Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T81735
(Former ID: TTDR01142)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic (PRKDC)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
p460; HYRC1; HYRC; DNPK1; DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit; DNA-PKcs; DNA-PK catalytic subunit
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PRKDC
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Rectum cancer [ICD-11: 2B92] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts as a molecular sensor for DNA damage. Involved in DNA non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) required for double-strand break (DSB) repair and V(D)J recombination. Must be bound to DNA to express its catalytic properties. Promotes processing of hairpin DNA structures in V(D)J recombination by activation of the hairpin endonuclease artemis (DCLRE1C). The assembly of the DNA-PK complex at DNA ends is also required for the NHEJ ligation step. Required to protect and align broken ends of DNA. May also act as a scaffold protein to aid the localization of DNA repair proteins to the site of damage. Found at the ends of chromosomes, suggesting a further role in the maintenance of telomeric stability and the prevention of chromosomal end fusion. Also involved in modulation of transcription. Recognizes the substrate consensus sequence [ST]-Q. Phosphorylates 'Ser-139' of histone variant H2AX/H2AFX, thereby regulating DNA damage response mechanism. Phosphorylates DCLRE1C, c-Abl/ABL1, histone H1, HSPCA, c-jun/JUN, p53/TP53, PARP1, POU2F1, DHX9, FH, SRF, XRCC1, XRCC1, XRCC4, XRCC5, XRCC6, WRN, MYC and RFA2. Can phosphorylate C1D not only in the presence of linear DNA but also in the presence of supercoiled DNA. Ability to phosphorylate p53/TP53 in the presence of supercoiled DNA is dependent on C1D. Contributes to the determination of the circadian period length by antagonizing phosphorylation of CRY1 'Ser-588' and increasing CRY1 protein stability, most likely through an indirect mechanism (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of DNA virus-mediated innate immune response by assembling into the HDP-RNP complex, a complex that serves as a platform for IRF3 phosphorylation and subsequent innate immune response activation through the cGAS-STING pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAGSGAGVRCSLLRLQETLSAADRCGAALAGHQLIRGLGQECVLSSSPAVLALQTSLVFS
RDFGLLVFVRKSLNSIEFRECREEILKFLCIFLEKMGQKIAPYSVEIKNTCTSVYTKDRA AKCKIPALDLLIKLLQTFRSSRLMDEFKIGELFSKFYGELALKKKIPDTVLEKVYELLGL LGEVHPSEMINNAENLFRAFLGELKTQMTSAVREPKLPVLAGCLKGLSSLLCNFTKSMEE DPQTSREIFNFVLKAIRPQIDLKRYAVPSAGLRLFALHASQFSTCLLDNYVSLFEVLLKW CAHTNVELKKAALSALESFLKQVSNMVAKNAEMHKNKLQYFMEQFYGIIRNVDSNNKELS IAIRGYGLFAGPCKVINAKDVDFMYVELIQRCKQMFLTQTDTGDDRVYQMPSFLQSVASV LLYLDTVPEVYTPVLEHLVVMQIDSFPQYSPKMQLVCCRAIVKVFLALAAKGPVLRNCIS TVVHQGLIRICSKPVVLPKGPESESEDHRASGEVRTGKWKVPTYKDYVDLFRHLLSSDQM MDSILADEAFFSVNSSSESLNHLLYDEFVKSVLKIVEKLDLTLEIQTVGEQENGDEAPGV WMIPTSDPAANLHPAKPKDFSAFINLVEFCREILPEKQAEFFEPWVYSFSYELILQSTRL PLISGFYKLLSITVRNAKKIKYFEGVSPKSLKHSPEDPEKYSCFALFVKFGKEVAVKMKQ YKDELLASCLTFLLSLPHNIIELDVRAYVPALQMAFKLGLSYTPLAEVGLNALEEWSIYI DRHVMQPYYKDILPCLDGYLKTSALSDETKNNWEVSALSRAAQKGFNKVVLKHLKKTKNL SSNEAISLEEIRIRVVQMLGSLGGQINKNLLTVTSSDEMMKSYVAWDREKRLSFAVPFRE MKPVIFLDVFLPRVTELALTASDRQTKVAACELLHSMVMFMLGKATQMPEGGQGAPPMYQ LYKRTFPVLLRLACDVDQVTRQLYEPLVMQLIHWFTNNKKFESQDTVALLEAILDGIVDP VDSTLRDFCGRCIREFLKWSIKQITPQQQEKSPVNTKSLFKRLYSLALHPNAFKRLGASL