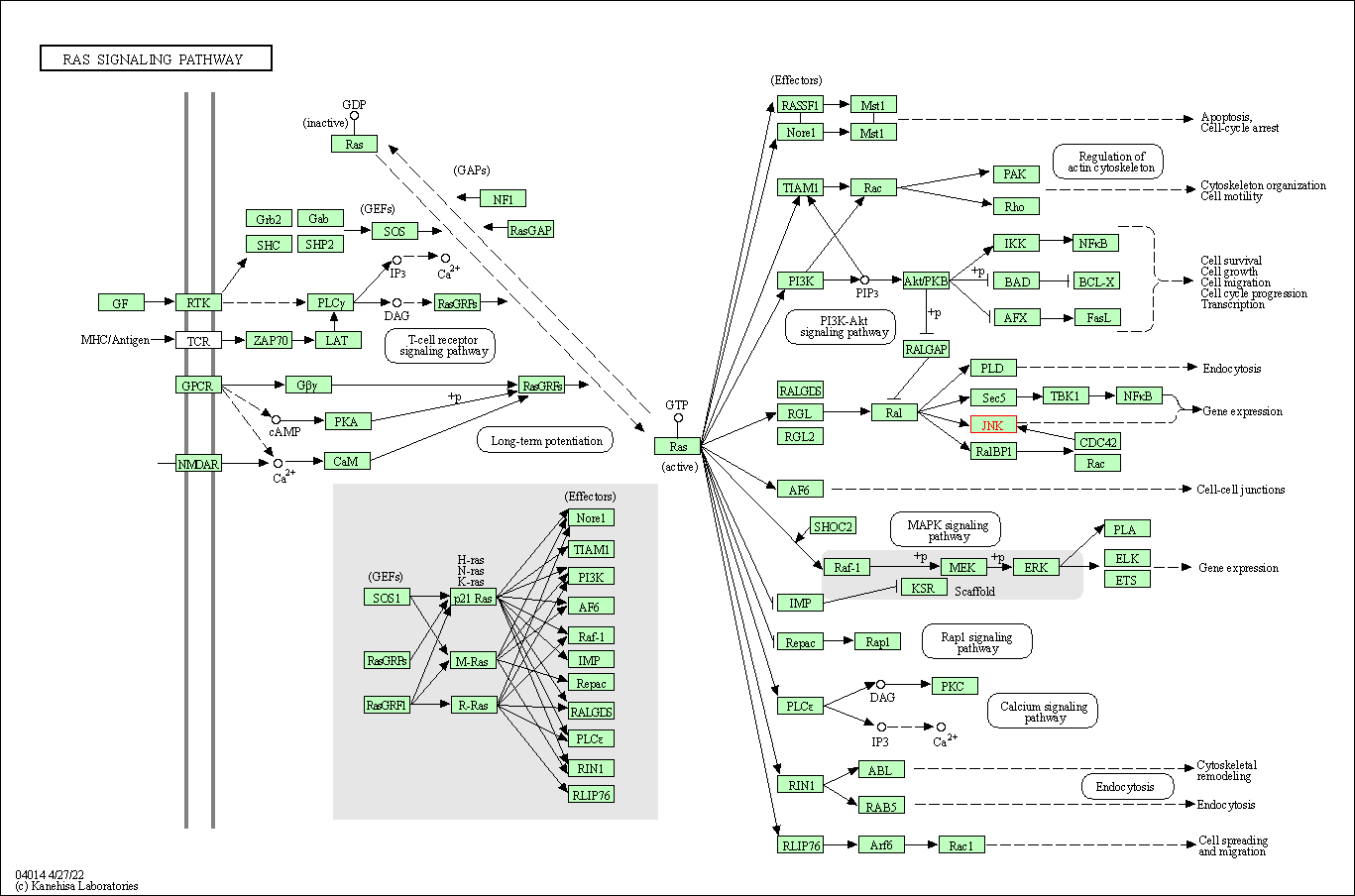
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |
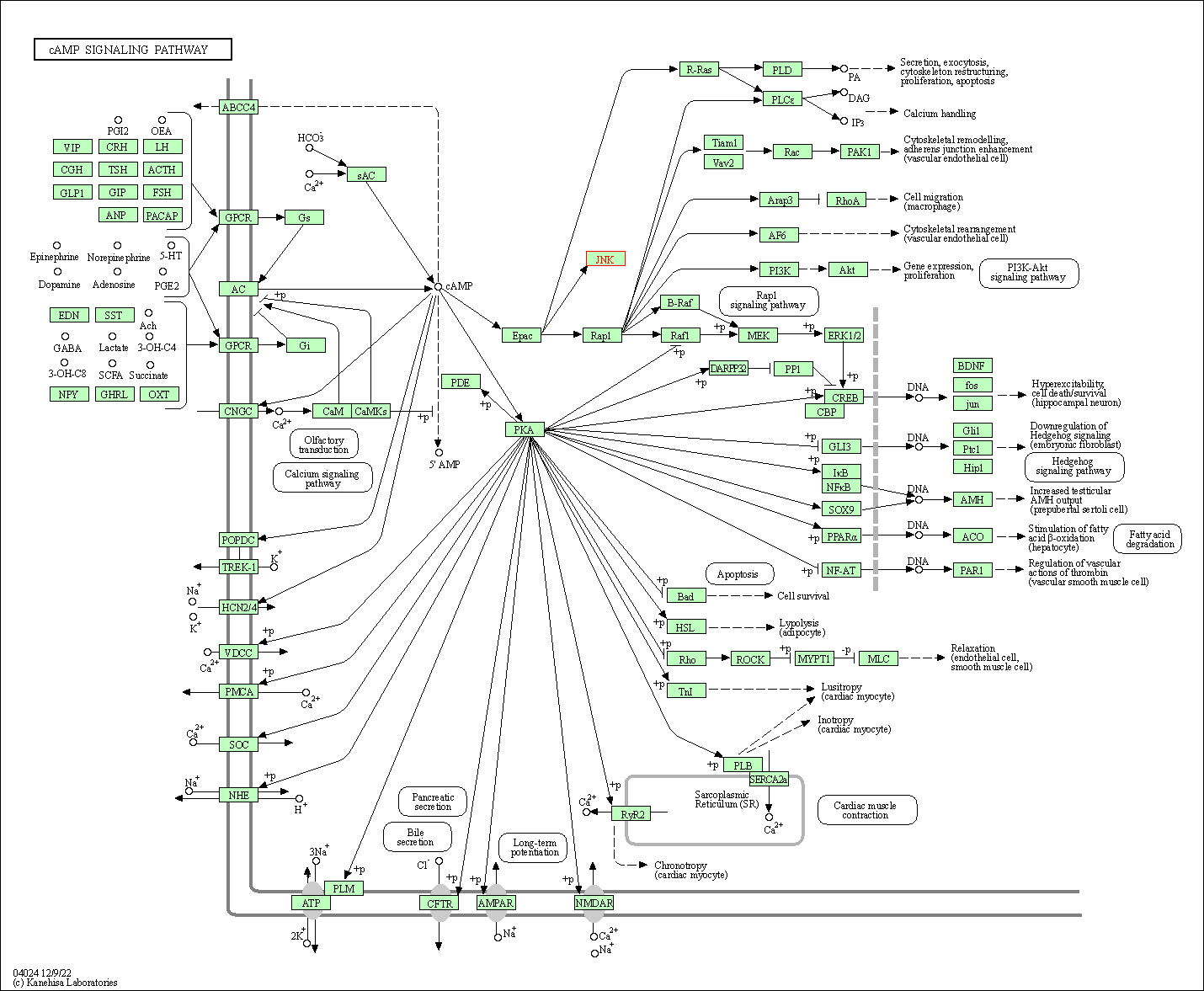
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |
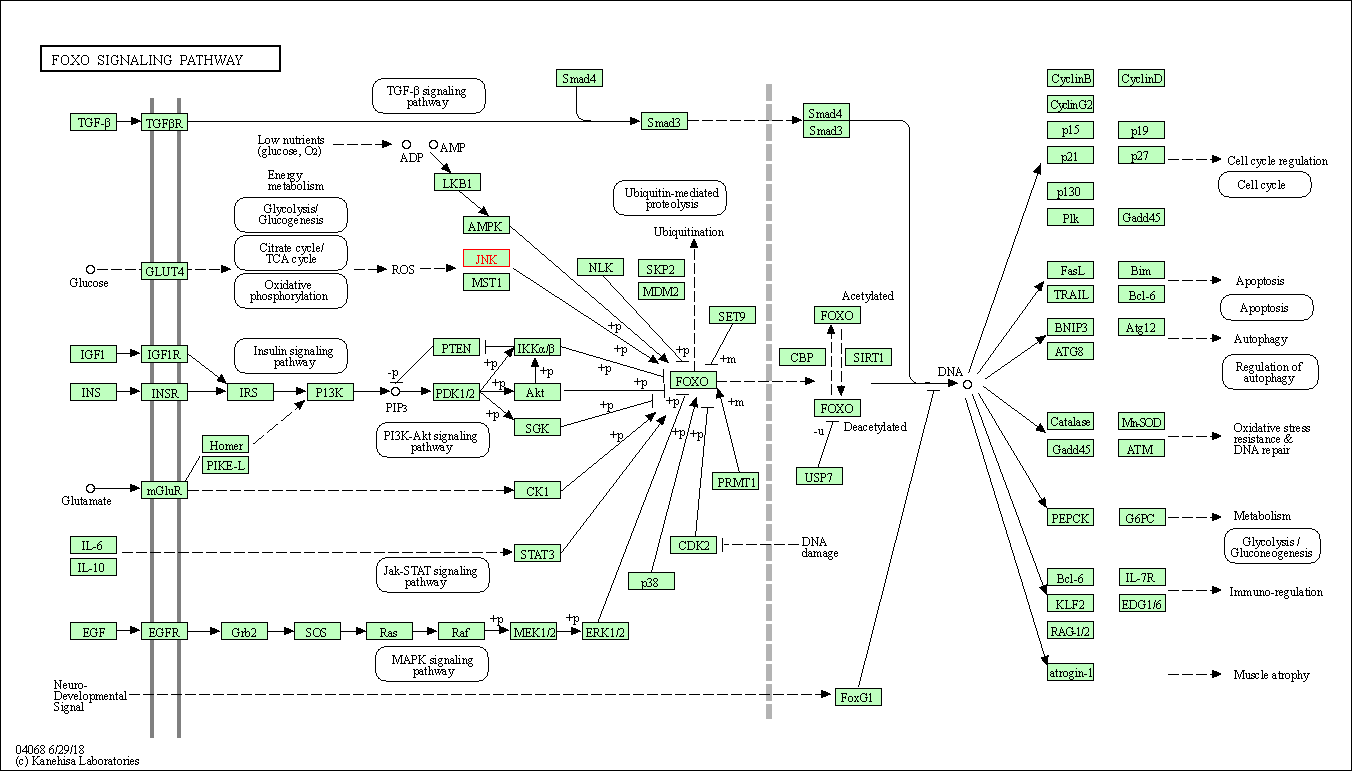
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |
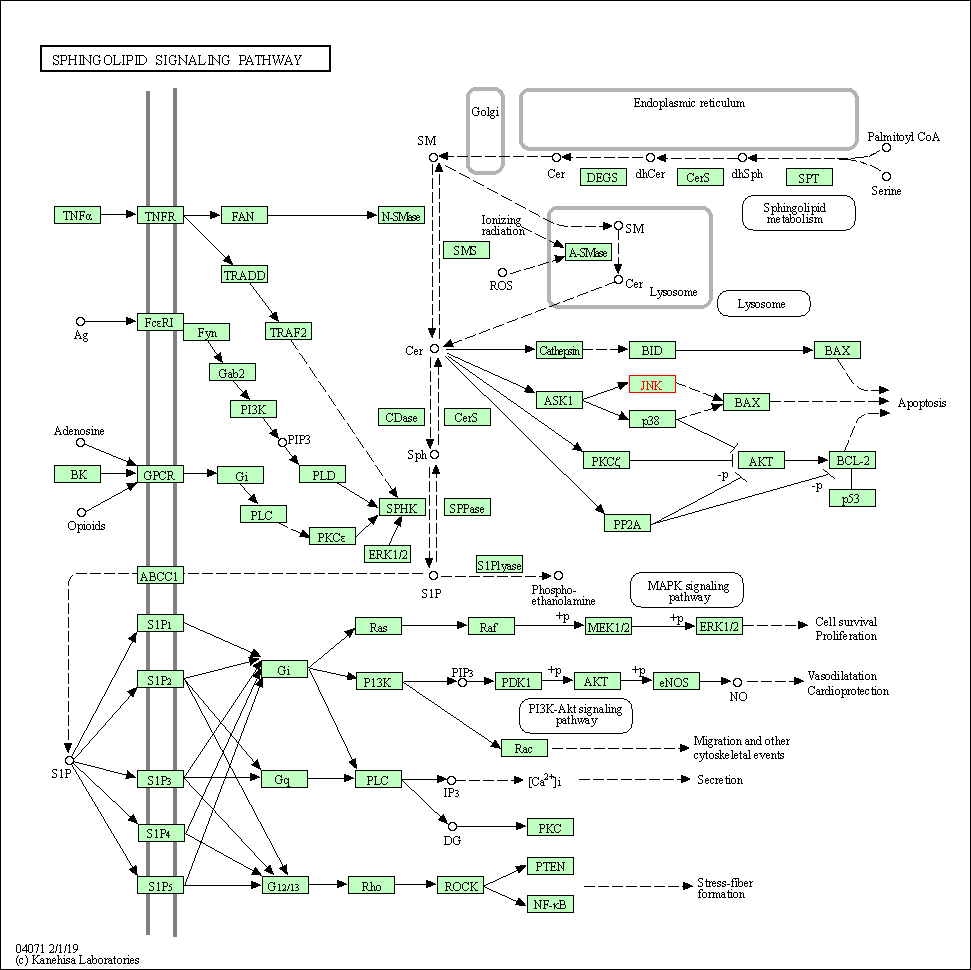
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Mitophagy - animal | hsa04137 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |
