Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T82739
(Former ID: TTDC00013)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Plasma kallikrein (KLKB1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Plasma prekallikrein; Plasma kallikrein light chain; Plasma kallikrein heavy chain; PKK; Kininogenin; KLK3; Fletcher factor
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
KLKB1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Innate/adaptive immunodeficiency [ICD-11: 4A00] | |||||
| 2 | Retinal vascular occlusion [ICD-11: 9B74] | |||||
| Function |
It activates, in a reciprocal reaction, factor XII after its binding to a negatively charged surface. It also releases bradykinin from HMW kininogen and may also play a role in the renin-angiotensin system by converting prorenin into renin. The enzyme cleaves Lys-Arg and Arg-Ser bonds.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Peptidase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.4.21.34
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MILFKQATYFISLFATVSCGCLTQLYENAFFRGGDVASMYTPNAQYCQMRCTFHPRCLLF
SFLPASSINDMEKRFGCFLKDSVTGTLPKVHRTGAVSGHSLKQCGHQISACHRDIYKGVD MRGVNFNVSKVSSVEECQKRCTNNIRCQFFSYATQTFHKAEYRNNCLLKYSPGGTPTAIK VLSNVESGFSLKPCALSEIGCHMNIFQHLAFSDVDVARVLTPDAFVCRTICTYHPNCLFF TFYTNVWKIESQRNVCLLKTSESGTPSSSTPQENTISGYSLLTCKRTLPEPCHSKIYPGV DFGGEELNVTFVKGVNVCQETCTKMIRCQFFTYSLLPEDCKEEKCKCFLRLSMDGSPTRI AYGTQGSSGYSLRLCNTGDNSVCTTKTSTRIVGGTNSSWGEWPWQVSLQVKLTAQRHLCG GSLIGHQWVLTAAHCFDGLPLQDVWRIYSGILNLSDITKDTPFSQIKEIIIHQNYKVSEG NHDIALIKLQAPLNYTEFQKPICLPSKGDTSTIYTNCWVTGWGFSKEKGEIQNILQKVNI PLVTNEECQKRYQDYKITQRMVCAGYKEGGKDACKGDSGGPLVCKHNGMWRLVGITSWGE GCARREQPGVYTKVAEYMDWILEKTQSSDGKAQMQSPA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A01502 ; BADD_A06794 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ecallantide | Drug Info | Approved | Retina venous occlusion | [3], [4] | |
| 2 | Lanadelumab | Drug Info | Approved | Hereditary angioedema | [5] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | KVD001 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic macular edema | [8] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 9 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ecallantide | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | KVD001 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 3 | (3-nitro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)(p-tolyl)methanone | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 4 | (3-nitro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)(phenyl)methanone | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 5 | (4-bromo-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)(p-tolyl)methanone | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 