AFNNIYREFREEESLVEQFVFEALVIYMESLALAHADEKSLGTIQQCCDAIDHLCRIIEK KHVSLNKAKKRRLPRGFPPSASLCLLDLVKWLLAHCGRPQTECRHKSIELFYKFVPLLPG NRSPNLWLKDVLKEEGVSFLINTFEGGGCGQPSGILAQPTLLYLRGPFSLQATLCWLDLL LAALECYNTFIGERTVGALQVLGTEAQSSLLKAVAFFLESIAMHDIIAAEKCFGTGAAGN RTSPQEGERYNYSKCTVVVRIMEFTTTLLNTSPEGWKLLKKDLCNTHLMRVLVQTLCEPA SIGFNIGDVQVMAHLPDVCVNLMKALKMSPYKDILETHLREKITAQSIEELCAVNLYGPD AQVDRSRLAAVVSACKQLHRAGLLHNILPSQSTDLHHSVGTELLSLVYKGIAPGDERQCL PSLDLSCKQLASGLLELAFAFGGLCERLVSLLLNPAVLSTASLGSSQGSVIHFSHGEYFY SLFSETINTELLKNLDLAVLELMQSSVDNTKMVSAVLNGMLDQSFRERANQKHQGLKLAT TILQHWKKCDSWWAKDSPLETKMAVLALLAKILQIDSSVSFNTSHGSFPEVFTTYISLLA DTKLDLHLKGQAVTLLPFFTSLTGGSLEELRRVLEQLIVAHFPMQSREFPPGTPRFNNYV DCMKKFLDALELSQSPMLLELMTEVLCREQQHVMEELFQSSFRRIARRGSCVTQVGLLES VYEMFRKDDPRLSFTRQSFVDRSLLTLLWHCSLDALREFFSTIVVDAIDVLKSRFTKLNE STFDTQITKKMGYYKILDVMYSRLPKDDVHAKESKINQVFHGSCITEGNELTKTLIKLCY DAFTENMAGENQLLERRRLYHCAAYNCAISVICCVFNELKFYQGFLFSEKPEKNLLIFEN LIDLKRRYNFPVEVEVPMERKKKYIEIRKEAREAANGDSDGPSYMSSLSYLADSTLSEEM SQFDFSTGVQSYSYSSQDPRPATGRFRRREQRDPTVHDDVLELEMDELNRHECMAPLTAL VKHMHRSLGPPQGEEDSVPRDLPSWMKFLHGKLGNPIVPLNIRLFLAKLVINTEEVFRPY AKHWLSPLLQLAASENNGGEGIHYMVVEIVATILSWTGLATPTGVPKDEVLANRLLNFLM KHVFHPKRAVFRHNLEIIKTLVECWKDCLSIPYRLIFEKFSGKDPNSKDNSVGIQLLGIV MANDLPPYDPQCGIQSSEYFQALVNNMSFVRYKEVYAAAAEVLGLILRYVMERKNILEES LCELVAKQLKQHQNTMEDKFIVCLNKVTKSFPPLADRFMNAVFFLLPKFHGVLKTLCLEV VLCRVEGMTELYFQLKSKDFVQVMRHRDDERQKVCLDIIYKMMPKLKPVELRELLNPVVE FVSHPSTTCREQMYNILMWIHDNYRDPESETDNDSQEIFKLAKDVLIQGLIDENPGLQLI IRNFWSHETRLPSNTLDRLLALNSLYSPKIEVHFLSLATNFLLEMTSMSPDYPNPMFEHP LSECEFQEYTIDSDWRFRSTVLTPMFVETQASQGTLQTRTQEGSLSARWPVAGQIRATQQ QHDFTLTQTADGRSSFDWLTGSSTDPLVDHTSPSSDSLLFAHKRSERLQRAPLKSVGPDF GKKRLGLPGDEVDNKVKGAAGRTDLLRLRRRFMRDQEKLSLMYARKGVAEQKREKEIKSE LKMKQDAQVVLYRSYRHGDLPDIQIKHSSLITPLQAVAQRDPIIAKQLFSSLFSGILKEM DKFKTLSEKNNITQKLLQDFNRFLNTTFSFFPPFVSCIQDISCQHAALLSLDPAAVSAGC LASLQQPVGIRLLEEALLRLLPAELPAKRVRGKARLPPDVLRWVELAKLYRSIGEYDVLR GIFTSEIGTKQITQSALLAEARSDYSEAAKQYDEALNKQDWVDGEPTEAEKDFWELASLD CYNHLAEWKSLEYCSTASIDSENPPDLNKIWSEPFYQETYLPYMIRSKLKLLLQGEADQS LLTFIDKAMHGELQKAILELHYSQELSLLYLLQDDVDRAKYYIQNGIQSFMQNYSSIDVL LHQSRLTKLQSVQALTEIQEFISFISKQGNLSSQVPLKRLLNTWTNRYPDAKMDPMNIWD DIITNRCFFLSKIEEKLTPLPEDNSMNVDQDGDPSDRMEVQEQEEDISSLIRSCKFSMKM KMIDSARKQNNFSLAMKLLKELHKESKTRDDWLVSWVQSYCRLSHCRSRSQGCSEQVLTV LKTVSLLDENNVSSYLSKNILAFRDQNILLGTTYRIIANALSSEPACLAEIEEDKARRIL ELSGSSSEDSEKVIAGLYQRAFQHLSEAVQAAEEEAQPPSWSCGPAAGVIDAYMTLADFC DQQLRKEEENASVIDSAELQAYPALVVEKMLKALKLNSNEARLKFPRLLQIIERYPEETL SLMTKEISSVPCWQFISWISHMVALLDKDQAVAVQHSVEEITDNYPQAIVYPFIISSESY SFKDTSTGHKNKEFVARIKSKLDQGGVIQDFINALDQLSNPELLFKDWSNDVRAELAKTP VNKKNIEKMYERMYAALGDPKAPGLGAFRRKFIQTFGKEFDKHFGKGGSKLLRMKLSDFN DITNMLLLKMNKDSKPPGNLKECSPWMSDFKVEFLRNELEIPGQYDGRGKPLPEYHVRIA GFDERVTVMASLRRPKRIIIRGHDEREHPFLVKGGEDLRQDQRVEQLFQVMNGILAQDSA CSQRALQLRTYSVVPMTSRLGLIEWLENTVTLKDLLLNTMSQEEKAAYLSDPRAPPCEYK DWLTKMSGKHDVGAYMLMYKGANRTETVTSFRKRESKVPADLLKRAFVRMSTSPEAFLAL RSHFASSHALICISHWILGIGDRHLNNFMVAMETGGVIGIDFGHAFGSATQFLPVPELMP FRLTRQFINLMLPMKETGLMYSIMVHALRAFRSDPGLLTNTMDVFVKEPSFDWKNFEQKM LKKGGSWIQEINVAEKNWYPRQKICYAKRKLAGANPAVITCDELLLGHEKAPAFRDYVAV ARGSKDHNIRAQEPESGLSEETQVKCLMDQATDPNILGRTWEGWEPWM Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T98QOA | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | M3814 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Locally advanced rectal cancer | [3] | |