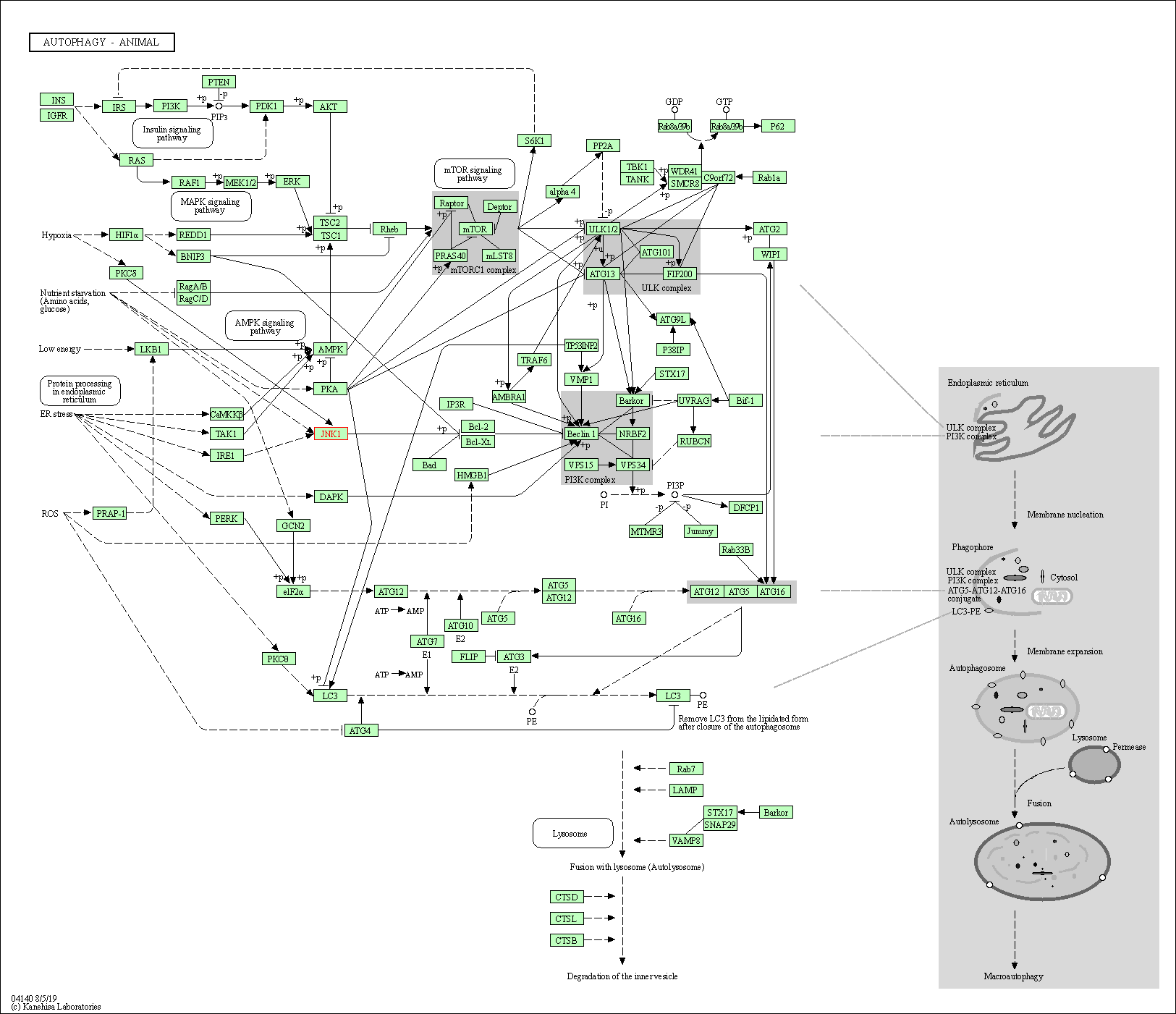
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | hsa04141 | Affiliated Target |
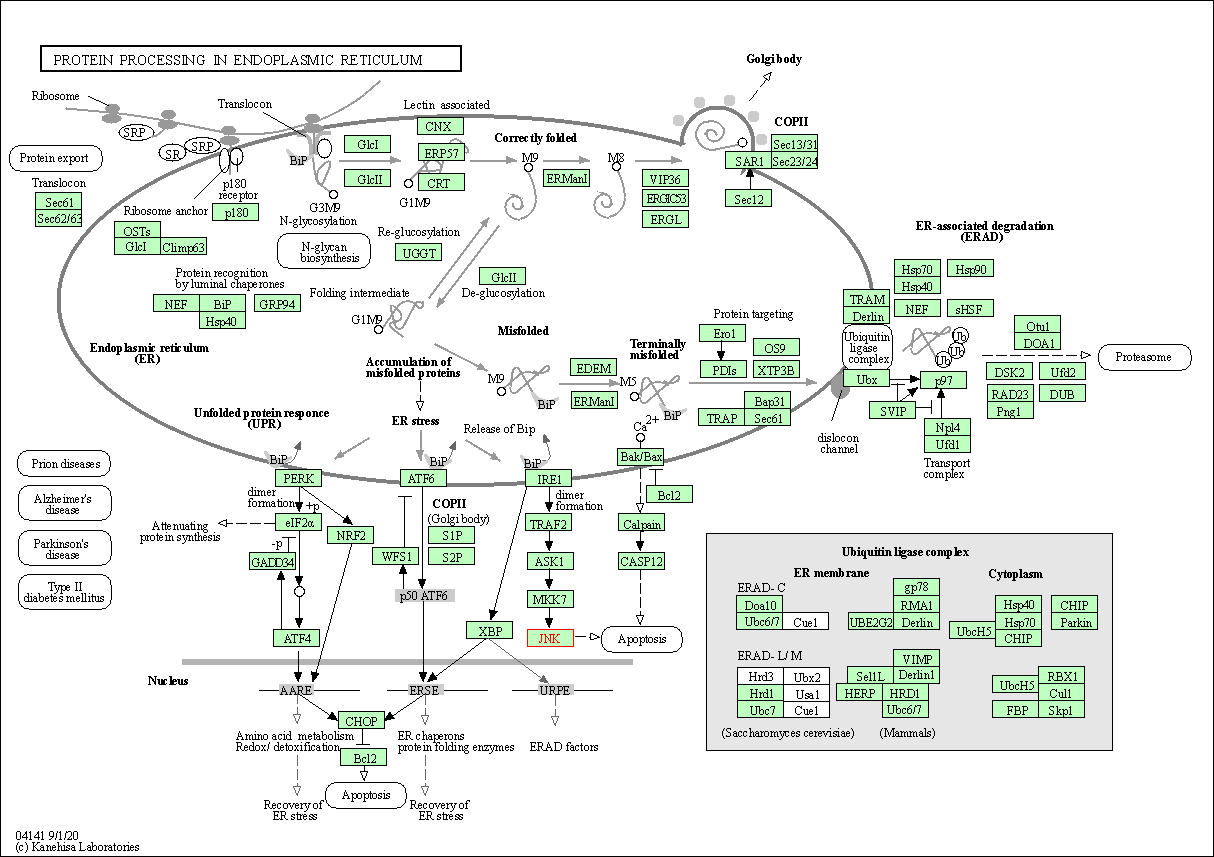
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |
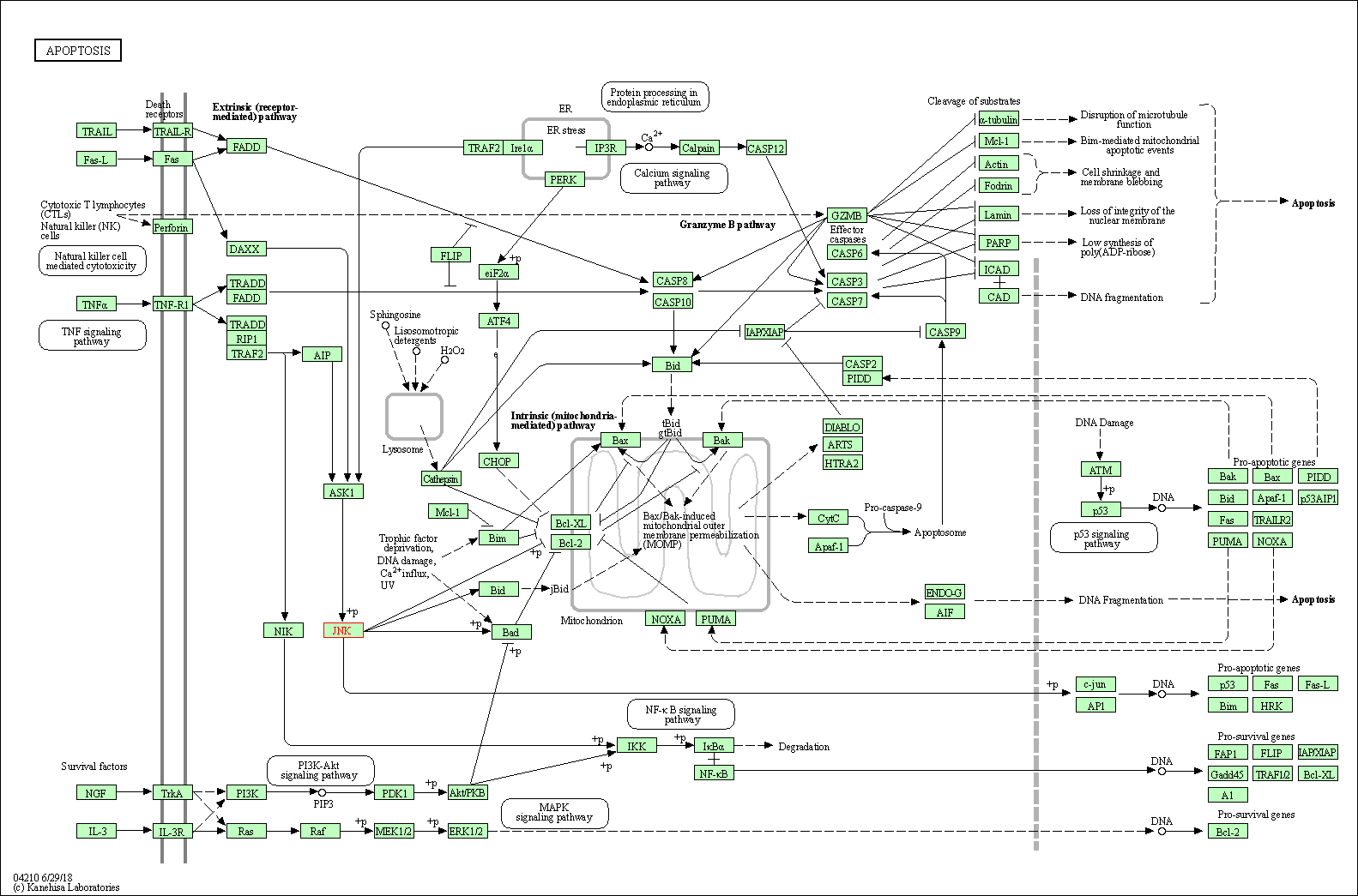
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis - multiple species | hsa04215 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
