Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T84780
(Former ID: TTDI02025)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 (BIRC2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
hIAP2; hIAP-2; TNFR2TRAFsignaling complex protein 2; TNFR2-TRAF-signaling complex protein 2; RNF48; RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase BIRC2; RING finger protein 48; MIHB; Inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2; IAP2; IAP homolog B; CIAP1; C-IAP1; Baculoviral IAP repeatcontaining protein 2; Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 2; API1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
BIRC2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Metastatic lymph node neoplasm [ICD-11: 2D60] | |||||
| Function |
Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase regulating NF-kappa-B signaling and regulates both canonical and non-canonical NF-kappa-B signaling by acting in opposite directions: acts as a positive regulator of the canonical pathway and suppresses constitutive activation of non-canonical NF-kappa-B signaling. The target proteins for its E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity include: RIPK1, RIPK2, RIPK3, RIPK4, CASP3, CASP7, CASP8, TRAF2, DIABLO/SMAC, MAP3K14/NIK, MAP3K5/ASK1, IKBKG/NEMO, IKBKE and MXD1/MAD1. Can also function as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase of the NEDD8 conjugation pathway, targeting effector caspases for neddylation and inactivation. Acts as an important regulator of innate immune signaling via regulation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs), Nodlike receptors (NLRs) and RIG-I like receptors (RLRs), collectively referred to as pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Protects cells from spontaneous formation of the ripoptosome, a large multi-protein complex that has the capability to kill cancer cells in a caspase-dependent