6 | 1-benzoyl-N-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 7 | D-Pro-Phe-Arg chloromethyl ketone | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 8 | ZK-810388 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 9 | ZK-814048 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Lanadelumab | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Glutathione | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | human plasmakallikrein protease domain in complex with active site directed inhibitor | PDB:6T7P | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.42 Å | Mutation | No | [13] |
| PDB Sequence |
IVGGTNSSWG
25 EWPWQVSLQV35 KLTAQRHLCG43 GSLIGHQWVL53 TAAHCFDGLP60C LQDVWRIYSG 69 ILNLSDITKD79 TPFSQIKEII89 IHQNYKVSEG99 NHDIALIKLQ109 APLNYTEFQK 119 PICLPSKGDT129 STIYTNCWVT139 GWGFSKEKGE150 IQNILQKVNI160 PLVTNEECQK 170 RYQDYKITQR179 MVCAGYKEGG187A KDACKGDSGG197 PLVCKHNGMW207 RLVGITSWGE 217 GCARREQPGV227 YTKVAEYMDW237 ILEKTQS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Benzamidine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Allosteric activation of human prekallikrein by apple domain disc rotation | PDB:6I44 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.36 Å | Mutation | No | [14] |
| PDB Sequence |
GCLTQLYENA
10 FFRGGDVASM20 YTPNAQYCQM30 RCTFHPRCLL40 FSFLPASSIN50 DMEKRFGCFL 60 KDSVTGTLPK70 VHRTGAVSGH80 SLKQCGHQIS90 ACHRDIYKGV100 DMRGVNFNVS 110 KVSSVEECQK120 RCTNNIRCQF130 FSYATQTFHK140 AEYRNNCLLK150 YSPGGTPTAI 160 KVLSNVESGF170 SLKPCALSEI180 GCHMNIFQHL190 AFSDVDVARV200 LTPDAFVCRT 210 ICTYHPNCLF220 FTFYTNVWKI230 ESQRNVCLLK240 TSESGTPSSS250 TPQENTISGY 260 SLLTCKRTLP270 EPCHSKIYPG280 VDFGGEELNV290 TFVKGVNVCQ300 ETCTKMIRCQ 310 FFTYSLLPED320 CKAEACKCFL330 RLSMDGSPTR340 IAYGTQGSSG350 YSLRLCNTVC 364 TIVGGTQSSW380 GEWPWQVSLQ390 VKLTAQRHLC400 GGSLIGHQWV410 LTAAHCFDGL 420 PLQDVWRIYS430 GILQLSDITK440 DTPFSQIKEI450 IIHQNYKVSE460 GNHDIALIKL 470 QAPLQYTEFQ480 KPICLPSIYT496 NCWVTGWGFS506 AEAGEIQNIL516 QKVNIPLVTN 526 EECQKRYQDY536 KITQRMVCAG546 YKEGGKDACK556 GDAGGPLVCK566 HNGMWRLVGI 576 TSWGEGCARR586 EQPGVYTKVA596 EYMDWILEKT606 QSSD
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | hsa04610 | Affiliated Target |
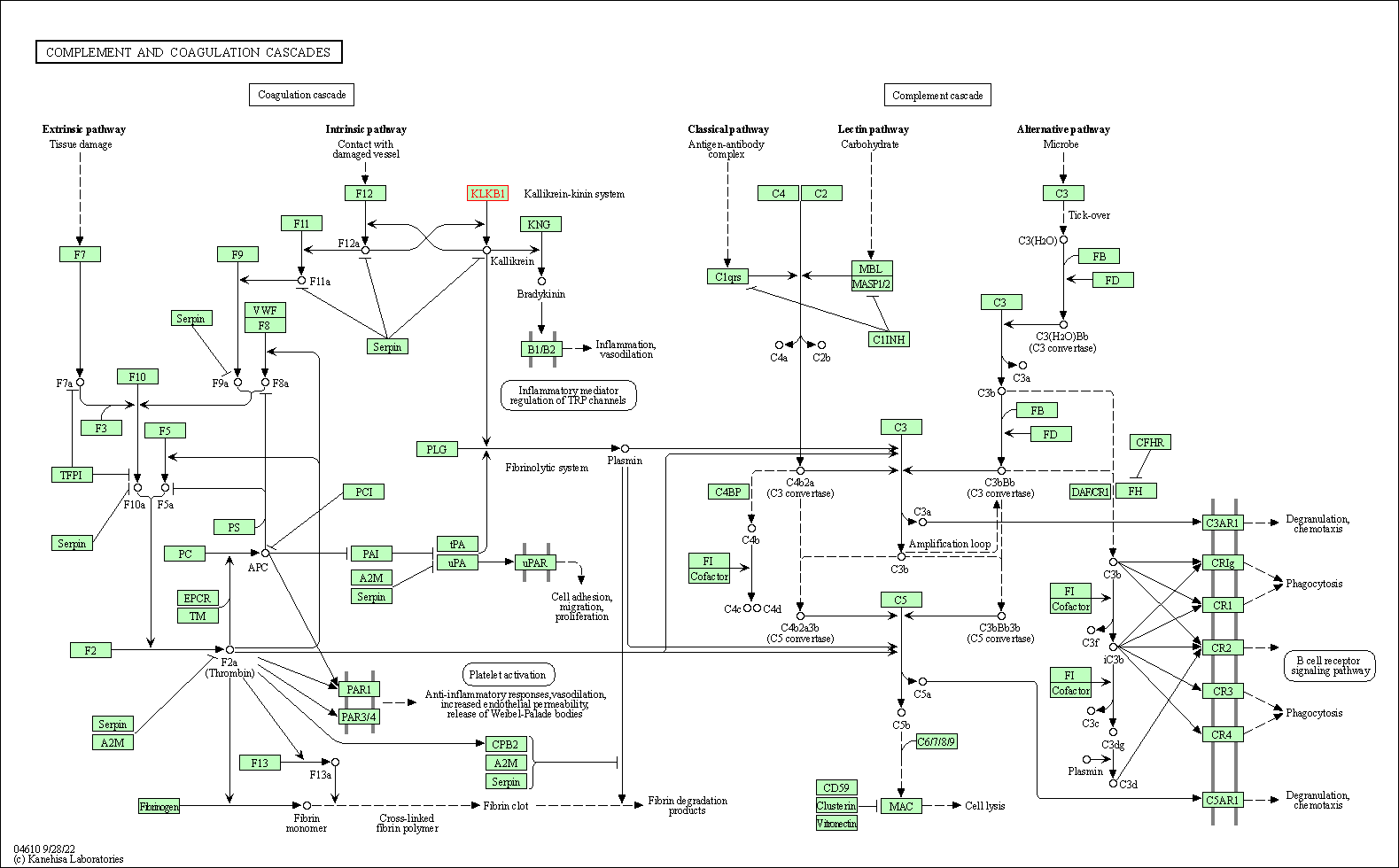
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 5 | Degree centrality | 5.37E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 6.85E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.79E-01 | Radiality | 1.30E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 7.20E+00 | Topological coefficient | 2.80E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 1 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Complement and coagulation cascades | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | AndrogenReceptor Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Blood coagulation | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Coagulation | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation | |||||