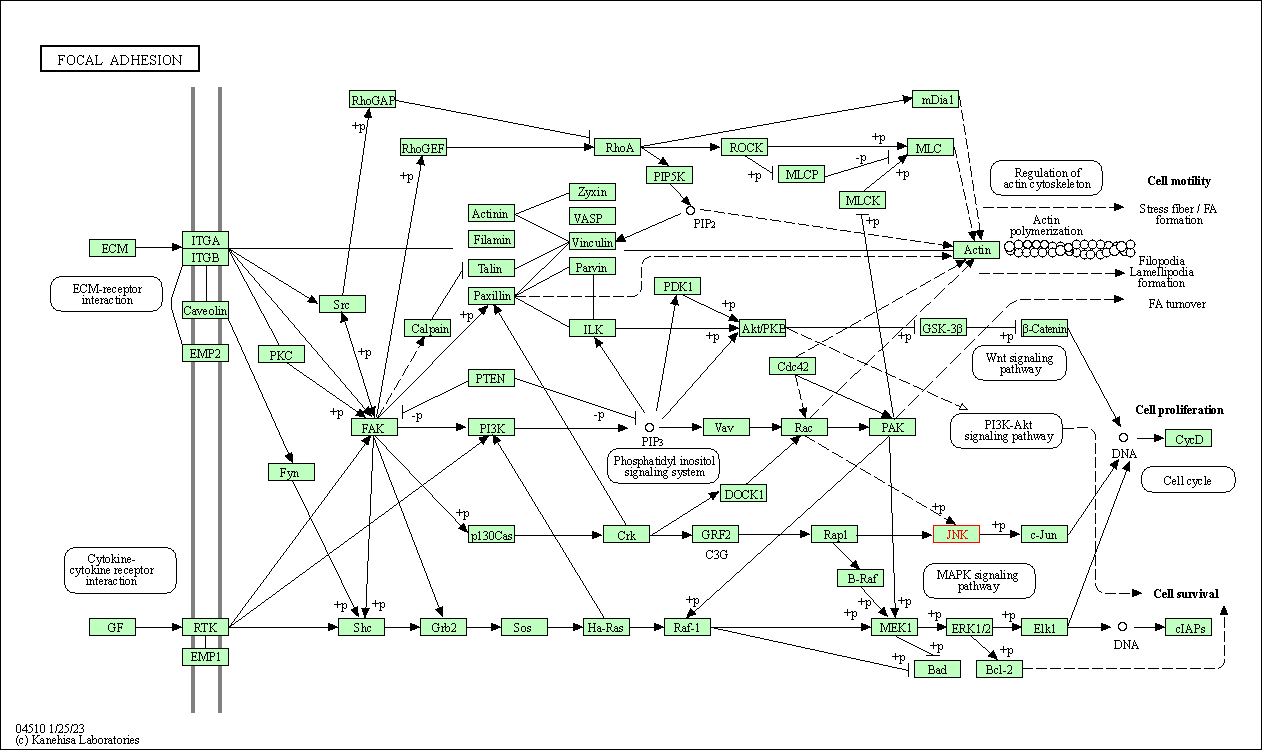
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Tight junction | hsa04530 | Affiliated Target |
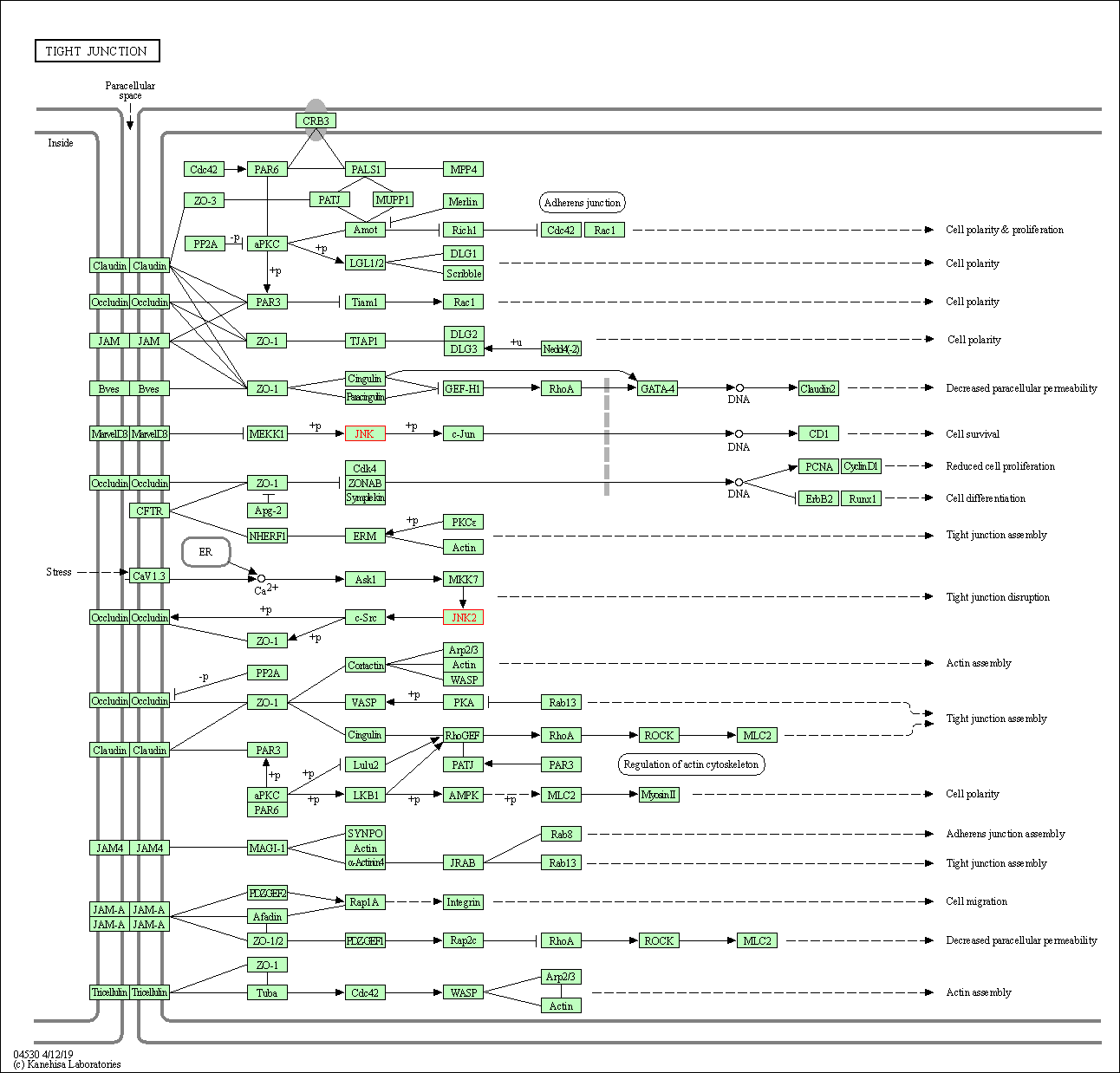
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |
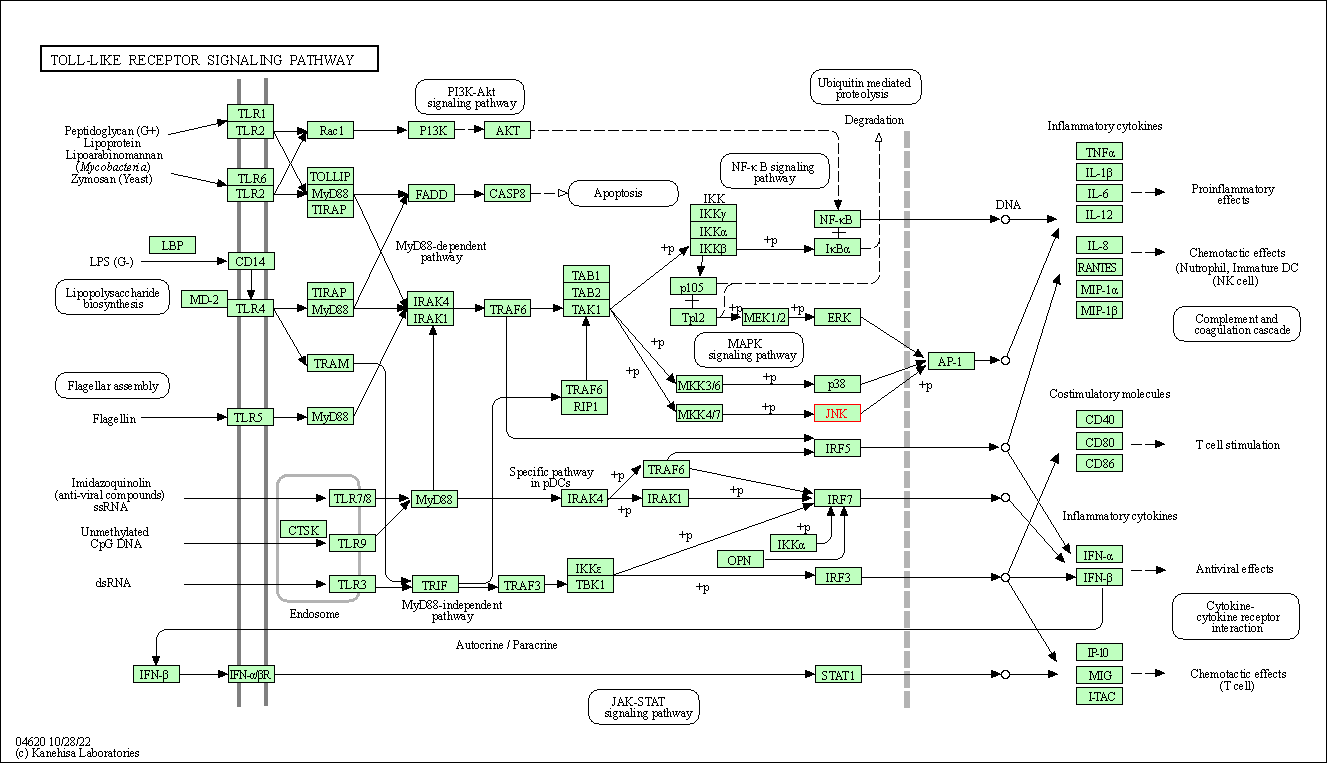
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |
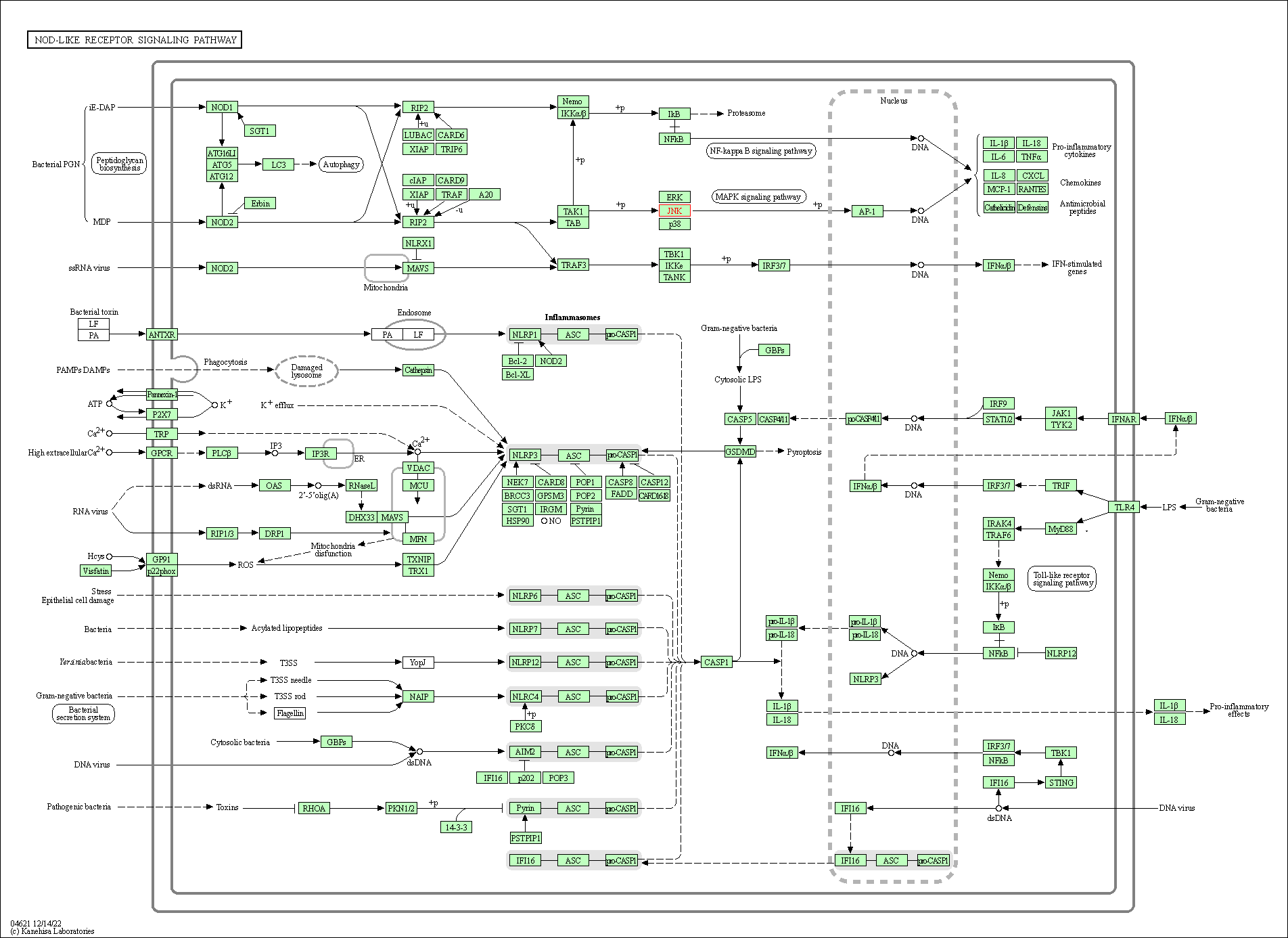
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | hsa04658 