Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T01575
(Former ID: TTDI02173)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (SGPL1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
hSPL; Sphingosine-1-phosphate aldolase; SPL 1; SP-lyase 1; S1PL; KIAA1252
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
SGPL1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Congenital ichthyosis [ICD-11: EC20] | |||||
| 2 | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||||
| Function |
Elevates stress-induced ceramide production and apoptosis. Required for global lipid homeostasis in liver and cholesterol homeostasis in fibroblasts. Involved in the regulation of pro-inflammatory response and neutrophil trafficking. Modulates neuronal autophagy via phosphoethanolamine production which regulates accumulation of aggregate-prone proteins such as APP. Seems to play a role in establishing neuronal contact sites and axonal maintenance. Cleaves phosphorylated sphingoid bases (PSBs), such as sphingosine-1-phosphate, into fatty aldehydes and phosphoethanolamine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Carbon-carbon lyase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 4.1.2.27
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MPSTDLLMLKAFEPYLEILEVYSTKAKNYVNGHCTKYEPWQLIAWSVVWTLLIVWGYEFV
FQPESLWSRFKKKCFKLTRKMPIIGRKIQDKLNKTKDDISKNMSFLKVDKEYVKALPSQG LSSSAVLEKLKEYSSMDAFWQEGRASGTVYSGEEKLTELLVKAYGDFAWSNPLHPDIFPG LRKIEAEIVRIACSLFNGGPDSCGCVTSGGTESILMACKAYRDLAFEKGIKTPEIVAPQS AHAAFNKAASYFGMKIVRVPLTKMMEVDVRAMRRAISRNTAMLVCSTPQFPHGVIDPVPE VAKLAVKYKIPLHVDACLGGFLIVFMEKAGYPLEHPFDFRVKGVTSISADTHKYGYAPKG SSLVLYSDKKYRNYQFFVDTDWQGGIYASPTIAGSRPGGISAACWAALMHFGENGYVEAT KQIIKTARFLKSELENIKGIFVFGNPQLSVIALGSRDFDIYRLSNLMTAKGWNLNQLQFP PSIHFCITLLHARKRVAIQFLKDIRESVTQIMKNPKAKTTGMGAIYGMAQTTVDRNMVAE LSSVFLDSLYSTDTVTQGSQMNGSPKPH Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LX2931 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Rheumatoid arthritis | [2] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LX-2932 | Drug Info | Terminated | Autoimmune diabetes | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 3 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LX2931 | Drug Info | [1], [4] | |||
| 2 | LX-2932 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 3 | PMID24809814C31 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: PMID24809814C31 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase in complex with inhibitor 6-[(2R)-4-(4-benzyl-7-chlorophthalazin-1-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-yl]pyridine-3-carbonitrile | PDB:4Q6R | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.40 Å | Mutation | No | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
EYVKALPSQG
120 LSSSAVLEKL130 KEYSSMDAFW140 QEGRASGTVY150 SGEEKLTELL160 VKAYGDFAWS 170 NPLHPDIFPG180 LRKIEAEIVR190 IACSLFNGGP200 DSCGCVTSGG210 TESILMACKA 220 YRDLAFEKGI230 KTPEIVAPQS240 AHAAFNKAAS250 YFGMKIVRVP260 LTKMMEVDVR 270 AMRRAISRNT280 AMLVCSTPQF290 PHGVIDPVPE300 VAKLAVKYKI310 PLHVDACLGG 320 FLIVFMEKAG330 YPLEHPFDFR340 VKGVTSISAD350 THYGYAPKGS361 SLVLYSDKKY 371 RNYQFFVDTD381 WQGGIYASPT391 IAGSRPGGIS401 AACWAALMHF411 GENGYVEATK 421 QIIKTARFLK431 SELENIKGIF441 VFGNPQLSVI451 ALGSRDFDIY461 RLSNLMTAKG 471 WNLNQLQFPP481 SIHFCITLLH491 ARKRVAIQFL501 KDIRESVTQI511 MKNPKAKTTG 521 MGAIYGMAQT531 TVDRNMVAEL541 SSVFLDSLYS551 TD