| 2 | Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 4 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Complement and Coagulation Cascades | |||||
| 2 | Human Complement System | |||||
| 3 | Blood Clotting Cascade | |||||
| 4 | Formation of Fibrin Clot (Clotting Cascade) | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Ecallantide (DX-88), a plasma kallikrein inhibitor for the treatment of hereditary angioedema and the prevention of blood loss in on-pump cardiothoracic surgery. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008 Aug;8(8):1187-99. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health Human Services. 2020 | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6955). | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00969293) Study to Assess the Safety and Tolerability of a Single Administration of FOV2302 (Ecallantide) in Patients With Macular Edema Associated With Central Retinal Vein Occlusion. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | 2018 FDA drug approvals.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 Feb;18(2):85-89. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04527107) A Study to Evaluate THR-149 Treatment for Diabetic Macular Oedema (KALAHARI). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of KalVista Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03466099) Study of the Intravitreal Plasma Kallikrein Inhibitor, KVD001, in Subjects With Center-involving Diabetic Macular Edema (ciDME). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 10 | N-benzoylpyrazoles are novel small-molecule inhibitors of human neutrophil elastase. J Med Chem. 2007 Oct 4;50(20):4928-38. | |||||
| REF 11 | Novel 3-carboxamide-coumarins as potent and selective FXIIa inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2008 Jun 12;51(11):3077-80. | |||||
| REF 12 | Thiophene-anthranilamides as highly potent and orally available factor Xa inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2007 Jun 28;50(13):2967-80. | |||||
| REF 13 | Structure-Based Design and Preclinical Characterization of Selective and Orally Bioavailable Factor XIa Inhibitors: Demonstrating the Power of an Integrated S1 Protease Family Approach. J Med Chem. 2020 Aug 13;63(15):8088-8113. | |||||
| REF 14 | Plasma kallikrein structure reveals apple domain disc rotated conformation compared to factor XI. J Thromb Haemost. 2019 May;17(5):759-770. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