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | hsa04750 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 44 | Degree centrality | 4.73E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.70E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.63E-01 | Radiality | 1.45E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 9.41E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.38E+01 | Topological coefficient | 4.12E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95-105. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01415297) Dose Escalation Study of NKP-1339 to Treat Advanced Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04022863) Ovarium Cancer Detection by TEP's and ctDNA. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1496). | |||||
| REF 5 | c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors: a patent review (2010 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(8):849-72. | |||||
| REF 6 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 7 | Discovery of a new class of 4-anilinopyrimidines as potent c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors: Synthesis and SAR studies. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Feb 1;17(3):668-72. | |||||
| REF 8 | Optimization of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6239-47. | |||||
| REF 9 | Aminopyridine-based c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors with cellular activity and minimal cross-kinase activity. J Med Chem. 2006 Jun 15;49(12):3563-80. | |||||
| REF 10 | The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J. 2007 Dec 15;408(3):297-315. | |||||
| REF 11 | Discovery of potent, highly selective, and orally bioavailable pyridine carboxamide c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2006 Jul 27;49(15):4455-8. | |||||
| REF 12 | Structural Basis for the Selective Inhibition of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase 1 Determined by Rigid DARPin-DARPin Fusions. J Mol Biol. 2018 Jul 6;430(14):2128-2138. | |||||
| REF 13 | Specificity of linear motifs that bind to a common mitogen-activated protein kinase docking groove. Sci Signal. 2012 Oct 9;5(245):ra74. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