and caspase-independent manner. Suppresses ripoptosome formation by ubiquitinating RIPK1 and CASP8. Can stimulate the transcriptional activity of E2F1. Plays a role in the modulation of the cell cycle. Multi-functional protein which regulates not only caspases and apoptosis, but also modulates inflammatory signaling and immunity, mitogenic kinase signaling, and cell proliferation, as well as cell invasion and metastasis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Acyltransferase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.3.2.27
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MHKTASQRLFPGPSYQNIKSIMEDSTILSDWTNSNKQKMKYDFSCELYRMSTYSTFPAGV
PVSERSLARAGFYYTGVNDKVKCFCCGLMLDNWKLGDSPIQKHKQLYPSCSFIQNLVSAS LGSTSKNTSPMRNSFAHSLSPTLEHSSLFSGSYSSLSPNPLNSRAVEDISSSRTNPYSYA MSTEEARFLTYHMWPLTFLSPSELARAGFYYIGPGDRVACFACGGKLSNWEPKDDAMSEH RRHFPNCPFLENSLETLRFSISNLSMQTHAARMRTFMYWPSSVPVQPEQLASAGFYYVGR NDDVKCFCCDGGLRCWESGDDPWVEHAKWFPRCEFLIRMKGQEFVDEIQGRYPHLLEQLL STSDTTGEENADPPIIHFGPGESSSEDAVMMNTPVVKSALEMGFNRDLVKQTVQSKILTT GENYKTVNDIVSALLNAEDEKREEEKEKQAEEMASDDLSLIRKNRMALFQQLTCVLPILD NLLKANVINKQEHDIIKQKTQIPLQARELIDTILVKGNAAANIFKNCLKEIDSTLYKNLF VDKNMKYIPTEDVSGLSLEEQLRRLQEERTCKVCMDKEVSVVFIPCGHLVVCQECAPSLR KCPICRGIIKGTVRTFLS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A05675 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T14JSQ | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AT-406 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Squamous head and neck cell carcinom | [2] | |
| 2 | Birinapant | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Lymphoma | [3], [4] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 2 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AT-406 | Drug Info | [5], [6] | |||