| 2 | M9831 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [1] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 90 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | M3814 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | M9831 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | 1-Morpholin-4-yl-benzo[f]chromen-3-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 4 | 2-(1H-indol-5-yl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 5 | 2-(2-aminophenyl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 6 | 2-(2-Fluoro-phenyl)-benzo[h]chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 7 | 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 8 | 2-(3-acetylphenyl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 9 | 2-(3-Fluoro-phenyl)-benzo[h]chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 10 | 2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 11 | 2-(4-Amino-phenyl)-benzo[h]chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 12 | 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 13 | 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 14 | 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 15 | 2-(benzofuran-2-yl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 16 | 2-(furan-2-yl)-6-morpholino-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 17 | 2-(piperidin-1-yl)-4H-benzo[h]chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 18 | 2-biphenyl-4-yl-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 19 | 2-dibenzofuran-4-yl-6-morpholin-4-yl-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 20 | 2-morpholin-4-yl-6-phenyl-4H-thiopyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 21 | 2-Morpholin-4-yl-6-phenyl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 22 | 2-morpholin-4-yl-8-naphthalen-2-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 23 | 2-morpholin-4-yl-8-phenoxathiin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 24 | 2-morpholin-4-yl-8-styrylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 25 | 2-morpholin-4-yl-8-thiophen-2-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 26 | 2-morpholin-4-yl-8-thiophen-3-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 27 | 2-Morpholin-4-yl-pyrimido[2,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 28 | 2-morpholino-6-(naphthalen-1-yl)-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 29 | 2-morpholino-6-(naphthalen-2-yl)-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 30 | 2-morpholino-6-(thianthren-1-yl)-4H-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 31 | 2-morpholino-6-(thiophen-2-yl)-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 32 | 2-morpholino-6-(thiophen-3-yl)-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 33 | 2-morpholino-6-phenyl-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 34 | 2-morpholino-6-styryl-4H-pyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 35 | 2-morpholinobenzo[h]quinolin-4(1H)-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 36 | 2-Pyridin-3-yl-benzo[h]chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 37 | 2-Thiomorpholin-4-yl-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 38 | 2-thiomorpholino-4H-benzo[h]chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 39 | 2-[1,4]Oxazepan-4-yl-benzo[h]chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 40 | 3-(6-morpholino-4-oxo-4H-pyran-2-yl)benzaldehyde | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 41 | 3-(6-morpholino-4-oxo-4H-pyran-2-yl)benzoic acid | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 42 | 3-(6-morpholino-4-oxo-4H-pyran-2-yl)benzonitrile | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 43 | 3-morpholino-1H-benzo[f]chromen-1-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 44 | 4-(6-morpholino-4-oxo-4H-pyran-2-yl)benzonitrile | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 45 | 4-Morpholin-4-yl-benzo[g]chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 46 | 4-Morpholin-4-yl-benzo[h]chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 47 | 4-Morpholin-4-yl-chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 48 | 4-morpholino-6-phenyl-2H-pyran-2-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 49 | 4-Piperidin-1-yl-chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 50 | 4-Thiomorpholin-4-yl-benzo[g]chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 51 | 6-(2-acetylphenyl)-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 52 | 6-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-2-morpholino-4H-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 53 | 6-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-morpholin-4-ylpyridin-4-ol | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 54 | 6-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-morpholino-2H-pyran-2-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 55 | 6-(4-fluorostyryl)-2-morpholino-4H-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 56 | 6-biphenyl-2-yl-2-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 57 | 6-Chloro-4-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 58 | 6-isopropyl-2-morpholin-4-yl-4H-thiopyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 59 | 6-Methoxy-4-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 60 | 6-Methyl-4-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 61 | 6-tert-Butyl-2-morpholin-4-yl-4H-thiopyran-4-one | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 62 | 7-benzoyloxy-2-(morpholin-4-yl)-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 63 | 7-benzyloxy-2-(morpholin-4-yl)-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 64 | 7-ethyloxyethoxy-2-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 65 | 7-hydroxy-2-(morpholin-4-yl)chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 66 | 7-Methoxy-4-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 67 | 7-phenylethoxy-2-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 68 | 7-phenyloxyethoxy-2-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 69 | 7-propoxy-2-(morpholin-4-yl)-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 70 | 8-(1H-indol-5-yl)-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 71 | 8-(2-acetylphenyl)-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 72 | 8-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 73 | 8-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 74 | 8-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 75 | 8-biphenyl-2-yl-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 76 | 8-dibenzofuran-4-yl-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 77 | 8-furan-2-yl-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 78 | 8-Methoxy-2-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 79 | 8-Methoxy-4-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-2-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 80 | 8-Methyl-2-morpholin-4-yl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 81 | 8-Phenyl-2-piperidin-1-yl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 82 | 