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: N6-((3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-5-((phosphonooxy)methyl)-4-pyridinyl)methylene)-L-lysine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase in complex with inhibitor 6-[(2R)-4-(4-benzyl-7-chlorophthalazin-1-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-yl]pyridine-3-carbonitrile | PDB:4Q6R | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.40 Å | Mutation | No | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
EYVKALPSQG
120 LSSSAVLEKL130 KEYSSMDAFW140 QEGRASGTVY150 SGEEKLTELL160 VKAYGDFAWS 170 NPLHPDIFPG180 LRKIEAEIVR190 IACSLFNGGP200 DSCGCVTSGG210 TESILMACKA 220 YRDLAFEKGI230 KTPEIVAPQS240 AHAAFNKAAS250 YFGMKIVRVP260 LTKMMEVDVR 270 AMRRAISRNT280 AMLVCSTPQF290 PHGVIDPVPE300 VAKLAVKYKI310 PLHVDACLGG 320 FLIVFMEKAG330 YPLEHPFDFR340 VKGVTSISAD350 THYGYAPKGS361 SLVLYSDKKY 371 RNYQFFVDTD381 WQGGIYASPT391 IAGSRPGGIS401 AACWAALMHF411 GENGYVEATK 421 QIIKTARFLK431 SELENIKGIF441 VFGNPQLSVI451 ALGSRDFDIY461 RLSNLMTAKG 471 WNLNQLQFPP481 SIHFCITLLH491 ARKRVAIQFL501 KDIRESVTQI511 MKNPKAKTTG 521 MGAIYGMAQT531 TVDRNMVAEL541 SSVFLDSLYS551 TD
|
|||||
|
|
TYR150
3.294
GLY209
4.117
GLY210
3.137
THR211
2.609
ILE214
3.617
HIS242
3.411
PRO288
3.867
GLN289
4.695
PHE290
3.869
ASP315
2.812
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sphingolipid metabolism | hsa00600 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |
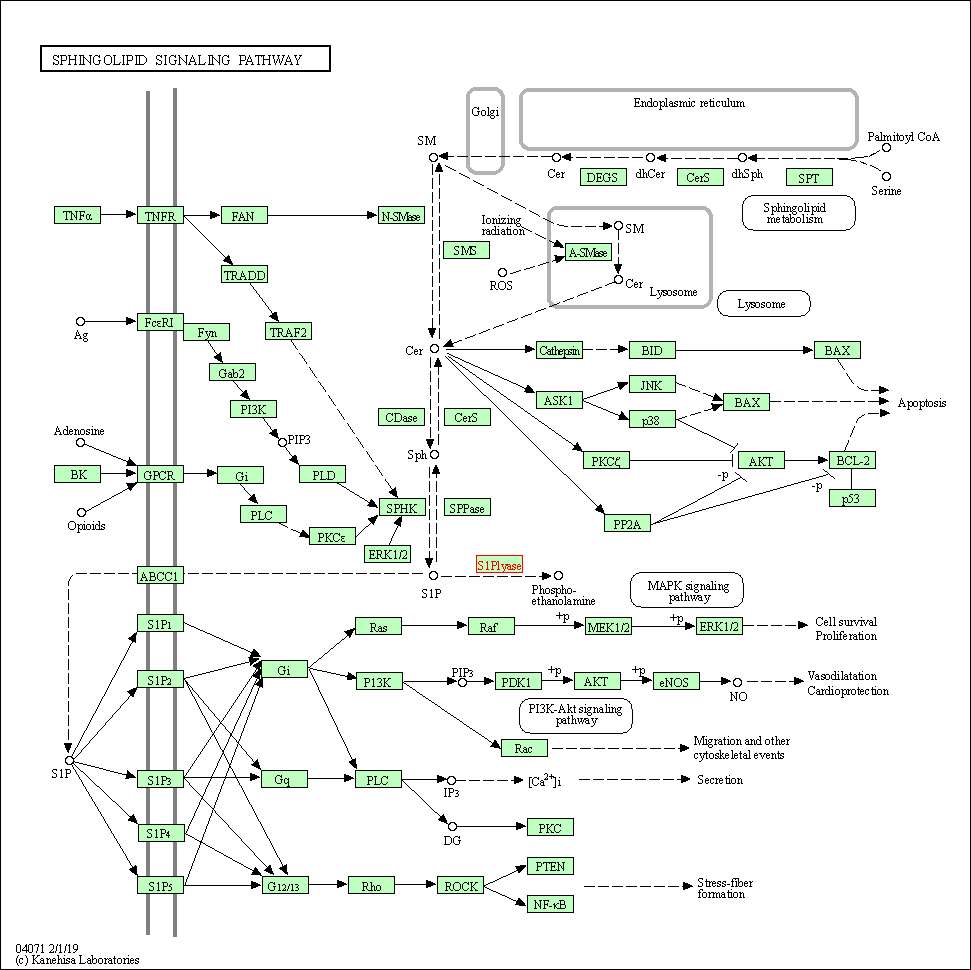
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 5 | Degree centrality | 5.37E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 3.33E-07 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.82E-01 | Radiality | 1.30E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 8.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.34E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.15E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 3 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Sphingolipid metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 3 | Sphingolipid signaling pathway | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Sphingolipid Metabolism | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) pathway | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Sphingolipid de novo biosynthesis | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 1 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Sphingolipid metabolism | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer, inflammation and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Sep;12(9):688-702. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00903383) Study of LX3305 in Subjects With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis on Stable Methotrexate. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021957) | |||||
| REF 4 | S1P is associated with protection in human and experimental cerebral malaria. Mol Med. 2011;17(7-8):717-25. | |||||
| REF 5 | Inhibition of sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: discovery of (E)-1-(4-((1R,2S,3R)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroxybutyl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl)ethanone oxime (LX2931) and (1R,2S,3R)-1-(2-(isoxazol-3-yl)-1H-imidazol-4-yl)butane-1,2,3,4-tetraol (LX2932). J Med Chem. 2010 Dec 23;53(24):8650-62. | |||||
| REF 6 | Orally active 7-substituted (4-benzylphthalazin-1-yl)-2-methylpiperazin-1-yl]nicotinonitriles as active-site inhibitors of sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. J MedChem. 2014 Jun 26;57(12):5074-84. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