| 2 | BV-6 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Birinapant | Drug Info | [1], [7] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 20 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PMID25980951-Compound-1 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 2 | PMID25980951-Compound-16 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 3 | PMID25980951-Compound-17 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 4 | PMID25980951-Compound-18 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 5 | PMID25980951-Compound-19 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 6 | PMID25980951-Compound-20 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 7 | PMID25980951-Compound-21 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 8 | PMID25980951-Compound-22 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 9 | PMID25980951-Compound-27 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 10 | PMID25980951-Compound-3 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 11 | PMID25980951-Compound-36 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 12 | PMID25980951-Compound-37 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 13 | PMID25980951-Compound-38 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 14 | PMID25980951-Compound-4 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 15 | PMID25980951-Compound-41 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 16 | PMID25980951-Compound-42 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 17 | PMID25980951-Compound-43 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 18 | PMID25980951-Compound-5 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 19 | PMID25980951-Compound-6 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 20 | PMID25980951-Compound-7 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: PMID25980951-Compound-16 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of cIAP1 BIR3 bound to T3256336 | PDB:4HY5 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.75 Å | Mutation | No | [10] |
| PDB Sequence |
GSSISNLSMQ
261 THAARMRTFM271 YWPSSVPVQP281 EQLASAGFYY291 VGRNDDVKCF301 CCDGGLRCWE 311 SGDDPWVEHA321 KWFPRCEFLI331 RMKGQEFVDE341 IQGRY
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: (3S,6S,7R,9aS)-N-benzyl-6-[[(2S)-2-(methylamino)propanoyl]amino]-5-oxo-7-[(propanoylamino)methyl]-3,6,7,8,9,9a-hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]azepine-3-carboxamide | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of cIAP1-BIR3 in complex with a covalently bound SM | PDB:6EXW | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.20 Å | Mutation | No | [11] |
| PDB Sequence |
SISNLSMQTH
263 AARMRTFMYW273 PSSVPVQPEQ283 LASAGFYYVG293 RNDDVKCFCC303 DGGLRCWESG 313 DDPWVEHAKW323 FPRCEFLIRM333 KGQEFVDEIQ343 GRYPHLLE
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |
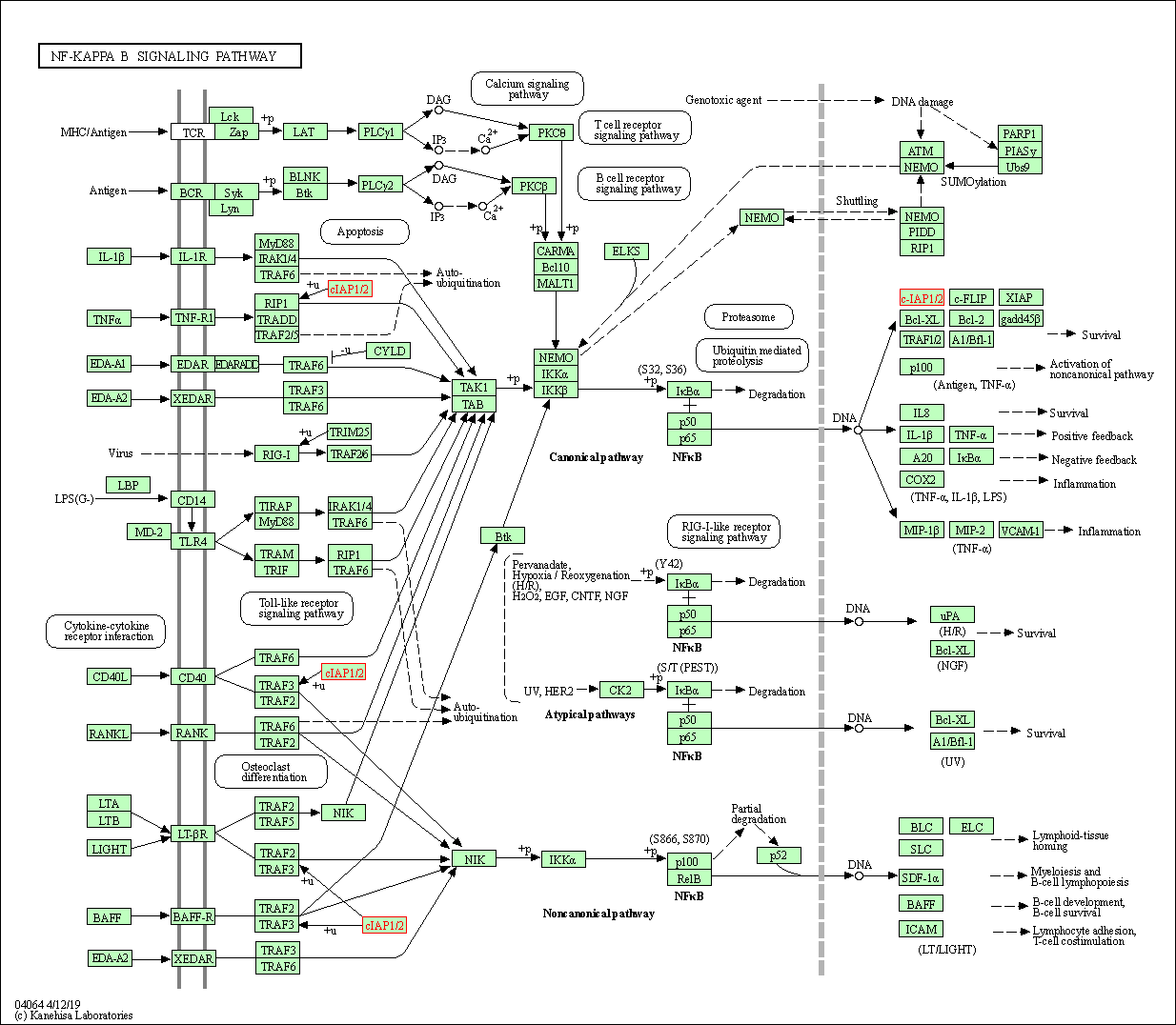
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | Affiliated Target |
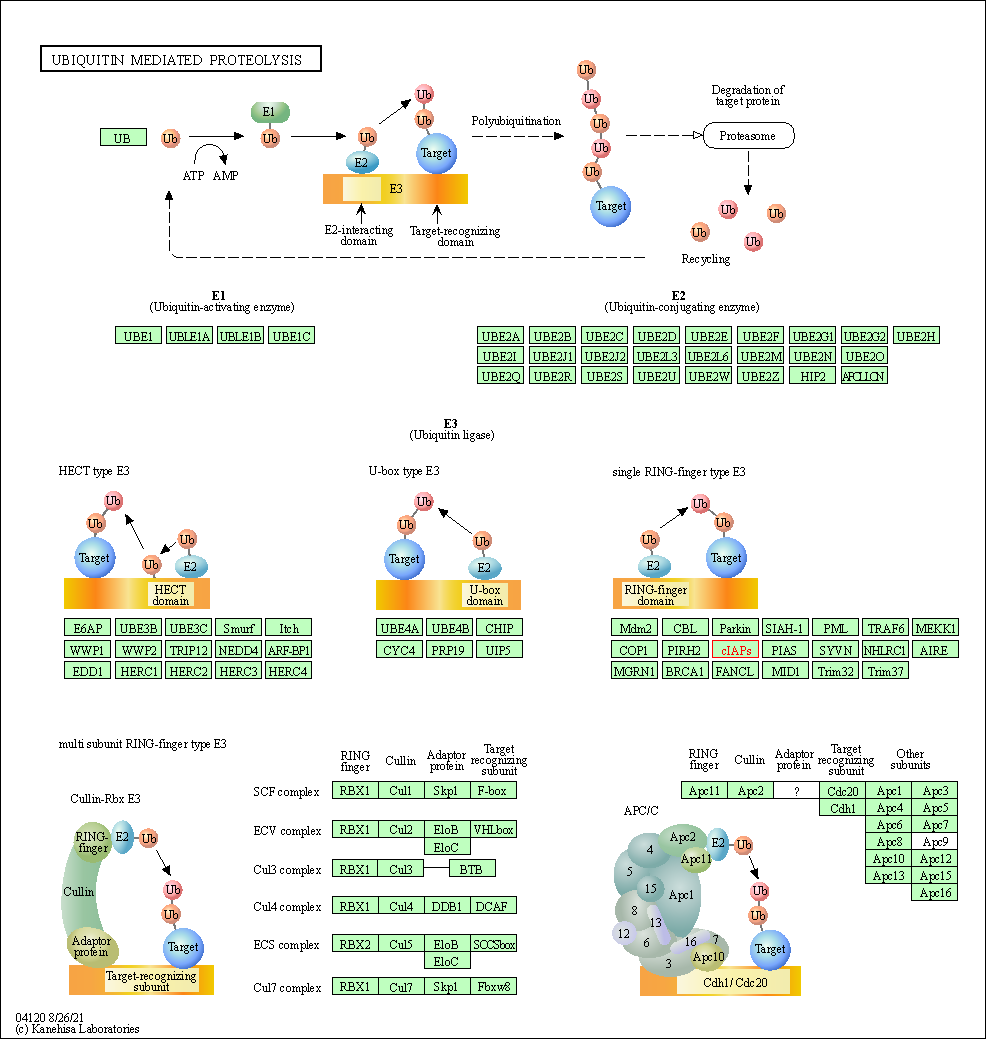
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |
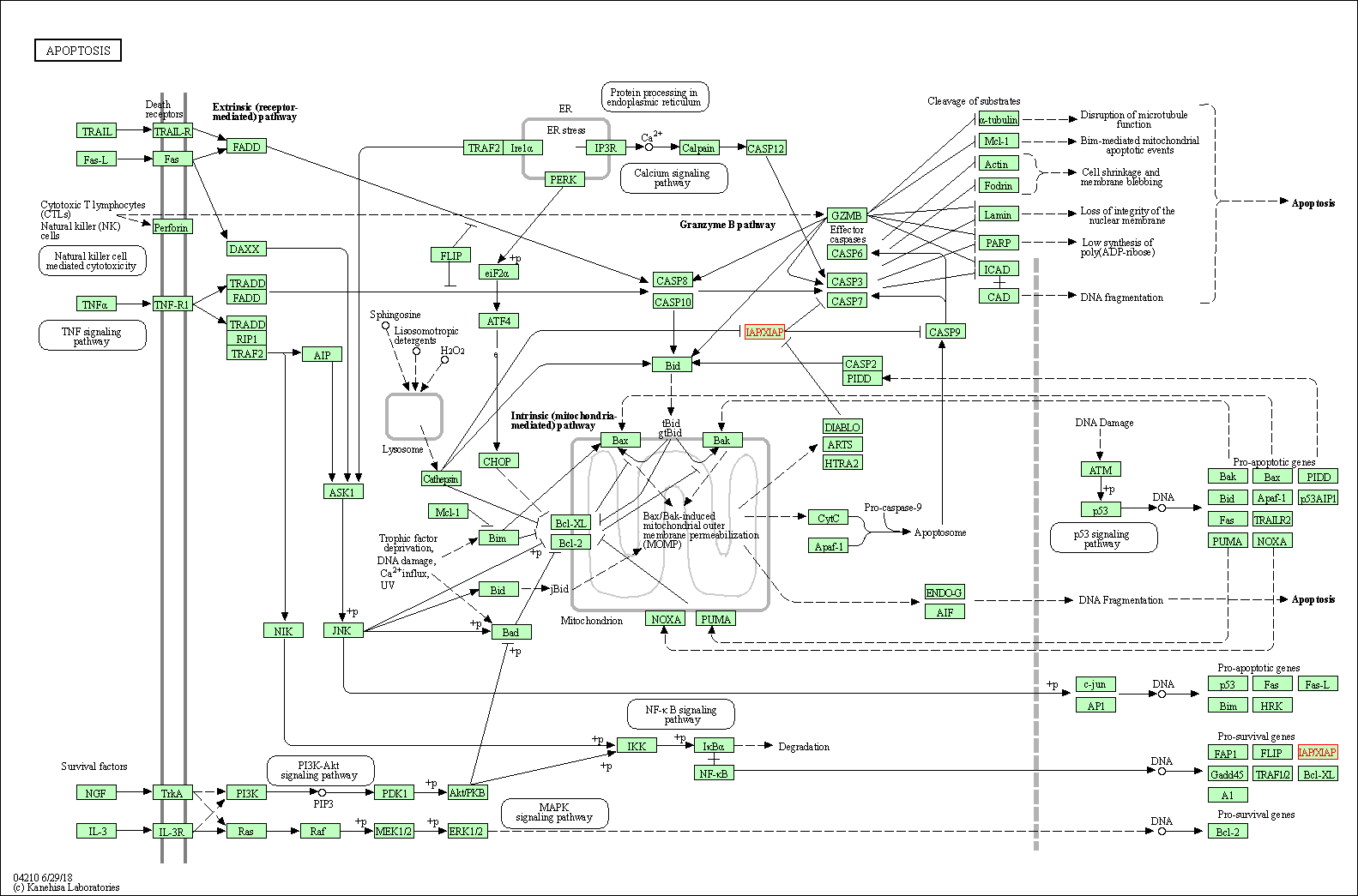
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis - multiple species | hsa04215 | Affiliated Target |
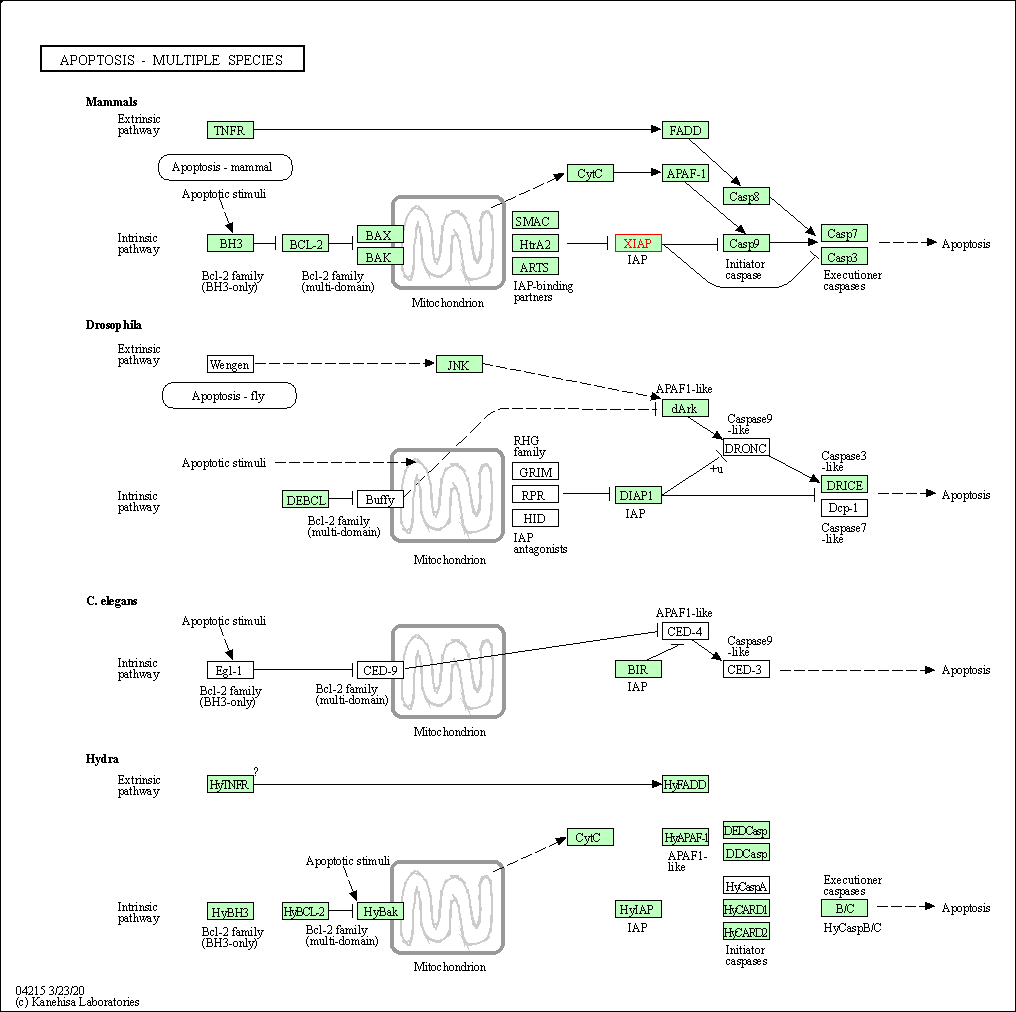
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 36 | Degree centrality | 3.87E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 6.15E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.43E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.51E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.51E+01 | Topological coefficient | 6.84E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | cIAPs and XIAP regulate myelopoiesis through cytokine production in an RIPK1- and RIPK3-dependent manner. Blood. 2014 Apr 17;123(16):2562-72. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04459715) A Study of Debio 1143 (Xevinapant) in Combination With Platinum-Based Chemotherapy and Standard Fractionation Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy in Participants With Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, Suitable for Definitive Chemoradiotherapy. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7432). | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02147873) Study of Azacitidine With or Without Birinapant in Subjects With MDS or CMMoL. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | Debio 1143, an antagonist of multiple inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins, activates apoptosis and enhances radiosensitization of non-small cell lung c... Am J Cancer Res. 2014 Nov 19;4(6):943-51. | |||||
| REF 6 | Debio 1143, an antagonist of multiple inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins, activates apoptosis and enhances radiosensitization of non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro. Am J Cancer Res. 2014; 4(6): 943-951. | |||||
| REF 7 | Birinapant (TL32711), a bivalent SMAC mimetic, targets TRAF2-associated cIAPs, abrogates TNF-induced NF- B activation, and is active in patient-derived xenograft models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Apr;13(4):867-79. | |||||
| REF 8 | Small molecule inhibitor of apoptosis proteins antagonists: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 Jul;25(7):755-74. | |||||
| REF 9 | IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell. 2007 Nov 16;131(4):669-81. | |||||
| REF 10 | Design and synthesis of potent inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins antagonists bearing an octahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine scaffold as a novel proline mimetic. J Med Chem. 2013 Feb 14;56(3):1228-46. | |||||
| REF 11 | Structure-based design and molecular profiling of Smac-mimetics selective for cellular IAPs. FEBS J. 2018 Sep;285(17):3286-3298. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