8-Phenyl-2-thiomorpholin-4-yl-chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 83 | ALPHA-NAPHTHOFLAVONE | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 84 | AMA37 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 85 | IC86621 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 86 | KU-0060648 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 87 | KU-55933 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 88 | LY-292223 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 89 | PIK-75 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 90 | PP121 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | DNA-PK complex of DNA end processing | PDB:7SGL | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.00 Å | Mutation | No | [14] |
| PDB Sequence |
MAGSGAGVRC
10 SLLRLQETLS20 AADRCGAALA30 GHQLIRGLGQ40 ECVLSSSPAV50 LALQTSLVFS 60 RDFGLLVFVR70 KSLNSIEFRE80 CREEILKFLC90 IFLEKMGQKI100 APYSVEIKNT 110 CTSVYTKDRA120 AKCKIPALDL130 LIKLLQTFRS140 SRLMDEFKIG150 ELFSKFYGEL 160 ALKKKIPDTV170 LEKVYELLGL180 LGEVHPSEMI190 NNAENLFRAF200 LGELKTQMTS 210 AVREPKLPVL220 AGCLKGLSSL230 LCNFTKSMEE240 DPQTSREIFN250 FVLKAIRPQI 260 DLKRYAVPSA270 GLRLFALHAS280 QFSTCLLDNY290 VSLFEVLLKW300 CAHTNVELKK 310 AALSALESFL320 KQVSNMVAKN330 AEMHKNKLQY340 FMEQFYGIIR350 NVDSNNKELS 360 IAIRGYGLFA370 GPCKVINAKD380 VDFMYVELIQ390 RCKQMFLTQT400 DTGDDRVYQM 410 PSFLQSVASV420 LLYLDTVPEV430 YTPVLEHLVV440 MQIDSFPQYS450 PKMQLVCCRA 460 IVKVFLALAA470 KGPVLRNCIS480 TVVHQGLIRI490 CSKPVVLPKG500 PESESEDHRA 510 SGEVRTGKWK520 VPTYKDYVDL530 FRHLLSSDQM540 MDSILADEAF550 FSVNSSSESL 560 NHLLYDEFVK570 SVLKIVEKLD580 LTLEIDPAAN611 LHPAKPKDFS621 AFINLVEFCR 631 EILPEKQAEF641 FEPWVYSFSY651 ELILQSTRLP661 LISGFYKLLS671 ITVRNAKKIK 681 YFEGVSDPEK700 YSCFALFVKF710 GKEVAVKMKQ720 YKDELLASCL730 TFLLSLPHNI 740 IELDVRAYVP750 ALQMAFKLGL760 SYTPLAEVGL770 NALEEWSIYI780 DRHVMQPYYK 790 DILPCLDGYL800 KTNWEVSALS819 RAAAISLEEI851 RIRVVQMLGS861 LGGQINKNLL 871 TVTSSDEMMK881 SYVAWDREKR891 LSFAVPFREM901 KPVIFLDVFL911 PRVTELALTA 921 SDRQTKVAAC931 ELLHSMVMFM941 LGKATQMPEG951 GQGAPPMYQL961 YKRTFPVLLR 971 LACDVDQVTR981 QLYEPLVMQL991 IHWFTNNKKF1001 ESQDTVALLE1011 AILDGIVDPV 1021 DSTLRDFCGR1031 CIREFLKWSI1041 KQITPQQQEK1051 SPVNTKSLFK1061 RLYSLALHPN 1071 AFKRLGASLA1081 FNNIYREFRE1091 EESLVEQFVF1101 EALVIYMESL1111 ALAHADEKSL 1121 GTIQQCCDAI1131 DHLCRIIEKK1141 HVSLNKAKKR1151 RLPRGFPPSA1161 SLCLLDLVKW 1171 LLAHCGRPQT1181 ECRHKSIELF1191 YKFVPLLPGN1201 RSPNLWLKDV1211 LKEEGVSFLI 1221 NTFEGGGCGQ1231 PSGILAQPTL1241 LYLRGPFSLQ1251 ATLCWLDLLL1261 AALECYNTFI 1271 GERTVGALQV1281 LGTEAQSSLL1291 KAVAFFLESI1301 AMHDIIAAEK1311 CFGTGAAGNR 1321 TSPQEGERYN1331 YSKCTVVVRI1341 MEFTTTLLNT1351 SPEGWKLLKK1361 DLCNTHLMRV 1371 LVQTLCEPAS1381 IGFNIGDVQV1391 MAHLPDVCVN1401 LMKALKMSPY1411 KDILETHLRE 1421 KITAQSIEEL1431 CAVNLYGPDA1441 QVDRSRLAAV1451 VSACKQLHRA1461 GLLHNILPSQ 1471 STDLHHSVGT1481 ELLSLVYKGI1491 APGDERQCLP1501 SLDLSCKQLA1511 SGLLELAFAF 1521 GGLCERLVSL1531 LLNPAVLSTS1549 VIHFSHGEYF1559 YSLFSETINT1569 ELLKNLDLAV 1579 LELMQSSVDN1589 TKMVSAVLNG1599 MLDQSFRERA1609 NQKHQGLKLA1619 TTILQHWKKC 1629 DSWWAKDSPL1639 ETKMAVLALL1649 AKILQIDSSV1659 SFNTSHGSFP1669 EVFTTYISLL 1679 ADTKLDLHLK1689 GQAVTLLPFF1699 TSLTGGSLEE1709 LRRVLEQLIV1719 AHFPMQSREF 1729 PPGTPRFNNY1739 VDCMKKFLDA1749 LELSQSPMLL1759 ELMTEVLCRE1769 QQHVMEELFQ 1779 SSFRRIARRG1789 SCVTQVGLLE1799 SVYEMFRKDD1809 PRLSFTRQSF1819 VDRSLLTLLW 1829 HCSLDALREF1839 FSTIVVDAID1849 VLKSRFTKLN1859 ESTFDTQITK1869 KMGYYKILDV 1879 MYSRLPKDDV1889 HAKESKINQV1899 FHGSCITEGN1909 ELTKTLIKLC1919 YDAFTENMAG 1929 ENQLLERRRL1939 YHCAAYNCAI1949 SVICCVFNEL1959 KFYQGFLFSE1969 KPEKNLLIFE 1979 NLIDLKRRYN1989 FPVEVEVPME1999 RKKKYIEIRK2009 EAREAANGDS2019 DGPSYMSSLS 2029 YLADSTLSEE2039 MSQFDFSTGV2049 QSYSYSSQLE2084 MDELNRHECM2094 APLTALVKHM 2104 HRSPRDLPSW2125 MKFLHGKLGN2135 PIVPLNIRLF2145 LAKLVINTEE2155 VFRPYAKHWL 2165 SPLLQLAASE2175 NNGGEGIHYM2185 VVEIVATILS2195 WTGLATPTGV2205 PKDEVLANRL 2215 LNFLMKHVFH2225 PKRAVFRHNL2235 EIIKTLVECW2245 KDCLSIPYRL2255 IFEKFSGKDP 2265 NSKDNSVGIQ2275 LLGIVMANDL2285 PPYDPQCGIQ2295 SSEYFQALVN2305 NMSFVRYKEV 2315 YAAAAEVLGL2325 ILRYVMERKN2335 ILEESLCELV2345 AKQLKQHQNT2355 MEDKFIVCLN 2365 KVTKSFPPLA2375 DRFMNAVFFL2385 LPKFHGVLKT2395 LCLEVVLCRV2405 EGMTELYFQL 2415 KSKDFVQVMR2425 HRDDERQKVC2435 LDIIYKMMPK2445 LKPVELRELL2455 NPVVEFVSHP 2465 STTCREQMYN2475 ILMWIHDNYR2485 DPESETDNDS2495 QEIFKLAKDV2505 LIQGLIDENP 2515 GLQLIIRNFW2525 SHETRLPSNT2535 LDRLLALNSL2545 YSPKIEVHFL2555 SLATNFLLEM 2565 TSMSPDYPNP2575 MFEHPLSECE2585 FQEYTIDSDW2595 RFRSTVLTPM2605 FVEQASQGPV 2631 AGQIRAQQQH2642 DFLQTQVVLY2772 RSYRHGDLPD2782 IQIKHSSLIT2792 PLQAVAQRDP 2802 IIAKQLFSSL2812 FSGILKEMDK2822 FKTLSEKNNI2832 TQKLLQDFNR2842 FLNTTFSFFP 2852 PFVSCIQDIS2862 CQHAALLSLD2872 PAAVSAGCLA2882 SLQQPVGIRL2892 LEEALLRLLP 2902 ALPPDVLRWV2924 ELAKLYRSIG2934 EYDVLRGIFT2944 SEIGTKQITQ2954 SALLAEARSD 2964 YSEAAKQYDE2974 ALNKQDWVDG2984 EPTEAEKDFW2994 ELASLDCYNH3004 LAEWKSLEYC 3014 STASIDSENP3024 PDLNKIWSEP3034 FYQETYLPYM3044 IRSKLKLLLQ3054 GEADQSLLTF 3064 IDKAMHGELQ3074 KAILELHYSQ3084 ELSLLYLLQD3094 DVDRAKYYIQ3104 NGIQSFMQNY 3114 SSIDVLLHQS3124 RLTKLQSVQA3134 LTEIQEFISF3144 ISKQGNLSSQ3154 VPLKRLLNTW 3164 TNRYPDAKMD3174 PMNIWDDIIT3184 NRCFFLSKIE3194 EKLTEDISSL3230 IRSCKFSMKM 3240 KMIDSARKQN3250 NFSLAMKLLK3260 ELHKESKTRD3270 DWLVSWVQSY3280 CRLSHCRSRS 3290 QGCSEQVLTV3300 LKTVSLLDEN3310 NVSSYLSKNI3320 LAFRDQNILL3330 GTTYRIIANA 3340 LSSEPACLAE3350 IEEDKARRIL3360 ELSGSSSEDS3370 EKVIAGLYQR3380 AFQHLSEAVQ 3390 AAEEEAQPPS3400 WSCGPAAGVI3410 DAYMTLADFC3420 DQQLRKEEEN3430 ASVIDSAELQ 3440 AYPALVVEKM3450 LKALKLNSNE3460 ARLKFPRLLQ3470 IIERYPEETL3480 SLMTKEISSV 3490 PCWQFISWIS3500 HMVALLDKDQ3510 AVAVQHSVEE3520 ITDNYPQAIV3530 YPFIISSESY 3540 SFKDTSTGHK3550 NKEFVARIKS3560 KLDQGGVIQD3570 FINALDQLSN3580 PELLFKDWSN 3590 DVRAELAKTP3600 VNKKNIEKMY3610 ERMYAALGDP3620 KAPGLGAFRR3630 KFIQTFGKEF 3640 DKHFGKGGSK3650 LLRMKLSDFN3660 DITNMLLLKM3670 NKDSKPPGNL3680 KECSPWMSDF 3690 KVEFLRNELE3700 IPGQYDGRGK3710 PLPEYHVRIA3720 GFDERVTVMA3730 SLRRPKRIII 3740 RGHDEREHPF3750 LVKGGEDLRQ3760 DQRVEQLFQV3770 MNGILAQDSA3780 CSQRALQLRT 3790 YSVVPMTSRL3800 GLIEWLENTV3810 TLKDLLLNTM3820 SQEEKAAYLS3830 DPRAPPCEYK 3840 DWLTKMSGKH3850 DVGAYMLMYK3860 GANRTETVTS3870 FRKRESKVPA3880 DLLKRAFVRM 3890 STSPEAFLAL3900 RSHFASSHAL3910 ICISHWILGI3920 GDRHLNNFMV3930 AMETGGVIGI 3940 DFGHAFGSAT3950 QFLPVPELMP3960 FRLTRQFINL3970 MLPMKETGLM3980 YSIMVHALRA 3990 FRSDPGLLTN4000 TMDVFVKEPS4010 FDWKNFEQKM4020 LKKGGSWIQE4030 INVAEKNWYP 4040 RQKICYAKRK4050 LAGANPAVIT4060 CDELLLGHEK4070 APAFRDYVAV4080 ARGSKDHNIR 4090 AQEPESGLSE4100 ETQVKCLMDQ4110 ATDPNILGRT4120 WEGWEPWM
|
|||||
|
|
PHE2597
4.309
MET3729
3.915
SER3731
3.843
ARG3733
4.969
PRO3735
4.207
LEU3751
3.741
LYS3753
2.920
TYR3791
4.497
ILE3803
3.697
GLU3804
3.160
TRP3805
3.217
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: M3814 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | DNA-PKcs in complex with M3814 | PDB:7OTY | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 2.96 Å | Mutation | No | [15] |
| PDB Sequence |
.
|
|||||
|
|
MET3729
3.781
ALA3730
2.650
SER3731
3.401
PRO3735
3.769
ARG3737
3.868
LEU3751
3.843
LYS3753
2.654
ASP3761
4.828
TYR3791
3.715
ILE3803
3.298
GLU3804
3.609
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-homologous end-joining | hsa03450 | Affiliated Target |
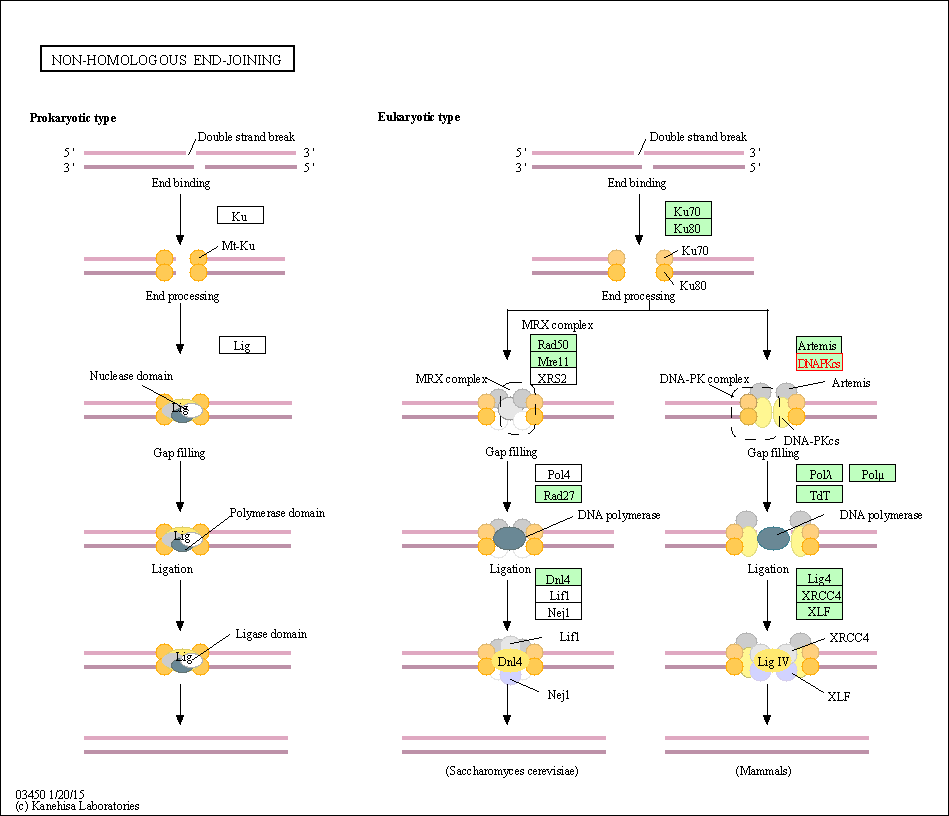
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Replication and repair | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | Affiliated Target |
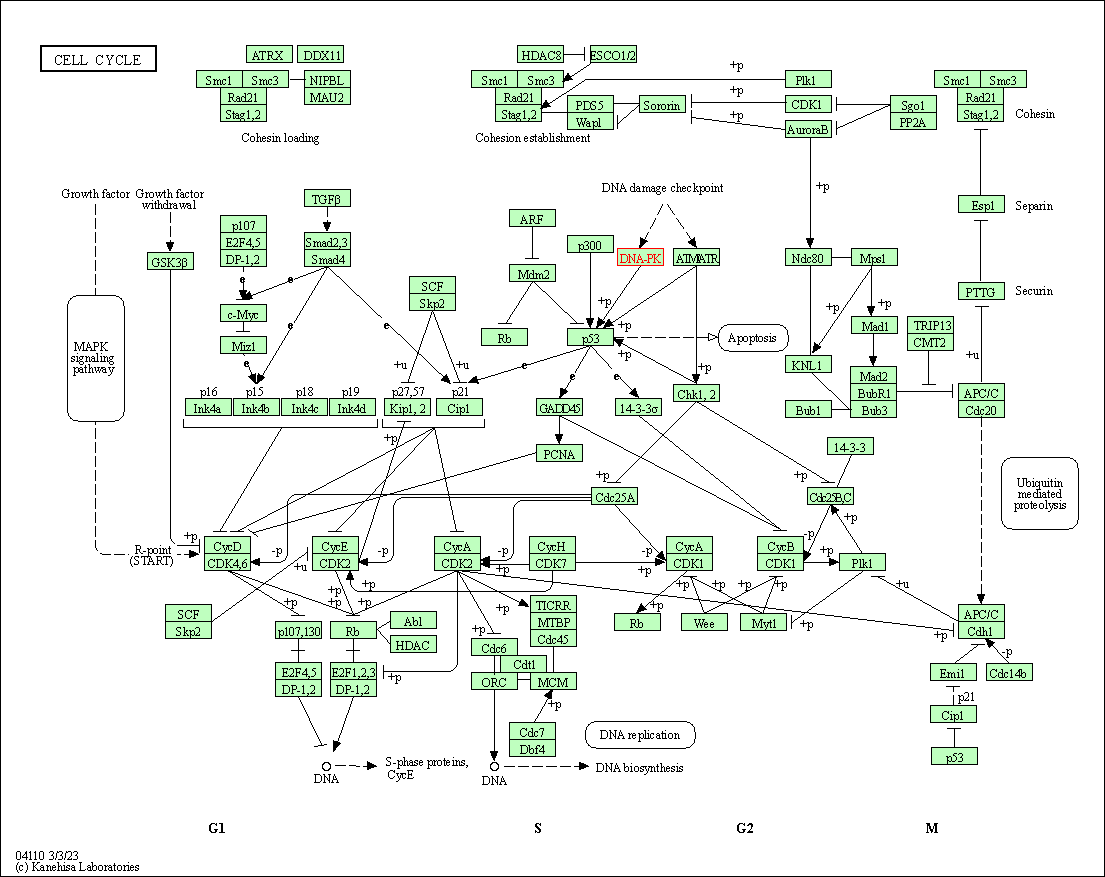
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 28 | Degree centrality | 3.01E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.79E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.51E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.86E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.46E+01 | Topological coefficient | 6.65E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 2 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Non-homologous end-joining | |||||
| 2 | Cell cycle | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL1 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 4 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | DNA-PK pathway in nonhomologous end joining | |||||
| 2 | Coregulation of Androgen receptor activity | |||||
| 3 | Class I PI3K signaling events mediated by Akt | |||||
| 4 | BARD1 signaling events | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 9 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | DNA Damage Response | |||||
| 2 | Non-homologous end joining | |||||
| 3 | FAS pathway and Stress induction of HSP regulation | |||||
| 4 | Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA | |||||
| 5 | Retinoblastoma (RB) in Cancer | |||||
| 6 | Prostate Cancer | |||||
| 7 | Double-Strand Break Repair | |||||
| 8 | Cell Cycle | |||||
| 9 | miRNA Regulation of DNA Damage Response | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03907969) A Clinical Trial to Evaluate AZD7648 Alone and in Combination With Other Anti-cancer Agents in Patients With Advanced Cancers.. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03770689) Study of Peposertib in Combination With Capecitabine and Radiotherapy in Rectal Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | Selective benzopyranone and pyrimido[2,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one inhibitors of DNA-dependent protein kinase: synthesis, structure-activity studies, and... J Med Chem. 2005 Jan 27;48(2):569-85. | |||||
| REF 5 | Pyranone, thiopyranone, and pyridone inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase related kinases. Structure-activity relationships for DNA-dependen... J Med Chem. 2007 Apr 19;50(8):1958-72. | |||||
| REF 6 | Discovery of potent chromen-4-one inhibitors of the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) using a small-molecule library approach. J Med Chem. 2005 Dec 1;48(24):7829-46. | |||||
| REF 7 | Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling by 2-(morpholin-1-yl)pyrimido[2,1-alpha]isoquinolin-4-one. J Biol Chem. 2007 Aug 17;282(33):24463-70. | |||||
| REF 8 | Modulation of DNA repair by pharmacological inhibitors of the PIKK protein kinase family. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Sep 1;22(17):5352-9. | |||||
| REF 9 | 1-substituted (Dibenzo[b,d]thiophen-4-yl)-2-morpholino-4H-chromen-4-ones endowed with dual DNA-PK/PI3-K inhibitory activity. J Med Chem. 2013 Aug 22;56(16):6386-401. | |||||
| REF 10 | Identification of a highly potent and selective DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) inhibitor (NU7441) by screening of chromenone libraries. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Dec 20;14(24):6083-7. | |||||
| REF 11 | A pharmacological map of the PI3-K family defines a role for p110alpha in insulin signaling. Cell. 2006 May 19;125(4):733-47. | |||||
| REF 12 | Targeted polypharmacology: discovery of dual inhibitors of tyrosine and phosphoinositide kinases. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Nov;4(11):691-9. | |||||
| REF 13 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2800). | |||||
| REF 14 | Autophosphorylation transforms DNA-PK from protecting to processing DNA ends. Mol Cell. 2022 Jan 6;82(1):177-189.e4. | |||||
| REF 15 | Structural insights into inhibitor regulation of the DNA repair protein DNA-PKcs. Nature. 2022 Jan;601(7894):643-648. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

